100g
Showing 2651–2700 of 2881 results
-
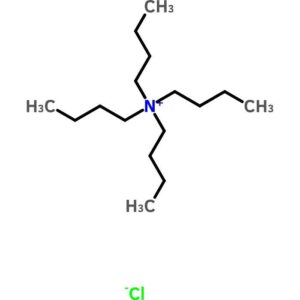
Tetrabutylammonium Chloride
$374.72 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Chloride
-

Tetrabutylammonium Chloride, Hydrate
$397.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Chloride, Hydrate
-

Tetrabutylammonium Fluoride, Hydrate
$615.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Fluoride, Hydrate
-
![Tetrabutylammonium Fluoride, Hydrate [for Catalyst of acylation, silylation and cleavage of silyl ether]](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/TCI-300x300.jpg.pagespeed.ce.remJNefMLx.jpg)
Tetrabutylammonium Fluoride, Hydrate [for Catalyst of acylation, silylation and cleavage of silyl ether]
$503.42 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Fluoride, Hydrate [for Catalyst of acylation, silylation and cleavage of silyl ether]
-
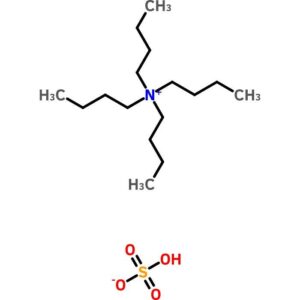
Tetrabutylammonium Hydrogen Sulfate
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Hydrogen Sulfate
-

Tetrabutylammonium Hydrogen Sulfate
$567.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Hydrogen Sulfate
-
![Tetrabutylammonium Hydrogen Sulfate, [Reagent for Ion-Pair Chromatography]](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/32503-27-8-300x300.jpg)
Tetrabutylammonium Hydrogen Sulfate, [Reagent for Ion-Pair Chromatography]
$282.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Hydrogen Sulfate, [Reagent for Ion-Pair Chromatography]
-
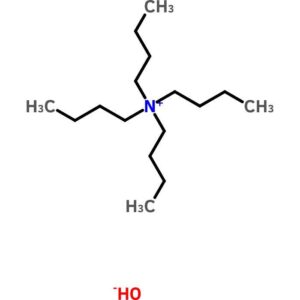
Tetrabutylammonium Hydroxide, (40 Percent in Water)
$104.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Hydroxide, (40 Percent in Water)
-
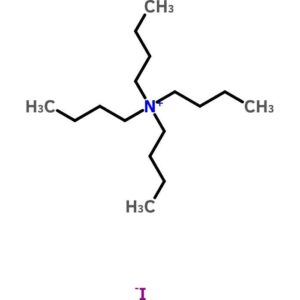
Tetrabutylammonium Iodide
$116.07 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Iodide
-

Tetrabutylammonium Iodide
$126.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Iodide
-

Tetrabutylammonium Tetrafluoroborate
$301.07 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Tetrafluoroborate
-
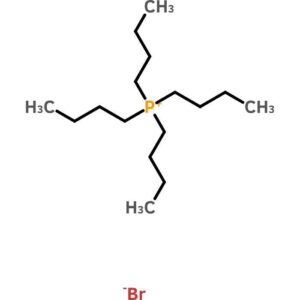
Tetrabutylphosphonium Bromide
$109.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylphosphonium Bromide
-

Tetracaine Hydrochloride ≥99% – 100G
$60.72 Add to cart View Product DetailsCAS Number 136-47-0 Molecular Weight 300.82 Molecular Formula C15H24N2O2 · HCl -

Tetracaine Hydrochloride, USP
$484.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetracaine Hydrochloride, USP
-

Tetracaine, USP
$1,311.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetracaine, USP
-

Tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone
$224.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrachloro-p-benzoquinone
-
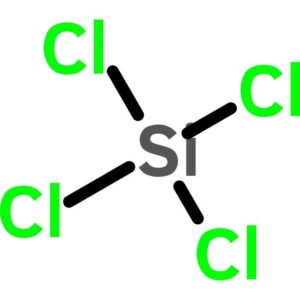
Tetrachlorosilane
$55.52 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrachlorosilane
-

