10g
Showing 2851–2900 of 4637 results
-
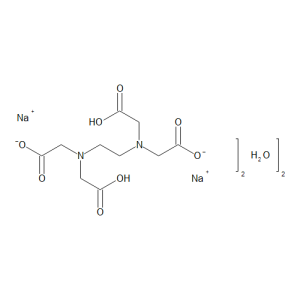
Ethylenediamine-N,N,N’,N’-tetraacetic Acid Disodium Dihydrate
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H14 N2 O8 . 2 Na . 2 H2 O
-

Ethylenediamine-N,N,N’,N’-tetraacetic Acid Calcium Disodium Hydrate
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H12 Ca N2 O8 . 2 Na . H2 O
-
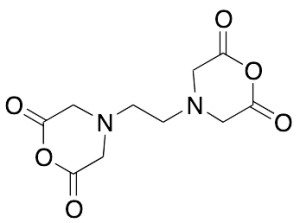
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Dianhydride
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H12N2O6
-
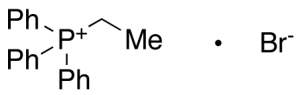
Ethyltriphenylphosphonium Bromide
$62.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H20 P . Br
-
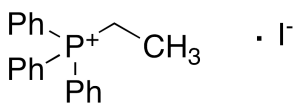
Ethyltriphenylphosphonium Iodide
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H20IP
-
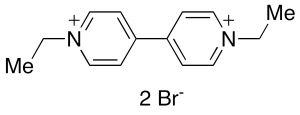
Ethylviologen Dibromide
$188.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H18 N2 . 2Br
-
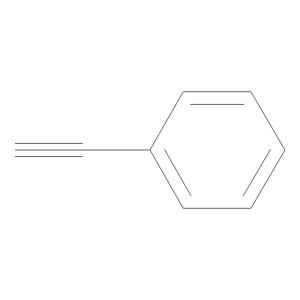
Ethynylbenzene
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H6
-
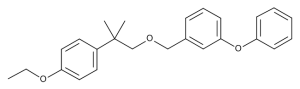
Etofenprox
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H28 O3
-
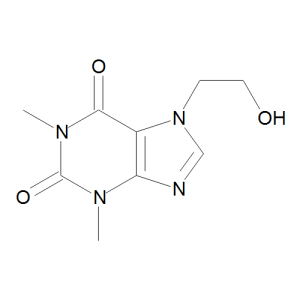
Etofylline
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H12 N4 O3
-
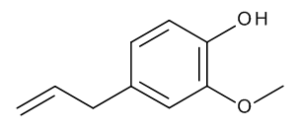
Eugenol
$117.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H12 O2
-
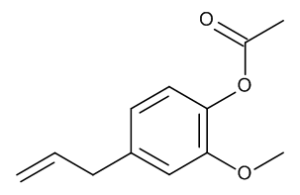
Eugenol Acetate
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H14 O3
-

Evans Blue
$86.22 Add to cart View Product DetailsEvans Blue
-

Evans blue (Technical Grade)
$264.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H24N6Na4O14S4
-

Fast Blue B Salt
$222.77 Add to cart View Product DetailsFast Blue B Salt
-
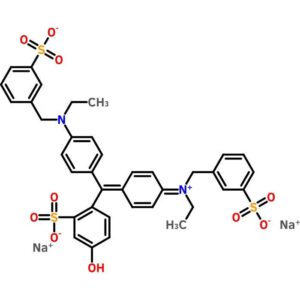
Fast Green FCF
$75.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsFast Green FCF
-

Fast Green FCF (Technical Grade)
$87.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C37 H34 N2 O10 S3 . 2 Na
-
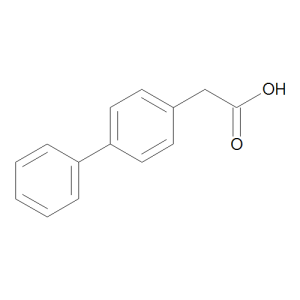
Felbinac
$98.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H12 O2
-
Fenazaquin
$1,229.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H22 N2 O
-
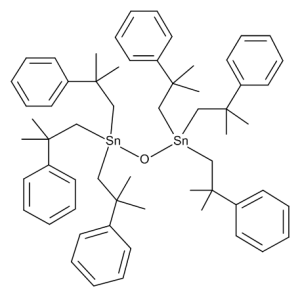
Fenbutatin Oxide (>90%)
$727.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C60 H78 O Sn2
-
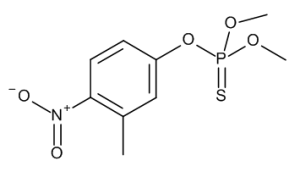
Fenitrothion
$1,105.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H12 N O5 P S
-
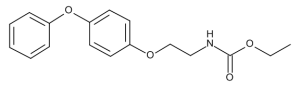
Fenoxycarb
$675.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H19 N O4
-
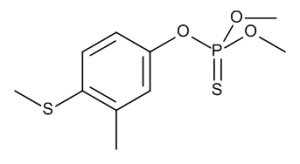
Fenthion
$326.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H15 O3 P S2
-

