10g
Showing 2301–2350 of 4637 results
-
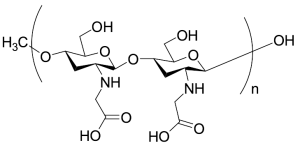
Carboxymethyl Chitosan
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : (C6H26N2O10)n
-
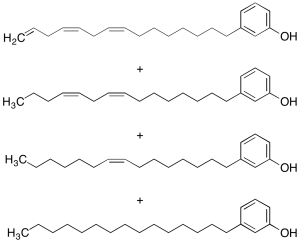
Cardanol (Mixture) (>80%)
$85.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C84 H132 O4
-

Cardiac Troponin I (cTnI), His, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsCardiac Troponin I (cTnI) is a subtype of the troponin family that is commonly used as a marker for myocardial damage. Cardiac troponin I is specific for cardiac tissue and is detected in the serum only if myocardial injury has occurred. Because cardiac troponin I is a very sensitive and specific indicator of heart muscle (myocardium) damage, serum levels can be used to help differentiate between unstable angina and myocardial infarction (heart attack) in people with chest pain or acute coronary syndrome.
-

Carmine
$127.27 Add to cart View Product DetailsCarmine
-
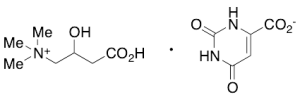
Carnitine Orotate
$217.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H16 N O3 . C5 H3 N2 O4
-
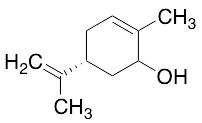
Carveol(Mixture of cis and trans)
$113.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H16 O
-

Catalase, Lyophilized
$1,355.07 Add to cart View Product DetailsCatalase, Lyophilized
-
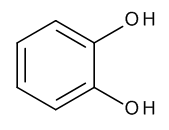
Catechol
$71.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H6 O2
-
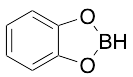
Catecholborane (Technical Grade)
$111.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H5BO2
-
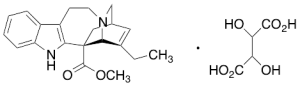
Catharanthine Tartrate
$847.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C21 H24 N2 O2 . C4 H6 O6
-

Cathepsin B, His, Human
$142.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsCathepsin B is an enzymatic protein that is a member of the peptidase (or protease) family. Elevated lev- els of cathepsin B occur in a wide variety of disease,causing numerous pathologies including cell death, inflammation, and the production of toxic peptides. For example, neuroscience research suggests that cathepsin B plays a role in inducing epilepsy resulting in a significant amount of cell death. Seizure-induced rats treated with a cathepsin B inhibitor exhibited improved neurological scores and learning ability with reduced neuronal cell death.
-

Cathepsin L, Human
$81.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsCathepsin L is an enzyme. Cathepsin L, a lysosomal endopeptidase expressed in most eukaryotic cells, is a member of the papain-like family of cysteine proteinases. Cathepsin L plays a major role in antigen processing, tumor invasion and metastasis, bone resorption, and turnover of intracellular and secreted proteins involved in growth regulation. Unlike the precursor forms of other papain family members, the 43 kDa pro-cathepsin L itself is secreted from various cells. Pro-cathepsin L is the major excreted protein of malignantly transformed mouse fibroblasts and is also one of the major acidic cysteine proteases in mammalian cells.
-
CD160 Fc Chimera, Human
$34.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD160 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored Ig domain protein that is expressed on almost all intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs), γδ T (gamma delta T) cells, NK (natural killer) cells, and a minor subset of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. In terms of function, work has centered on the role of CD160 in enhancing NK or CD8 T cell activation. Such effects have been attributed to the ability of CD160 to bind classical and nonclassical MHC class I molecules, although with apparent low affinity, requiring clustering of MHC class I molecules or overexpression of CD160 or MHC class I for detection of the interaction.
-

