10g
Showing 2901–2950 of 4637 results
-

Fladrafinil Powder – 10G
$65.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsCAS Number 90212-80-9 Molecular Weight 325.33 Molecular Formula C15H13F2NO3S -
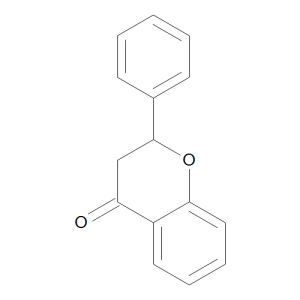
Flavanone
$1,022.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H12 O2
-

Flt-3L, His, Mouse
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsFlt3L, also known as Fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 ligand and SL cytokine, is a single-pass type I membrane protein. It is expressed by stromal cells and T cells. Flt3L signals through tyrosine kinase receptor Flt3/Flk2 to stimulate the proliferation of early hematopoietic progenitor cells. It synergizes with other growth factors, such as GM-CSF, IL-3 and CSF, to promote the differentiation of both myeloid and lymphoid cells. Alternative splicing and proteolytic cleavage of membrane-bound Flt3L generates a soluble extracellular domain (ECD) isoform with full biological activity.
-

Flt-3L, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsFms-related tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (Flt3L) is growth fator stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic multipotent progenitors and promotes proliferation of NK cells and dendritic cell subgroups by combination with other growth factors. Flt3L is produced by T cells and stromal fibroblasts, and targeted various cells including hematopoietic stem cells, B cells, T cells, dendritic cells, and NK cells. Flt3L binds to it cognate tyrosine kinase receptor Flt3 and activates JAK/STAT signaling pathway.Flt3L is a hematopoietic four helical bundle cytokine with structurally homologous to stem cell factor (SCF) and colony stimulating facor 1 (CSF-1) demonstrated four conserved cysteines and two glycosylation sites. Flt3L naturally as a non-disulfide-linked homodimer with multiple isoforms. The extracellular portion is approximately 160 amino acid residues in length and the cytoplasmic segment is approximately 20-30 amino acid residues in length.
-

Fludrocortisone Acetate
$652.91 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H31 F O6
-
Flufenacet
$1,382.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H13 F4 N3 O2 S
-

Flufenoxuron
$1,060.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H11 Cl F6 N2 O3
-
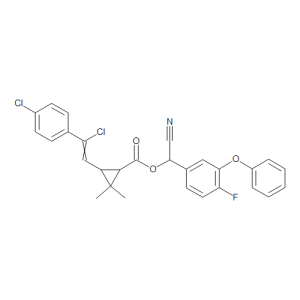
Flumethrin
$683.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28 H22 Cl2 F N O3
-
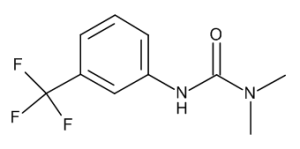
Fluometuron
$1,061.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H11 F3 N2 O
-

Fluorescein 5-Isothiocyanate, Isomer 1, 95%
$942.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H11 N O5 S
-
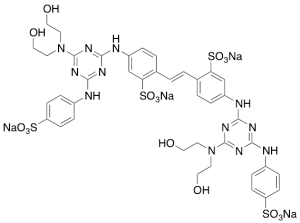
Fluorescent Brightener 87 (Technical Grade)
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C40H40N12Na4O16S4
-
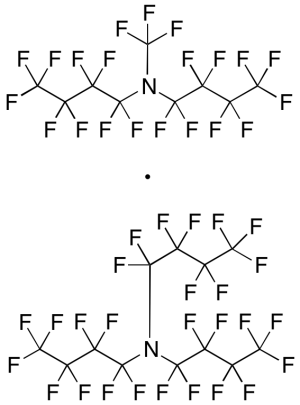
Fluorinert FC 40 (Technical Grade)
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9F21N •C12F27N
-

Fluoroiodomethane
$1,226.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C H2 F I
-

Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-OH, 97+ Percent
$74.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsFmoc-Glu(OtBu)-OH, 97+ Percent
-
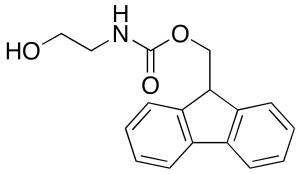
Fmoc-Glycinol
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H17NO3
-
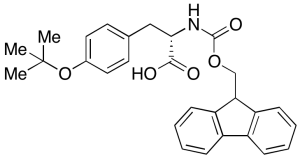
Fmoc-L-Tyr(tBu)-OH
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H29NO5
-
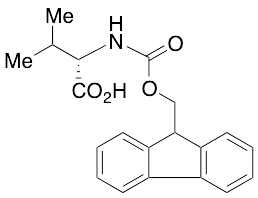
Fmoc-valine
$122.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H21NO4
-

Folic Acid, Powder, USP
$97.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsFolic Acid, Powder, USP
-

