100g
Showing 2851–2900 of 3537 results
-

Propranolol Hydrochloride, USP
$2,385.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropranolol Hydrochloride, USP
-
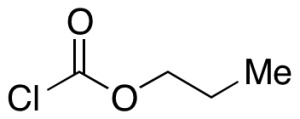
Propyl Chloroformate
$179.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H7 Cl O2
-

Propyl Gallate
$72.57 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropyl Gallate
-

Propyl Gallate, FCC
$110.77 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropyl Gallate, FCC
-

Propyl Gallate, NF
$104.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropyl Gallate, NF
-

Propylparaben Sodium, NF
$137.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropylparaben Sodium, NF
-

Propylparaben, NF, BP, EP
$57.90 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropylparaben, NF, BP, EP
-

Propylthiouracil, USP
$1,749.92 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropylthiouracil, USP
-
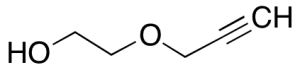
Propynol Ethoxylate (>80%)
$319.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H8O2
-

Protease, 300 TU/mg
$159.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtease, 300 TU/mg
-

PSMA Fc Chimera, Human
$258.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsProstate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) also known as Folate hydrolase 1 (FOLH1), Folylpoly-gamma-glutamate carboxypeptidase (FGCP), Glutamate carboxypeptidase 2 (GCP2), N-acetylated-alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase I (NAALAD1), is a type II membrane glycoprotein that is expressed in prostate tissue and to a lesser extent in the peripheral and central nervous system, small intestinal, and salivary gland tissues. PSMA has both folate hydrolase and N-acetylated-alpha-linked-acidic dipeptidase (NAALADase) activity and has a preference for tri-alpha-glutamate peptides. The catalytic activity of PSMA involves the release of unsubstituted C-terminal glutamyl residues, typically from Ac-Asp-Glu or folylpoly-gamma-glutamates. PSMA is used as a diagnostic and prognostic indicator of prostate cancer, and as a possible marker for various neurological disorders such as schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s disease, and Huntington’s disease.
-

PSMA, His, Human
$232.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsProstate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) also known as Folate hydrolase 1 (FOLH1), Folylpoly-gamma-glutamate carboxypeptidase (FGCP), Glutamate carboxypeptidase 2 (GCP2), N-acetylated-alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase I (NAALAD1), is a type II membrane glycoprotein that is expressed in prostate tissue and to a lesser extent in the peripheral and central nervous system, small intestinal, and salivary gland tissues. PSMA has both folate hydrolase and N-acetylated-alpha-linked-acidic dipeptidase (NAALADase) activity and has a preference for tri-alpha-glutamate peptides. The catalytic activity of PSMA involves the release of unsubstituted C-terminal glutamyl residues, typically from Ac-Asp-Glu or folylpoly-gamma-glutamates. PSMA is used as a diagnostic and prognostic indicator of prostate cancer, and as a possible marker for various neurological disorders such as schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s disease, and Huntington’s disease.
-

PTH (7-34aa), Human
$232.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolypeptide hormones secreted by the parathyroid glands, which promote release of calcium from bone to extracellular fluid by activating osteoblasts and inhibiting osteoclasts, indirectly promote increased intestinal absorption of calcium, and promote renal tubular reabsorption of calcium and increased renal excretion of phosphates. It is a major regulator of bone metabolism. Secretion of parathyroid hormone increases when the level of calcium in the extracellular fluid is low. Its action is opposed by calcitonin.
-

Pullulan
$369.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPullulan
-

PVR/CD155 Fc Chimera, Human
$215.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsPVR is a Type I transmembrane glycoprotein in the immunoglobulin superfamily. Commonly known as Poliovirus Receptor (PVR) due to its involvement in the cellular poliovirus infection in primates. PVR’s normal cellular function is in the establishment of intercellular adherens junctions between epithelial cells. PVR/CD155 was originally isolated based on its ability to mediate polio virus attachment to host cells. The full length (or PVR alpha isoform) is synthesized as a 417 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains a 20aa signal sequence, a 323aa extracellular region, a 24aa TM segment and a 50aa cytoplasmic tail. PVR binds other molecules including Vitronectin, Nectin-3, DNAM-1/CD226, CD96, and TIGIT but does not bind homotypically. PVR is up-regulated on endothelial cells by IFN-gamma and is highly expressed on immature thymocytes, lymph node dendritic cells, and tumor cells of epithelial and neuronal origin.
-

Pyrazine
$376.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyrazine
-
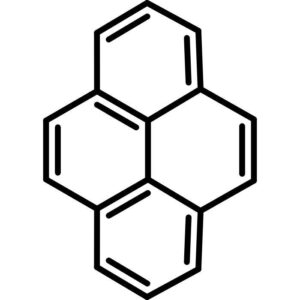
Pyrene
$229.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyrene
-

Pyrene, Powder
$166.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyrene, Powder
-
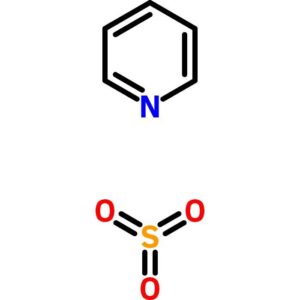
Pyridine – Sulfur Trioxide Complex
$205.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridine – Sulfur Trioxide Complex
-

Pyridine Hydrochloride
$147.02 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridine Hydrochloride
-