CD25/IL-2Rα Fc Chimera, Human
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe IL-2 receptor system consists of three non-covalently linked subunits termed IL-2Rα, IL-2Rβ, and IL-2Rγ. The IL-2Rα is a type I transmembrane protein consisting of a 219 amino acid (a.a.) extracellular domain, a 19 a.a. transmembrane domain and a 13 a.a. intracellular domain, which is not involved in the transduction of IL-2 signal. Activated T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs) and NK cells express high levels of CD25 and expression of the high-affinity IL-2Rα is mostly limited to these cell populations. Signaling via IL-2Rα mediates multiple biological processes in various cell populations, e.g. proliferation and differentiation of B cells and NK cells. A soluble form of IL-2Rα (IL-2Rα) appears in serum, concomitant with its increased expression on cells. The function of the soluble IL-2Rα is unclear. Increased levels of IL-2Rα in biological fluids reportedly correlate with increased T and B cell activation and immune system activation. Increased serum concentration of IL-2Rα has been observed in patients with a variety of inflammatory conditions and in the course of some leukemias and lymphomas.
-

CD40L/CD154/TRAP, Human
$64.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD40 Ligand (CD40L/CD154/TRAP) is a membrane glycoprotein and differentiation antigen expressed on the surface of T-cells. The CD40 ligand stimulates B-cell proliferation and secretion of all immunoglobulin isotypes in the presence of cytokines. It also costimulates proliferation of activated T-cell and this is accompanied by the production of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL2. CD40 ligand has been shown to induce cytokine production and tumoricidal activity in peripheral blood monocytes.
-
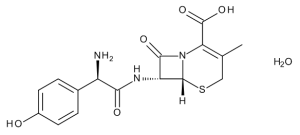
Cefadroxil Monohydrate
$199.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H17 N3 O5 S . H2 O
-
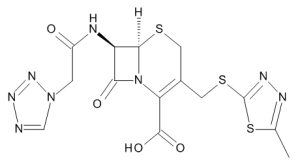
Cefazolin
$558.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H14 N8 O4 S3
-
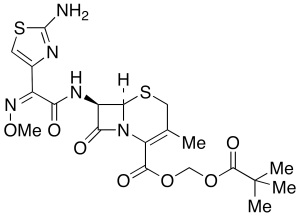
Cefetamet Pivoxil
$159.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H25 N5 O7 S2
-

Cellulose Sulfate Gel (Technical Grade)
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-
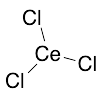
Cerium Chloride
$122.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CeCl3
-
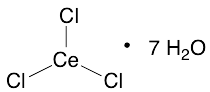
Cerium(III) Chloride Heptahydrate
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CeCl3 . 7(H2O)
-
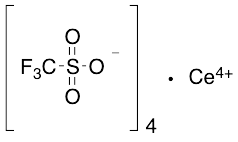
Cerium(IV) trifluoromethanesulfonate
$264.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4CeF12O12S4
-

Cetalkonium Chloride
$118.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H46 N . Cl
-
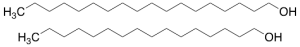
Cetearyl Alcohol
$95.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H38O . C16H34O
-
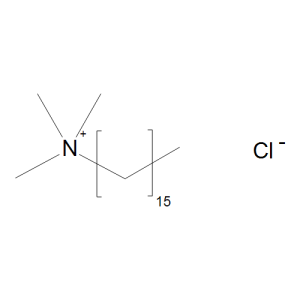
Cetrimonium Chloride
$157.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H42 N . Cl
-
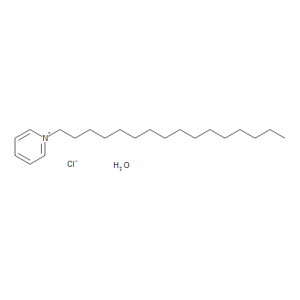
Cetylpyridinium Chloride Monohydrate
$83.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H38 N . Cl . H2 O
-

