10g
Showing 2701–2750 of 4637 results
-
DKK-1, Human
$47.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsDickkopf related protein 1 (DKK-1) is a chemokine that belongs to the DKK protein family, which also includes DKK-2, DKK-3 and DKK-4. DKK-1 was originally identified as a Xenopus head forming molecule that behaves as an antagonist for Wnt signaling. It is one of the most up-regulated genes during androgen-potentiated balding, with DKK-1 messenger RNA up-regulated a few hours after DHT treatment of hair follicles at the dermal papilla in vitro. Neutralizing bodies against DKK-1 reverses DHT effects on outer root sheath keratinocytes. DKK-1 expression is attenuated by L-threonate, a metabolite of ascorbate in vitro. DKK-1 promotes LRP6 internalization and degradation as it forms a ternary complex with the cell surface receptor Kremen. DKK-1 not only functions as a head inducer during development, but also regulates joint remodeling and bone formation, which indicate sits role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and multiple myeloma.
-

DKK-1, Mouse
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsDickkopf related protein 1 (DKK-1) is a chemokine that belongs to the DKK protein family, which also includes DKK-2, DKK-3 and DKK-4. DKK-1 was originally identified as a Xenopus head forming molecule that behaves as an antagonist for Wnt signaling. It is one of the most up-regulated genes during androgen-potentiated balding, with DKK-1 messenger RNA up-regulated a few hours after DHT treatment of hair follicles at the dermal papilla in vitro. Neutralizing bodies against DKK-1 reverses DHT effects on outer root sheath keratinocytes. DKK-1 expression is attenuated by L-threonate, a metabolite of ascorbate in vitro. DKK-1 promotes LRP6 internalization and degradation as it forms a ternary complex with the cell surface receptor Kremen. DKK-1 not only functions in head formation during development, but also regulates joint remodeling and bone formation indicating its potential role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and multiple myeloma.
-
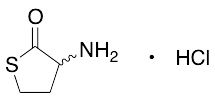
dl Homocysteine Thiolactone Hydrochloride
$56.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H7 N O S . Cl H
-
DL-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid
$151.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H16 O4 S
-
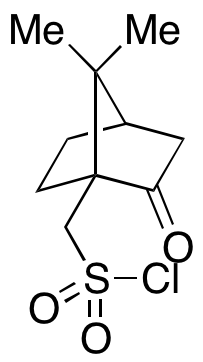
DL-10-Camphorsulfonyl Chloride
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H15ClO3S
-
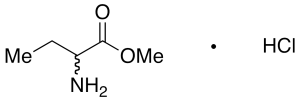
DL-2-Aminobutyric Acid Methyl Ester Hydrochloride
$341.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H12ClNO2
-

DL-2-Pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic Acid
$152.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H7NO3
-
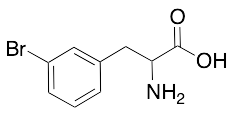
DL-3-Bromophenylalanine
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H10BrNO2
-
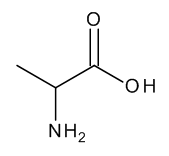
DL-Alanine
$128.51 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H7 N O2
-