Tetracosane
$283.82 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetracosane
-

Tetracycline Hydrochloride
$205.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetracycline Hydrochloride
-

Tetraethylammonium Bromide
$119.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetraethylammonium Bromide
-

Tetraethylammonium Chloride
$218.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetraethylammonium Chloride
-
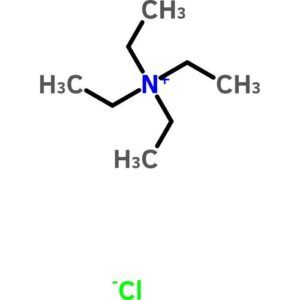
Tetraethylammonium Chloride
$135.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetraethylammonium Chloride
-

Tetraethylammonium Chloride, Monohydrate, Crystal, Reagent
$257.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetraethylammonium Chloride, Monohydrate, Crystal, Reagent
-

Tetraethylammonium Tosylate
$164.51 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetraethylammonium Tosylate
-

Tetraethylenepentamine
$65.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetraethylenepentamine
-

Tetrahydrofurfuryl Alcohol
$83.52 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrahydrofurfuryl Alcohol
-

Tetramethylammonium Bromide, Reagent, ACS
$279.37 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetramethylammonium Bromide, Reagent, ACS
-

Tetramethylammonium Chloride, Crystal, Reagent
$42.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetramethylammonium Chloride, Crystal, Reagent
-

Tetramethylammonium Chloride, High Purity
$77.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetramethylammonium Chloride, High Purity
-

Tetramethylammonium Hydroxide, Pentahydrate
$301.42 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetramethylammonium Hydroxide, Pentahydrate
-
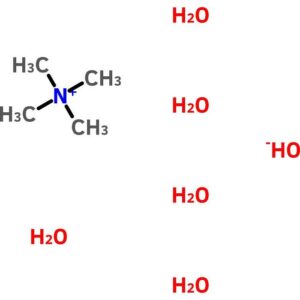
Tetramethylammonium Hydroxide, Pentahydrate
$234.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetramethylammonium Hydroxide, Pentahydrate
-

Tetramethylthiourea
$278.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetramethylthiourea
-

Tetraphenylphosphonium Bromide
$251.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetraphenylphosphonium Bromide
-

Tetrazolium Blue Chloride
$2,586.17 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrazolium Blue Chloride
-

TGFβ1, Bovine
$589.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsTGF-β1 (transforming growth factor beta 1) is one of three closely related mammalian members of the large TGF-β1 superfamily that share a characteristic cystine knot structure. TGF-β1, -2 and -3 are highly pleiotropic cytokines that act as cellular switches to regulate processes such as immune function, proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Each TGF-β isoform has some non-redundant function; for TGF-β1, mice with targeted deletion show defects in hematopoiesis and endothelial differentiation and died of overwhelming inflammation. TGF-β1 signaling begins with high-affinity binding to a type II ser/thr kinase receptor termed TGF-β RII. This receptor then phosphorylates and activates a second ser/thr kinase receptor, TGF-β RI (also called activin receptor‑like kinase (ALK)-5), or alternatively, ALK-1. This complex phosphorylates and activates Smad proteins that regulate transcription.
-
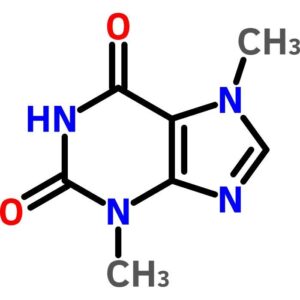
Theobromine
$157.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsTheobromine
-
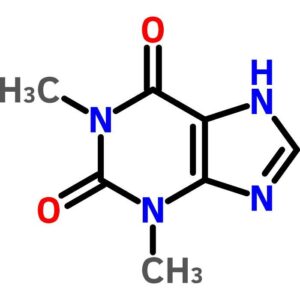
Theophylline
$82.02 Add to cart View Product DetailsTheophylline
-

Theophylline, Anhydrous, USP
$127.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsTheophylline, Anhydrous, USP
-