CHAPSO
$539.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsCHAPSO
-
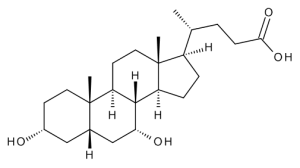
Chenodeoxycholic Acid
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24 H40 O4
-
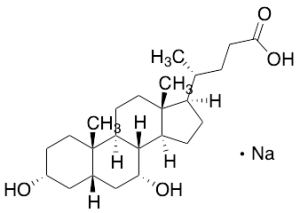
Chenodeoxycholic Acid Sodium Salt
$352.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24 H39 O4 . Na
-
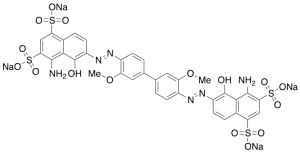
Chicago Sky Blue 6B (Technical Grade)
$69.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H24N6Na4O16S4
-
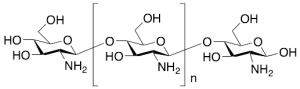
Chitosan
$66.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : [C7H15NO4]n
-
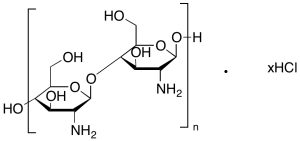
Chitosan Oligosaccharide Hydrochloride Salt (Technical Grade)
$66.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : (C12H24N2O9)n • xHCl
-
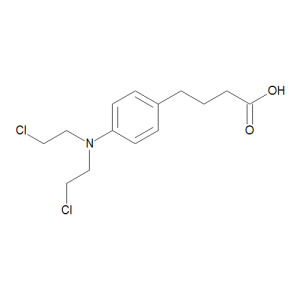
Chlorambucil
$666.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H19 Cl2 N O2
-
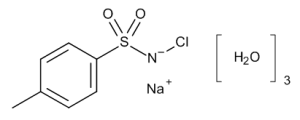
Chloramine-T Trihydrate
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 3C7H7ClNO2S.3Na.3H2O
-
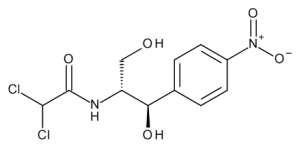
Chloramphenicol
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H12 Cl2 N2 O5
-
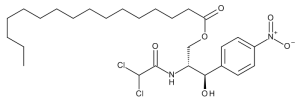
Chloramphenicol Palmitate
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H42 Cl2 N2 O6
-
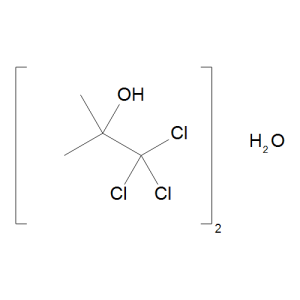
Chlorbutanol Hemihydrate
$62.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C4 H7 Cl3 O . H2 O
-
Chlorfluazuron
$1,110.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H9 Cl3 F5 N3 O3
-

Chlorhexidine Digluconate (20% in water)
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H30 Cl2 N10 . 2 C6 H12 O7
-
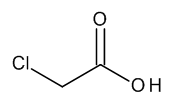
Chloroacetic Acid
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2 H3 Cl O2
-
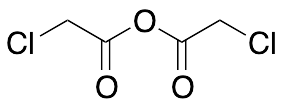
Chloroacetyl Anhydride
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H4Cl2O3
-
Chlorobis(4-fluorophenyl)methane
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H9 Cl F2
-
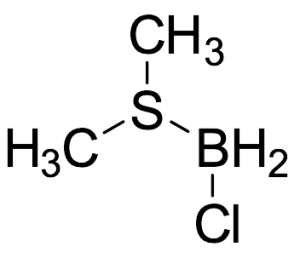
Chloroborane Methyl Sulfide Complex (Technical Grade)
$253.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H8BClS
-
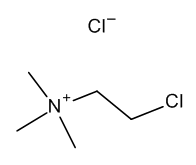
Chlorocholine Chloride
$157.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H13 Cl N . Cl
-

Chloroform-d
$319.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CDCl3
-
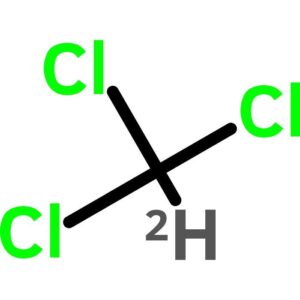
Chloroform-d, 99.6atom PercentD (stabilized with Silver chip)
$32.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsChloroform-d, 99.6atom PercentD (stabilized with Silver chip)
-
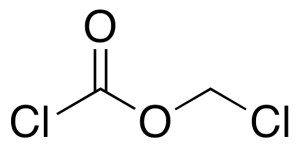
Chloroformic Acid Chloromethyl Ester
$87.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H2Cl2O2
-
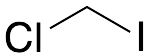
Chloroiodomethane
$79.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C H2 Cl I
-
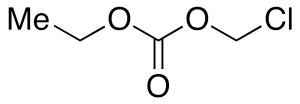
Chloromethyl Ethyl Carbonate
$1,878.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H7ClO3
-

Chloromethyl Isopropyl Carbonate
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H9 Cl O3






