Showing 246801–246850 of 271967 results
-

TG-WAXMS B 0.25 um, 0.25 mm x 30 m GC Column
$1,083.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG-WAXMS B 0.25 um, 0.25 mm x 30 m GC Column
-

TG-WAXMS B 0.25 um, 0.32 mm x 30 m GC Column
$1,197.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG-WAXMS B 0.25 um, 0.32 mm x 30 m GC Column
-

TG-WAXMS B 0.50 um, 0.25 mm x 30 m GC Column
$1,126.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG-WAXMS B 0.50 um, 0.25 mm x 30 m GC Column
-

TG-WAXMS B 1 um, 0.53 mm x 30 m GC Column
$1,394.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG-WAXMS B 1 um, 0.53 mm x 30 m GC Column
-

TG-XLBMS 0.18 um, 0.18 mm x 20 m GC Column
$957.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG-XLBMS 0.18 um, 0.18 mm x 20 m GC Column
-

TG-XLBMS 0.25 um, 0.25 mm x 15 m GC Column
$708.17 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG-XLBMS 0.25 um, 0.25 mm x 15 m GC Column
-

TG-XLBMS 0.25 um, 0.25 mm x 30 m GC Column
$1,083.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG-XLBMS 0.25 um, 0.25 mm x 30 m GC Column
-

TG-XLBMS 0.25 um, 0.25 mm x 60 m GC Column
$1,871.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG-XLBMS 0.25 um, 0.25 mm x 60 m GC Column
-

TG-XLBMS 0.25 um, 0.32 mm x 30 m GC Column
$1,189.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG-XLBMS 0.25 um, 0.32 mm x 30 m GC Column
-

TG-XLBMS 0.25 um, 0.32 mm x 60 m GC Column
$2,164.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG-XLBMS 0.25 um, 0.32 mm x 60 m GC Column
-

TG-XLBMS 0.50 um, 0.25 mm x 30 m GC Column
$1,137.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG-XLBMS 0.50 um, 0.25 mm x 30 m GC Column
-

TG100 80uM 50MM 100/PK
$232.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsTG100 80uM 50MM 100/PK
-
TG100-115
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H14N6O2
-
TG100-115
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H14N6O2
-

TG101348
$98.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H36 N6 O3 S
-

TG101348
$131.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H36 N6 O3 S
-
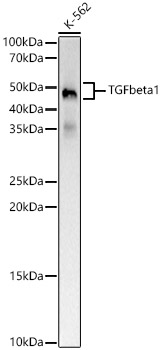
TGF beta 1 Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta 1 Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta 1 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta 1 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta induced (TGFBI) Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta induced (TGFBI) Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta induced (TGFBI) Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-
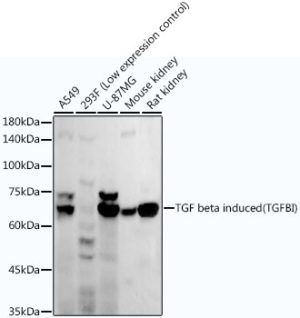
TGF beta induced (TGFBI) Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta induced (TGFBI) Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta induced (TGFBI) Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta induced (TGFBI) Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta induced (TGFBI) Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
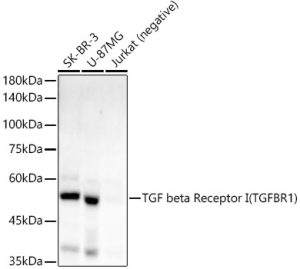
TGF beta Receptor I (TGFBR1) Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta Receptor I (TGFBR1) Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta Receptor I (TGFBR1) Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta Receptor I (TGFBR1) Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
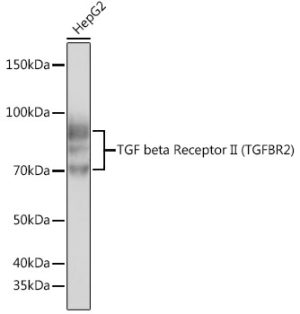
TGF beta Receptor II Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta Receptor II Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta Receptor II Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta Receptor II Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta Receptor II Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta Receptor II Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta Receptor II Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

TGF beta Receptor II Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

TGF-α, Human
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtransforming Growth Factor-alpha (TGF-alpha), also known as sarcoma growth factor, TGF-type I and ETGF, is a member of the EGF family of cytokines. It is expressed in monocytes, brain cells, keratinocytes and various tumor cells. ProTGF-alpha signals through EGFR and acts synergistically with TGF-beta to promote the proliferation of a wide range of epidermal and epithelial cells. It may function as either a membrane-bound ligand or a soluble ligand. Membrane-bound proTGF-alpha plays a role in cell-cell adhesion and juxtacrine stimulation of adjacent cells. The soluble form of the cytokine is released from the membrane-bound form by proteolytic cleavage and acts as a mitogen for cell proliferation.
-

TGF-α, Human
$29.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtransforming Growth Factor-alpha (TGF-alpha), also known as sarcoma growth factor, TGF-type I and ETGF, is a member of the EGF family of cytokines. It is expressed in monocytes, brain cells, keratinocytes and various tumor cells. ProTGF-alpha signals through EGFR and acts synergistically with TGF-beta to promote the proliferation of a wide range of epidermal and epithelial cells. It may function as either a membrane-bound ligand or a soluble ligand. Membrane-bound proTGF-alpha plays a role in cell-cell adhesion and juxtacrine stimulation of adjacent cells. The soluble form of the cytokine is released from the membrane-bound form by proteolytic cleavage and acts as a mitogen for cell proliferation.
-

