Showing 29001–29050 of 29153 results
-

α1-Acid Glycoprotein
$115.68 Add to cart View Product Detailsα1-Acid Glycoprotein
-

β-2-Glycoprotein I
$452.41 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-2-Glycoprotein I
-

β-2-microglobulin
$49.99 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-2-Microglobulin is a cancer and renal biomarker. Excellent for controls or calibrators in enzyme assays. Beta 2-microglobulin is present in small amounts in serum, csf, and urine of normal people, and to a much greater degree in the urine and plasma of patients with tubular proteinaemia, renal failure, or kidney transplants. Human Beta 2 microglobulin levels can rise either because its rate of synthesis has increased (e.g. in AIDS, malignant monoclonal plasma cell dyscrasia, solid tumors and autoimmune disease) or because of impaired renal filtration (e.g. due to renal insufficiency, graft rejection or nephrotoxicity induced by post-transplantation immunosuppressive therapy). Beta-2 microglobulin levels might also be elevated in multiple myeloma and lymphoma cases. Dialysis-related amyloidosis develops after a long-term hemodialysis, it can aggregate into amyloid fibers that deposit in joint spaces.
-

β-2-microglobulin
$80.60 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-2-Microglobulin is a cancer and renal biomarker. Excellent for controls or calibrators in enzyme assays. Beta 2-microglobulin is present in small amounts in serum, csf, and urine of normal people, and to a much greater degree in the urine and plasma of patients with tubular proteinaemia, renal failure, or kidney transplants. Human Beta 2 microglobulin levels can rise either because its rate of synthesis has increased (e.g. in AIDS, malignant monoclonal plasma cell dyscrasia, solid tumors and autoimmune disease) or because of impaired renal filtration (e.g. due to renal insufficiency, graft rejection or nephrotoxicity induced by post-transplantation immunosuppressive therapy). Beta-2 microglobulin levels might also be elevated in multiple myeloma and lymphoma cases. Dialysis-related amyloidosis develops after a long-term hemodialysis, it can aggregate into amyloid fibers that deposit in joint spaces.
-

β-2-microglobulin
$178.46 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-2-Microglobulin is a cancer and renal biomarker. Excellent for controls or calibrators in enzyme assays
-
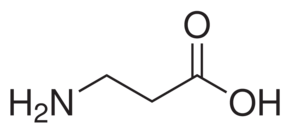
β-Alanine
$45.07 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Alanine
-

β-Alanine
$80.68 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Alanine
-

β-Alanine
$143.66 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Alanine
-

β-Amyloid, fragment 1-42
$889.57 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Amyloid, Fragment 1-42
-

β-AMYLOID, Fragment 25-35
$626.34 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-AMYLOID, Fragment 25-35
-
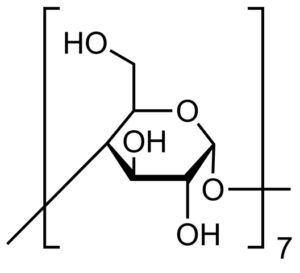
β-Cyclodextrin
$33.49 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Cyclodextrin
-

β-Cyclodextrin
$42.95 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Cyclodextrin
-

β-Cyclodextrin
$59.97 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Cyclodextrin
-

β-Cyclodextrin
$208.46 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Cyclodextrin
-
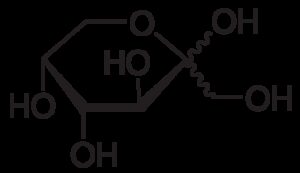
β-D-(-)-Fructose
$78.94 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-(-)-Fructose
-

β-D-(-)-Fructose
$128.24 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-(-)-Fructose
-

β-D-(-)-Fructose
$505.24 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-(-)-Fructose
-