THE™ alpha Tubulin Antibody, mAb, Mouse
$215.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsTHE™ alpha Tubulin Antibody, mAb, Mouse reacts with mouse, human, hamster, monkey, and pig α-tubulin. This product has not yet been tested in other species.
-
![THE™ beta Actin Antibody [HRP], mAb, Mouse](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/genscriptlogo.png.pagespeed.ce.m81Yfeq9O5.png)
THE™ beta Actin Antibody [HRP], mAb, Mouse
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsTHE™ beta Actin Antibody [HRP], mAb, Mouse reacts with mouse, rabbit, chicken, human, hamster, cow, goat, fish, and pig substrates.It has not yet been tested in other species.
-

THE™ beta Actin Antibody, mAb, Mouse
$172.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsTHE™ beta Actin Antibody, mAb, Mouse reacts with mouse, rabbit, chicken, human, hamster, cow, goat, fish, and pig.It has not yet been tested in other species.
-
![THE™ c-Myc Antibody [HRP], mAb, Mouse](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/genscriptlogo.png.pagespeed.ce.m81Yfeq9O5.png)
THE™ c-Myc Antibody [HRP], mAb, Mouse
$159.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsGenScript THE™ c-Myc Antibody [HRP], mAb, Mouse recognizes C-terminal, N-terminal, and internal c-Myc-tagged fusion proteins expressed in prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells.It also recognizes the c-Myc gene in human cancers, such as Hela whole cell lysate.
-

THE™ c-Myc Tag Antibody, mAb, Mouse
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsTHE™ c-Myc Tag Antibody, mAb, Mouse recognizes C-terminal, N-terminal, and internal c-Myc tagged fusion proteins expressed in prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells.It also recognizes c-Myc protein in human cancers or cell lines such as Hela cell lysates.
-

THE™ cAMP Antibody, mAb, Mouse
$301.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe specificity of the antibody is defined as the ratio of antigen concentration to cross-reactant concentration at 50% inhibition of maximum binding.
-
![THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [Biotin], mAb, Mouse](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/genscriptlogo.png.pagespeed.ce.m81Yfeq9O5.png)
THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [Biotin], mAb, Mouse
$133.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsTHE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [Biotin], mAb, Mouse recognizes C-terminal, N-terminal, and internal tagged fusion proteins.
-
![THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [FITC], mAb, Mouse](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/genscriptlogo.png.pagespeed.ce.m81Yfeq9O5.png)
THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [FITC], mAb, Mouse
$133.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsGenScript THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [FITC], mAb, Mouse recognizes C-terminal, N-terminal, and internal DYKDDDDK tagged fusion proteins.
-
![THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [HRP], mAb, Mouse](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/genscriptlogo.png.pagespeed.ce.m81Yfeq9O5.png)
THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [HRP], mAb, Mouse
$133.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsTHE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [HRP], mAb, Mouse recognizes C-terminal, N-terminal, and internal tagged fusion proteins.
-
![THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [iFluor 488], mAb, Mouse](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/genscriptlogo.png.pagespeed.ce.m81Yfeq9O5.png)
THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [iFluor 488], mAb, Mouse
$150.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsTHE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [iFluor 488], mAb, Mouse recognizes N-terminal, internal and C-terminal Flag-tagged proteins.
-
![THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [iFluor 555], mAb, Mouse](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/genscriptlogo.png.pagespeed.ce.m81Yfeq9O5.png)
THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [iFluor 555], mAb, Mouse
$150.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsTHE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [iFluor 555], mAb, Mouse recognizes N-terminal, internal and C-terminal Flag-tagged proteins.
-
![THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [iFluor 647], mAb, Mouse](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/genscriptlogo.png.pagespeed.ce.m81Yfeq9O5.png)
THE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [iFluor 647], mAb, Mouse
$150.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsTHE™ DYKDDDDK Tag Antibody [iFluor 647], mAb, Mouse recognizes N-terminal, internal and C-terminal DYKDDDDK-tagged proteins.