Fenvalerate
$494.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H22 Cl N O3
-

Ferric Carboxymaltose (Technical Grade)
$428.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-
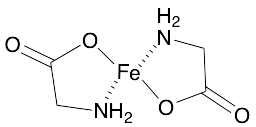
Ferrous Bisglycinate
$1,667.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C2 H4 N O2 . Fe
-
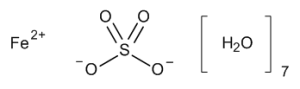
Ferrous Sulfate Heptahydrate
$136.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Fe . O4 S . 7[H2 O]
-

Ferulic Acid Ethyl Ester
$324.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H14 O4
-

FGF-10, Human
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-10 (FGF-10) is a mitogen mainly produced by mesenchymal stem cells in the lung. FGF-10 belongs to the heparin binding FGF family, and is also known as Keratinocyte Growth Factor-2 (KGF-2). It shares homology with KGF and receptor binding to FGFR2-IIIb. However, while KGF induces proliferation and differentiation of various epithelial cells, FGF-10 promotes budding and branching morphogenesis during the multi-organ development via mesenchymal-epithelial cell interactions. FGF-10 is critical for lung and limb development, and is regulated by Shh during early development.
-

FGF-10, Mouse
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-10 (FGF-10) is a mitogen mainly produced by mesenchymal stem cells in lung. FGF-10 belongs to the heparin binding FGF family, and is also known as Keratinocyte Growth Factor-2 (KGF-2). It shares homology with KGF, and both KGF and FGF-10 activate the receptor FGFR2-IIIb. However, unlike KGF, which induces the proliferation and differentiation of various epithelial cells, FGF-10 is an essential factor for the budding and branching morphogenesis during multi-organ development via mesenchymal-epithelial interactions. FGF-10 is crucial for lung and limb development and is regulated by Shh during early development.
-

FGF-16, Human
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-16 (FGF-16) is a heparin binding growth factor, a member of the FGF family. All FGF family members are heparinbinding growth factors with a core 120 amino acid (aa) FGF domain that allows for a common tertiary structure. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. The rat homolog is predominantly expressed in embryonic brown adipose tissue and has significant mitogenic activity, which suggests a role in proliferation of embryonic brown adipose tissue. FGF-16 is most similar to FGF-9 (73 % amino acid identity). The protein sequence of human FGF-16 displays 98.6% identity with rat FGF-16. Chimpanzee FGF-16 (207 amino acids), chicken FGF-16 (207 amino acids), and zebrafish FGF-16 (203 amino acids) show 100 %, 89.9 %, and 79.2 % total amino acid identity with human FGF-16.
-
FGF-18, Human
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-18 (FGF-18) is a heparin-binding growth factor that is a member of the FGF family. FGF-18 signals through FGFR 1c, 2c, 3c, and 4. FGF-18 plays an important role in the regulation of cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cell migration. FGF-18 is required for normal ossification and bone development. It can also stimulate hepatic and intestinal proliferation.
-

FGF-18, Rat
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor 18 (FGF-18) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the heparin-binding FGF family, which has 23 different members. Structurally, FGF-18 is closely related to FGF-8 and FGF-17. Like other FGFs, FGF-18 can bind to different FGF receptors in vivo. FGF-18 is expressed in various tissues and has multiple functions: during long bone growth, FGF-18 is expressed in perichondrium and developing joints, and regulates bone formation by inhibiting chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation; FGF-18 knock-out mice survive embryonic development, but exhibit skeletal abnormalities and die in the early neonatal period. FGF-18 also induces ectopic cartilage formation in the lung, and alters the morphology of the pulmonary mesenchyma.
-

FGF-21, His, Human
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsFGF-21, also known as fibroblast growth factor-21 and FGFL, is a secreted growth factor belonging to theheparin-binding growth factor family. It is produced by hepatocytes in response to fatty acid stimulation. FGF-21 couples with its co-factor beta-Klotho to signal through FGFR1c and FGFR4. Signal transduction results in insulin-independent uptake of glucose by adipocytes. Clinical administration of FGF-21 induces energy expenditure, fat utilization and lipid excretion.
-
FGF-21, Human
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-21 (FGF-21) is a metabolic cytokine belonging to the heparin-binding FGF family. Along with FGF-19/15 and FGF-23, FGF-21 is categorized as a member of the atypical FGF subfamily, as it must be complexed to the Klotho co-receptor in order to bind to the FGF receptors and activate the downstream signaling pathway. In vivo FGF-21 is expressed in liver, pancreas, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle, and it plays a central role in the energy metabolism. The expression of FGF-21 is stimulated by free fatty acids and insulin resistant states and is correlated with whole-body insulin resistance. FGF-21 activates glucose uptake in adipocytes and increases insulin sensitivity, implicating it as a novel target with potential anti-diabetic properties.
-