β-D-Glucose, ≥80%
$49.12 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-Glucose
-
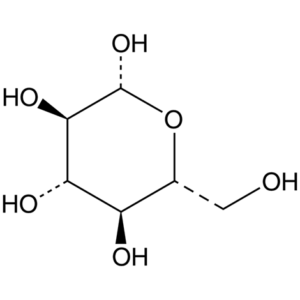
β-D-Glucose, ≥80%
$84.63 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-Glucose
-
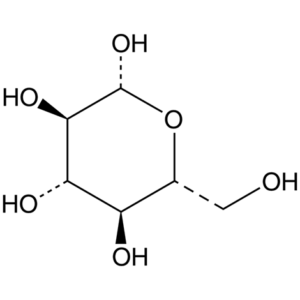
β-D-Glucose, ≥80%
$603.42 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-Glucose
-

β-D-Glucose, ≥80%
$2,053.49 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-Glucose
1,785.64 -

β-D-Glucose, ≥97%
$68.92 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-Glucose
-

β-D-Glucose, ≥97%
$118.11 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-Glucose
-

β-D-Glucose, ≥97%
$334.49 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-Glucose
-

β-D-Glucose, ≥97%
$1,409.98 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-Glucose, ≥97%
1,226.07 -

β-D-Glucose, ≥97%
$2,361.30 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-Glucose
2,053.30 -

β-D-RIBOPYRANOSYLAMINE
$508.81 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-D-RIBOPYRANOSYLAMINE
-

β-DENDROTOXIN
$614.86 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-DENDROTOXIN
-

β-Endorphin, Human
$208.37 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Endorphin, Human
-

β-Endorphin, Human
$358.58 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Endorphin, Human
-

β-Escin
$74.85 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Escin
-

β-Escin
$284.38 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Escin
-
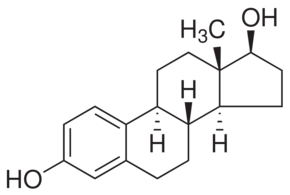
β-Estradiol
$46.95 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Estradiol
-

β-Estradiol
$69.54 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Estradiol
-

β-Estradiol
$276.28 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Estradiol
-

β-Estradiol
$1,172.70 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Estradiol
1,019.74 -

β-Estradiol
$2,936.63 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Estradiol
2,553.59 -

β-Estradiol
$160.93 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Estradiol
-

β-Estradiol-3-benzoate
$81.91 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Estradiol-3-Benzoate
-

β-Estradiol-3-benzoate
$320.57 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Estradiol-3-Benzoate
-
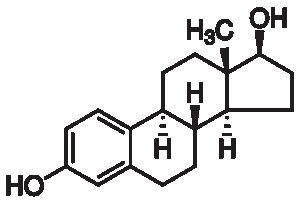
β-Estradiol, cell culture reagent
$42.98 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Estradiol
-

β-Estradiol, cell culture reagent
$81.26 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Estradiol
-

β-Estradiol, cell culture reagent
$324.58 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Estradiol
-

β-Galactosidase, ≥300 U/mg solid
$168.57 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Galactosidase
-

β-Galactosidase, ≥300 U/mg solid
$340.63 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Galactosidase
-

β-Galactosidase, ≥50 U/mg
$168.57 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Galactosidase
-

β-Galactosidase, ≥50 U/mg
$562.17 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Galactosidase
-

β-Galactosidase, ≥50 U/mg
$873.40 Add to cart View Product Detailsβ-Galactosidase
-

β-glucuronidase
$72.52 Add to cart View Product DetailsBeta-glucuronidases are members of the glycosidase family of enzymes that catalyze breakdown of complex carbohydrates. Human β-glucuronidase is a type of glucuronidase that catalyzes hydrolysis of β-D-glucuronic acid residues from the non-reducing end of mucopolysaccharides such as heparan sulfate. In human gut β-glucuronidase converts conjugated bilirubin to the unconjugated form for reabsorption.
-

β-glucuronidase
$131.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsBeta-glucuronidases are members of the glycosidase family of enzymes that catalyze breakdown of complex carbohydrates. Human β-glucuronidase is a type of glucuronidase that catalyzes hydrolysis of β-D-glucuronic acid residues from the non-reducing end of mucopolysaccharides such as heparan sulfate. In human gut β-glucuronidase converts conjugated bilirubin to the unconjugated form for reabsorption.