dl-Alpha-Tocopherol Acetate
$185.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31 H52 O3
-
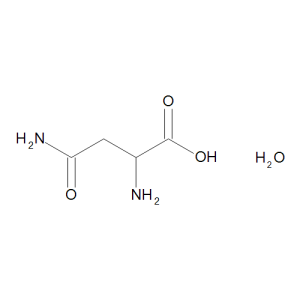
DL-Asparagine Monohydrate
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H8 N2 O3 . H2 O
-
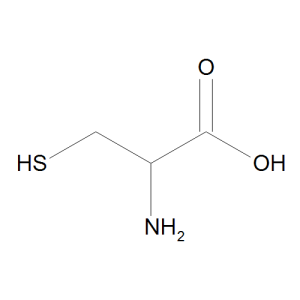
DL-Cysteine
$95.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H7 N O2 S
-
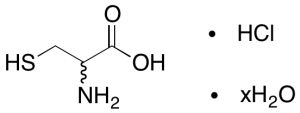
DL-Cysteine Hydrochloride Hydrate
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H7NO2S .HCl .xH2O
-
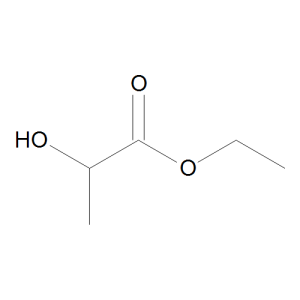
DL-Ethyl Lactate
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H10O3
-
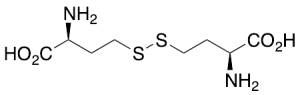
DL-Homocystine
$66.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H16 N2 O4 S2
-
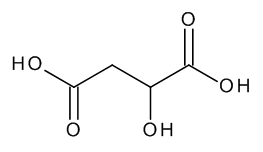
DL-Malic Acid
$149.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H6 O5
-
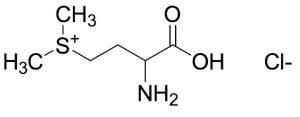
DL-Methionine Methylsulfonium Chloride
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H14ClNO2S
-
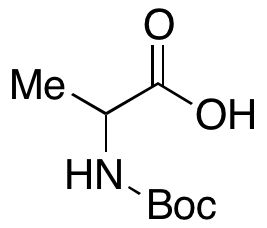
DL-N-Boc-alanine
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H15NO4
-
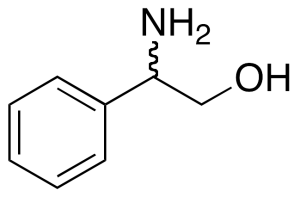
DL-Phenylglycinol
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H11NO
-

DL-Pipecolic Acid
$1,278.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H11 N O2
-
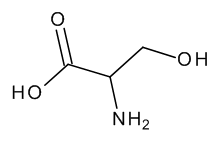
DL-Serine
$131.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H7 N O3
-
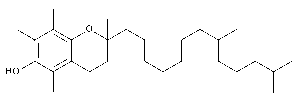
dl-α-Tocopherol
$194.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29 H50 O2
-

DNAM-1/CD226 Fc Chimera, Human
$34.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsDNAM-1 (DNAX accessory molecule-1), also known as CD226, platelet and T cell activation antigen 1 (PTA1) and TLiSA1, is a member of the Ig superfamily containing two Ig-like domains of the V set and is encoded by a gene on human chromosome 18q22.3. DNAM-1 is an activating receptor expressed on natural killer (NK) cells, CD8+ T cells, and other immune cells. Upon recognition of its ligands, CD155 and CD112, DNAM-1 promotes NK cell–mediated elimination of transformed and virus-infected cells. It also has a key role in expansion and maintenance of virus-specific memory NK cells. DNAM-1 is the cell surface receptor of NECTIN2. Upon ligand binding, it stimulates T cell proliferation and cytokine production, including that of IL2, IL5, IL10, IL13 and IFNG.
-

DNAM-1/CD226, His, Human
$34.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD226 (Cluster of Differentiation 226), also known as PTA1 (outdated term, ‘platelet and T cell activation antigen 1’)[5] or DNAM-1 (DNAX Accessory Molecule-1), is a ~65 kDa glycoprotein expressed on the surface of natural killer cells, platelets, monocytes and a subset of T cells. It is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. This protein is involved in intercellular adhesion, lymphocyte signaling, cytotoxicity and lymphokine secretion mediated by cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) and NK cell. It is the cell surface receptor for NECTIN2 and its main ligands are CD112 and CD155. It stimulates T-cell proliferation and cytokine production, including that of IL-2, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13, and IFNγ upon ligand binding.
-
Docosanoic Acid Methyl Ester
$371.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H46 O2
-
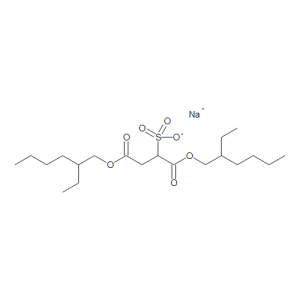
Docusate Sodium
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H37 O7 S . Na
-
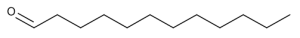
Dodecanal
$111.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H24 O
-
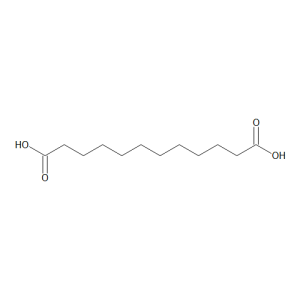
Dodecanedioic Acid
$1,154.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H22 O4
-
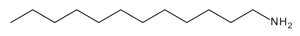
Dodecylamine
$127.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H27 N
-