Pyridinium Bromide Perbromide, 85+ Percent, Technical
$73.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridinium Bromide Perbromide, 85+ Percent, Technical
-

Pyridinium Chlorochromate
$109.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridinium Chlorochromate
-
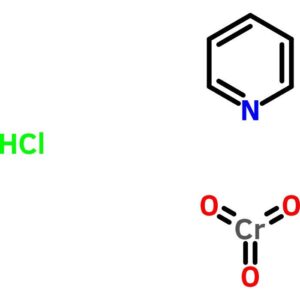
Pyridinium Chlorochromate
$56.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridinium Chlorochromate
-
Pyridinium Chlorochromate
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H5N.ClCrO3.H
-
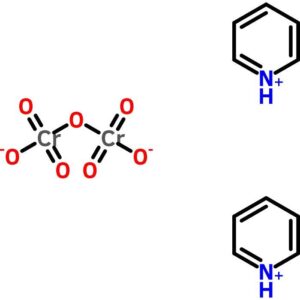
Pyridinium Dichromate
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridinium Dichromate
-
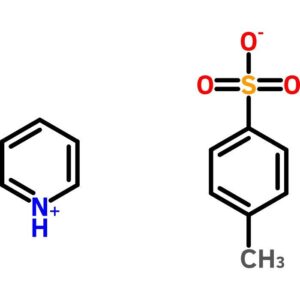
Pyridinium p-Toluenesulfonate
$63.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridinium p-Toluenesulfonate
-
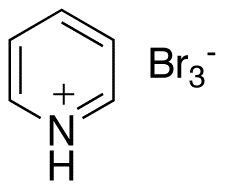
Pyridinium Tribromide (>90%)
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H6Br3N
-

Pyridoxal Hydrochloride
$1,180.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridoxal Hydrochloride
-

Pyridoxal-5-phosphate, Monohydrate
$1,796.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridoxal-5-phosphate, Monohydrate
-
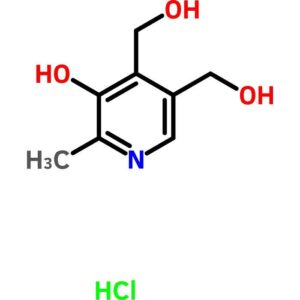
Pyridoxine Hydrochloride
$135.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridoxine Hydrochloride
-

Pyridoxine Hydrochloride
$146.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridoxine Hydrochloride
-

Pyridoxine Hydrochloride, FCC
$313.82 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridoxine Hydrochloride, FCC
-

Pyridoxine Hydrochloride, USP
$315.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridoxine Hydrochloride, USP
-

Pyrilamine Maleate, USP
$726.77 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyrilamine Maleate, USP
-
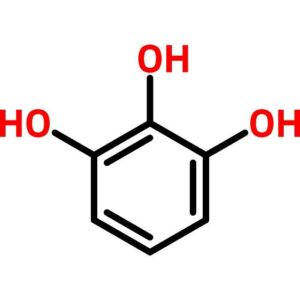
Pyrogallol
$100.91 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyrogallol
-
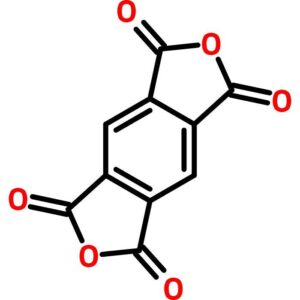
Pyromellitic Dianhydride
$44.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyromellitic Dianhydride
-
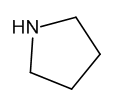
Pyrrolidine
$357.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H9 N
-

Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate, Ammonium Derivative
$441.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate, Ammonium Derivative
-

Quercetin, Anhydrous
$395.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsQuercetin, Anhydrous
-

Quercetin, Dihydrate
$299.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsQuercetin, Dihydrate
-

Quinacrine Dihydrochloride
$720.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsQuinacrine Dihydrochloride
-

Quinhydrone
$201.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsQuinhydrone
-
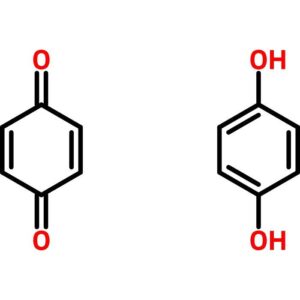
Quinhydrone
$118.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsQuinhydrone
-

Quinidine Sulfate, Dihydrate, USP
$553.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsQuinidine Sulfate, Dihydrate, USP
-

Quinine Sulfate, Dihydrate, USP
$860.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsQuinine Sulfate, Dihydrate, USP
-
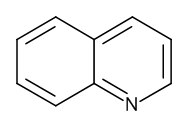
Quinoline
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H7 N
-

R-(-)-Mandelic Acid
$251.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsR-(-)-Mandelic Acid
-
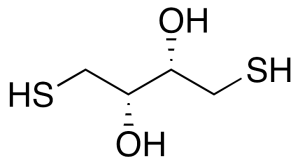
rac Dithiothreitol
$708.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H10 O2 S2
-
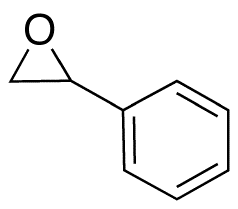
rac Styrene Oxide
$71.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H8O
-
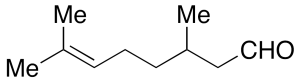
rac-Citronellal (>90%)
$266.51 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H18 O