FGF-21, Mouse
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast growth factor-21 (FGF21) belongs to the large FGF family which has at least 23 members. Along with FGF-19/15 and FGF-23, FGF-21 is categorized as a member of the atypical FGF subfamily, as it must be complexed to the Klotho co-receptor in order to bind to the FGF receptors and activate the downstream signaling pathway. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities and are involved in a variety of biological processes including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion.
-

FGF-6, Human
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-6 (FGF-6) is a cytokine belonging to the heparin-binding FGF family, and is structurally related to other members of FGF family, particularly FGF-4. In vivo, FGF-6 exhibits an expression profile predominantly restricted tothe myogenic lineage, and it preferentially binds to two of the FGF receptors: FGFR1 and FGFR4. FGF-6 functions in muscle regeneration, myoblast proliferation and migration, and muscle differentiation in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo high concentration of recombinant FGF-6 up-regulates and down-regulates FGFR1 and FGFR4, respectively, as FGFR1 promotes the proliferation while FGFR4 promotes the differentiation in the muscle. Besides its dual function in muscle regeneration, FGF-6 may act as a regulator of bone metabolism as well.
-

FGF-8, Human
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-8 (FGF-8) is a heparin-binding growth factor of the FGF family. There are 4 known forms of FGF8 produced by alternative splicing: FGF8a, FGF-8b, FGF-8e and FGF-8f. The human and mouse FGF8b are identical of aa sequences. FGF-8 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cell migration. FGF-8 is required for normal brain, eye, ear and limb development during embryogenesis. It is also required for normal development of the gonadotropin- releasing hormone (GnRH) neuronal system.
-

FGF-8a, Human
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor 8a (FGF-8a) is a cytokine belonging to the heparin-binding FGF family, which has at least 23 members. FGF-8 has 8 different isoforms, named FGF-8a through FGF-8h. Different FGF-8 isoforms have different affinities to the receptors, and thus participate in different signaling cascade pathways. FGF-8 has very widespread expression during embryonic development, and is an organizer and inducer for gastrulation, somitogenesis, morphogenesis, and limb induction. However, FGF-8 is also a potential oncogene: in normal adult cells, FGF-8 has very low expression, but FGF-8 is highly expressed in cancer cells of breast, prostate, and ovarian tumors. FGF-8 promotes tumor angiogenesis by increasing neovascularization, and induces osteoblastic differentiation.
-

FGF-8e, Human
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor 8e (FGF-8e) is a cytokine belonging to the heparin-binding FGF family, which has at least 23 members. FGF-8 has 8 different isoforms, named FGF-8a through FGF-8h. Different FGF-8 isoforms have different receptor affinities, and thus participate in different signaling cascade pathways. FGF-8 has widespread expression during embryonic development, promoting gastrulation, somitogenesis, morphogenesis, and limb formation. FGF-8 also has oncogenic potential. While in normal cells FGF-8 is expressed at very low levels, in breast, prostate and ovarian cancer FGF-8 is highly expressed.FGF-8 promotes tumor angiogenesis by increasing neovascularization, and inducing osteoblastic differentiation.
-

FGF-9, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-9 (FGF-9) is a heparin binding growth factor that belongs to the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF-9 was isolated as a secreted factor that exhibits a growth-stimulating effect on cultured glial cells. In nervous system, this protein is produced mainly by neurons and may be important for glial cell development.
-
FGF-acidic, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor- acidic (FGF-acidic), also known as FGF-1 and endothelial cell growth factor, is a member of the FGF family which currently contain 23 members. FGF acidic and basic, unlike the other members of the family, lack signal peptides and are apparently secreted by mechanisms other than the classical protein secretion pathway. FGF acidic has been detected in large amounts in the brain. Other cells known to express FGF acidic include hepatocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells, CNS neurons, skeletal muscle cells, fibroblasts, keratinocytes, endothelial cells, intestinal columnar epithelium cells and pituitary basophils and acidophils. As with other FGF’s, FGF acidic exhibits considerable species cross reactivity. FGF acidic and FGF basic stimulate the proliferation of all cells of mesodermal origin, and many cells of neuroectodermal, ectodermal and endodermal origin.
-