TGF-α, Human
$836.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming Growth Factor-alpha (TGF-α) , also known as sarcoma growth factor, TGF-type I and ETGF, is a member of the EGF family of cytokines. It is expressed in monocytes, brain cells, keratinocytes and various tumor cells. TGF-α signals through EGFR and acts synergistically with TGF-beta to promote the proliferation of a wide range of epidermal and epithelial cells. TGF-α is a transforming growth factor that is a ligand for the epidermal growth factor receptor, which activates a signaling pathway for cell proliferation, differentiation and development. This protein may act as either a transmembrane-bound ligand or a soluble ligand. The biological actions of TGF-α and EGF are similar. For instance, TGF-α and EGF bind to the same receptor. When TGF-α binds to EGFR it can initiate multiple cell proliferation events.
-

TGF-α, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming Growth Factor-alpha (TGF-α) , also known as sarcoma growth factor, TGF-type I and ETGF, is a member of the EGF family of cytokines. It is expressed in monocytes, brain cells, keratinocytes and various tumor cells. TGF-α signals through EGFR and acts synergistically with TGF-beta to promote the proliferation of a wide range of epidermal and epithelial cells. TGF-α is a transforming growth factor that is a ligand for the epidermal growth factor receptor, which activates a signaling pathway for cell proliferation, differentiation and development. This protein may act as either a transmembrane-bound ligand or a soluble ligand. The biological actions of TGF-α and EGF are similar. For instance, TGF-α and EGF bind to the same receptor. When TGF-α binds to EGFR it can initiate multiple cell proliferation events.
-

TGF-α, Human
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming Growth Factor-alpha (TGF-α) , also known as sarcoma growth factor, TGF-type I and ETGF, is a member of the EGF family of cytokines. It is expressed in monocytes, brain cells, keratinocytes and various tumor cells. TGF-α signals through EGFR and acts synergistically with TGF-beta to promote the proliferation of a wide range of epidermal and epithelial cells. TGF-α is a transforming growth factor that is a ligand for the epidermal growth factor receptor, which activates a signaling pathway for cell proliferation, differentiation and development. This protein may act as either a transmembrane-bound ligand or a soluble ligand. The biological actions of TGF-α and EGF are similar. For instance, TGF-α and EGF bind to the same receptor. When TGF-α binds to EGFR it can initiate multiple cell proliferation events.
-

TGF-β 1, Mouse
$2,876.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFβ1) is the prototype of a growing superfamily of peptide growth factors and plays a prominent role in a variety of cellular processes, including cell-cycle progression, cell differentiation, reproductive function, development, motility, adhesion, neuronal growth, bone morphogenesis, wound healing, and immune surveillance. TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and TGF-β3 signal via the same heteromeric receptor complex, consisting of a ligand binding TGF-β receptor type II (TβR-II), and a TGF-β receptor type I (TβR-I). Signal transduction from the receptor to the nucleus is mediated via SMADs. TGF-β expression is found in cartilage, bone, teeth, muscle, heart, blood vessels, hematopoietic cells, lung, kidney, gut, liver, eye, ear, skin, and the nervous system.
-

TGF-β 1, Mouse
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFβ1) is the prototype of a growing superfamily of peptide growth factors and plays a prominent role in a variety of cellular processes, including cell-cycle progression, cell differentiation, reproductive function, development, motility, adhesion, neuronal growth, bone morphogenesis, wound healing, and immune surveillance. TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and TGF-β3 signal via the same heteromeric receptor complex, consisting of a ligand binding TGF-β receptor type II (TβR-II), and a TGF-β receptor type I (TβR-I). Signal transduction from the receptor to the nucleus is mediated via SMADs. TGF-β expression is found in cartilage, bone, teeth, muscle, heart, blood vessels, hematopoietic cells, lung, kidney, gut, liver, eye, ear, skin, and the nervous system.
-

TGF-β 1, Mouse
$543.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFβ1) is the prototype of a growing superfamily of peptide growth factors and plays a prominent role in a variety of cellular processes, including cell-cycle progression, cell differentiation, reproductive function, development, motility, adhesion, neuronal growth, bone morphogenesis, wound healing, and immune surveillance. TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and TGF-β3 signal via the same heteromeric receptor complex, consisting of a ligand binding TGF-β receptor type II (TβR-II), and a TGF-β receptor type I (TβR-I). Signal transduction from the receptor to the nucleus is mediated via SMADs. TGF-β expression is found in cartilage, bone, teeth, muscle, heart, blood vessels, hematopoietic cells, lung, kidney, gut, liver, eye, ear, skin, and the nervous system.
-

TGF-β 2, Human
$2,876.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming growth factor beta-2 (TGF-β2) is a secreted protein which belongs to the TGF-beta family. It is known as a cytokine that performs many cellular functions and has a vital role during embryonic development. The precursor is cleaved into mature TGF-beta-2 and LAP, which remains non-covalently linked to mature TGF-beta-2 rendering it inactive. It is an extracellular glycosylated protein. It is known to suppress the effects of interleukin dependent T-cell tumors. Defects in TGFB2 may be a cause of non-syndromic aortic disease (NSAD).
-

TGF-β 2, Human
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming growth factor beta-2 (TGF-β2) is a secreted protein which belongs to the TGF-beta family. It is known as a cytokine that performs many cellular functions and has a vital role during embryonic development. The precursor is cleaved into mature TGF-beta-2 and LAP, which remains non-covalently linked to mature TGF-beta-2 rendering it inactive. It is an extracellular glycosylated protein. It is known to suppress the effects of interleukin dependent T-cell tumors. Defects in TGFB2 may be a cause of non-syndromic aortic disease (NSAD).