Dodecylbenzene
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H30
-
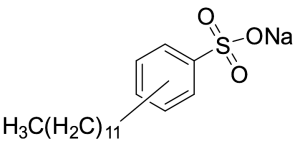
Dodecylbenzenesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt (Technical Grade)
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H29NaO3S
-

Dowex 1X4 Chloride Form
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : (C10 H12 . C10 H10 . C8 H8 . C3 H9 N)x
-

Dowex 50X2-100, Ion-exchange Resin, ACROS Organics
$105.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-

Doxycycline Hydrochloride
$513.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsDoxycycline Hydrochloride
-
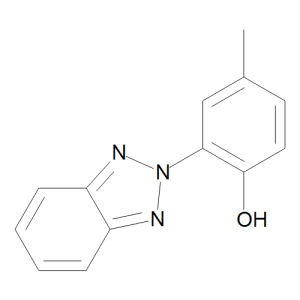
Drometrizole
$96.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H11 N3 O
-
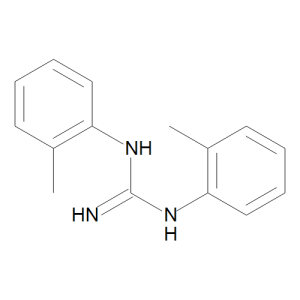
DTG
$77.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H17 N3
-
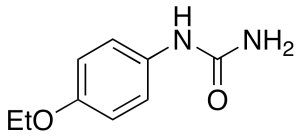
Dulcin
$765.90 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H12 N2 O2
-

Dyclonine Hydrochloride
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H27 N O2 . Cl H
-
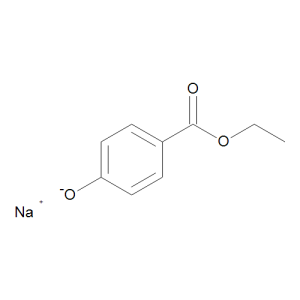
E 215
$313.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H9 O3 . Na
-

Ectoine
$1,014.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsEctoine
-
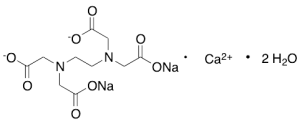
Edetate Calcium Disodium Dihydrate
$66.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H12CaN2O8 . 2H2O . 2Na
-
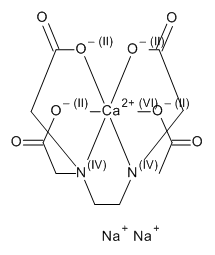
EDTA Calcium Disodium Salt
$64.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H12 Ca N2 O8 . 2 Na
-

EGF Fc Chimera, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-

EGF R, His, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsEGF Receptor, also known as ERBB, ERBB1 and HER1, is a type I transmembrane protein belonging to the tyrosine protein kinase family. It belongs to a family of tyrosine kinase receptors including Human EGF Receptors (HER) 2, 3, and 4 which all play important roles in cell growth and differentiation. Their primary ligands are EGF, Heparin-Binding EGF and Transforming Growth Factor α. Upon ligand binding, EGFR undergoes asymmetric dimerization, composed of an “activator” and a “receiver”. EGFR and its family members are disregulated in numerous cancers. In particular, EGFR is overexpressed in many epithelial solid tumors. Evidence suggests EGFR is an excellent target for pharmacologic intervention in Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) due to its high level of expression and prominent role in tumor growth and metastasis.
-
EGF, His, Human
$29.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-
EGF, Human
$34.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-

EGF, Mouse
$34.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-

EGF, Rat (CHO-expressed)
$36.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-

Eicosane
$1,152.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H42
-
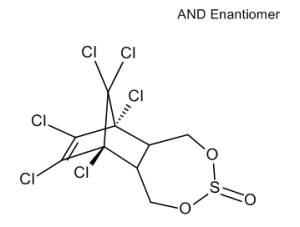
Endosulfan (Mixture of Diastereomers)
$319.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H6 Cl6 O3 S