FGF-acidic, Mouse
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor- acidic (FGF-acidic) is a mitogen targeting at the endothelial cells, and belongs to the heparin binding FGF family, which contains 22 members. FGF-acidic binds to the receptor family FGFR1-4 in vivo with the assistance of heparin. However, along with FGF -basic, FGF-acidic lacks the signal peptide segment, and thus is not secreted via endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi bodies. Studies have shown that FGF-acidic is highly regulated, and it is a direct angiogenesis factor. If unregulated, angiogenesis could contribute to several diseases including arthritis, diabetes, ocular neovascularization, and especially tumors. Therefore, FGF-acidic is treated as a potential oncogene, and its overexpression is correlated tightly with several cancers.
-

FGF-basic (145aa), Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-basic (FGF-basic), also known as FGF-2, is a pleiotropic cytokine and one of the prototypic members of the heparin-binding FGF family. Like other FGF family members, FGF-basic has the β trefoil structure. In vivo, FGF-basic is produced by a variety of cells, including cardiomycotes, fibroblasts, and vascular cells. FGF-basic regulates a variety of processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, adhesion, motility, apoptosis, limb formation and wound healing. FGF-basic can be tumorigenic due to its role in angiogenesis and blood vessel remodeling. The angiogenic effects of FGF-basic can produce beneficial cardioprotection during acute heart injury.
-

FGF-basic (146aa), Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-basic (FGF-basic), also known as FGF-2, is a pleiotropic cytokine and one of the prototypic members of the heparin-binding FGF family. Like other FGF family members, FGF-basic has the β trefoil structure. In vivo, FGF-basic is produced by a variety of cells, including cardiomycotes, fibroblasts, and vascular cells. FGF-basic regulates a variety of processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, adhesion, motility, apoptosis, limb formation and wound healing. FGF-basic can be tumorigenic due to its role in angiogenesis and blood vessel remodeling. The angiogenic effects of FGF-basic can produce beneficial cardioprotection during acute heart injury.
-

FGF-basic (154aa), Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-basic (FGF-basic), also known as FGF-2, is a pleiotropic cytokine and one of the prototypic members of the heparin-binding FGF family. Like other FGF family members, bFGF has the β trefoil structure. In vivo, bFGF is produced by a variety of cells, including cardiomycotes, fibroblasts, and vascular cells. bFGF regulates a variety of processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, adhesion, motility, apoptosis, limb formation and wound healing. bFGF can be tumorigenic due to its role in angiogenesis and blood vessel remodeling. The angiogenic effects of bFGF can produce beneficial cardioprotection during acute heart injury.
-

FGF-basic, Bovine
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-basic (FGF-basic), also known as FGF-2, is a pleiotropic cytokine and one of the prototypic members of the heparin-binding FGF family. Like other FGF family members, FGF-basic has the β trefoil structure. In vivo, FGF-basic is produced by a variety of cells, including cardiomycotes, fibroblasts, and vascular cells. FGF-basic regulates a variety of processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, adhesion, motility, apoptosis, limb formation and wound healing. FGF-basic can be tumorigenic due to its role in angiogenesis and blood vessel remodeling. The angiogenic effects of FGF-basic can produce beneficial cardioprotection during acute heart injury.
-
FGF-basic, Mouse
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-basic (FGF-basic), also known as HBGF-2, is a non-glycosylated heparin-binding growth factor that belongs to the FGF family. FGF-basic is present in basement membranes and in the subendothelial extracellular matrix of blood vessels. FGF-basic signals through FGFR1, 2, 3 and 4 that plays an important role in the regulation of cell survival, cell division, angiogenesis, cell differentiation and cell migration.
-
FGF-basic, Rat
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-basic (FGF-basic), also known as FGF-2, is a pleiotropic cytokine and one of the prototypic members of the heparin-binding FGF family. Like other FGF family members, FGF-basic has the β trefoil structure. In vivo, FGF-basic is produced by a variety of cells, including cardiomycotes, fibroblasts, and vascular cells. FGF-basic regulates a variety of processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, adhesion, motility, apoptosis, limb formation and wound healing. FGF-basic can be tumorigenic due to its role in angiogenesis and blood vessel remodeling. The angiogenic effects of FGF-basic can produce beneficial cardioprotection during acute heart injury.
-

FGF-basic, Salmon
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsFibroblast Growth Factor-basic (FGF-basic), also known as FGF-2, is a pleiotropic cytokine and one of the prototypic members of the heparin-binding FGF family. Like other FGF family members, FGF-basic has the β trefoil structure. In vivo, FGF-basic is produced by a variety of cells, including cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, and vascular cells. FGF-basic regulates a variety of processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, adhesion, motility, apoptosis, limb formation and wound healing. FGF-basic can be tumorigenic due to its role in angiogenesis and blood vessel remodeling. The angiogenic effects of FGF-basic can produce beneficial cardioprotection during acute heart injury.
-

Finasteride Powder – 10G
$81.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsCAS Number 98319-26-7 Molecular Weight 372.54Molecular Formula C23H36N2O2