Folpet
$265.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H4 Cl3 N O2 S
-
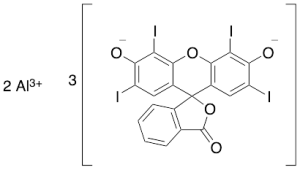
Food Red No.3 Aluminum Lake (Technical Grade)
$189.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H6 I4 O5
-
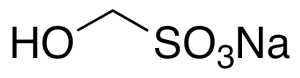
Formaldehyde Sodium Bisulfite
$77.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CH3NaO4S
-
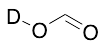
Formic Acid-d
$610.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C D H O2
-
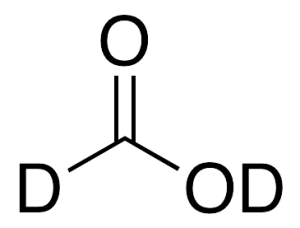
Formic Acid-d2 (95% w/w in D2O)
$1,957.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CD2O2
-
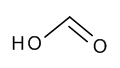
Formic Acid, 85%
$110.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C H2 O2
-

Fosfomycin Disodium Salt
$244.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H5 O4 P . 2 Na
-
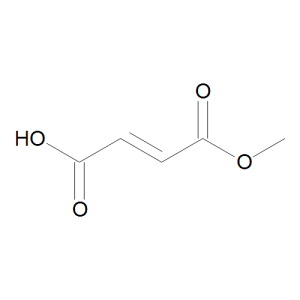
Fumaric Acid Monomethyl Ester
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H6 O4
-

Furazolidone
$65.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H7 N3 O5
-

Furosemide
$98.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H11 Cl N2 O5 S
-

G-CSF, Human
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) contains internal disulfide bonds. Among the family of colony-stimulating factors, Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is the most potent inducer of terminal differentiation to granulocytes and macrophages of leukemic myeloid cell lines. The synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) can be induced by bacterial endotoxins, TNF, Interleukin-1 and GM-CSF. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF). In epithelial, endothelial, and fibroblastic cells secretion of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is induced by Interleukin-17.
-

G-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) contains internal disulfide bonds. Among the family of colony-stimulating factors, Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is the most potent inducer of terminal differentiation to granulocytes and macrophages of leukemic myeloid cell lines. The synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) can be induced by bacterial endotoxins, TNF, Interleukin-1 and GM-CSF. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF). In epithelial, endothelial, and fibroblastic cells, the secretion of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is induced by Interleukin-17.
-

G-CSF, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF), also known as CSF-3 and MGI-1G, is a cytokine and hormone belonging to the IL-6 superfamily. It is expressed by monocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and bone marrow stroma. G-CSF stimulates the bone marrow to produce granulocytes and stem cells, and specifically stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of the neutrophilic granulocyte lineage. G-CSF has been used to stimulate white blood cell production after chemotherapy. It has also been used to boost the number of hematopoietic stem cells after bone marrow transplantation.
-

gAcrp30/Adipolean, Mouse
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsgAcrp30 is the globular head domain of Adipocyte complement-related protein of 30 kDa (Acrp30), a cytokine expressed in adipocytes. The name of Acrp30 is bases on its closest homolog, complement factor c1q, and the globular domain of Acrp30 has an unexpected homology with the Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) family of cytokines. Acrp30 is recognized by two receptors: adipoR1 expressed in skeletal muscle, and adipoR2 expressed in liver. The expression level of Acrp30 in adipocytes is negatively correlated with body weight and is lower in obese mouse than normal mouse. The globular domain of Acrp30 induces free fatty acid oxidation in muscle and weight reduction in mouse, suggesting its potential use as a pharmacological agent in obesity.
-
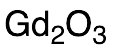
Gadolinium (III) Oxide
$116.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Gd2O3
-
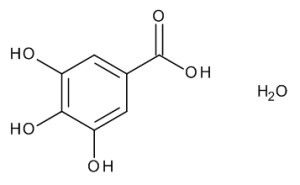
Gallic Acid Monohydrate
$64.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H8O6
-
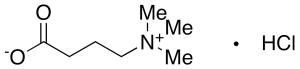
gamma-Butyrobetaine Hydrochloride
$1,539.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H16 N O2 . Cl
-
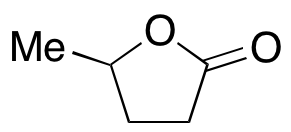
gamma-Valerolactone
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H8 O2
-

Garlic Extract (Contains Diallyl Trisulfide, Technical Grade)
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-
GDNF, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGlial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a neurotrophic factor belonging to the TGF-beta super family and is necessary for neuron survival and phenotypic maintenance in the central and peripheral nervous systems. G-DNF has the potential to support the differentiation and survival of many neuron subpopulations, especially dopaminergic neurons and motor neurons, as well as Purkinje cells and sympathetic neurons. Sertoli cells, type 1 astrocytes, Schwann cells, neurons, pinealocytes and skeletal muscle cells are known to express GDNF in human. GDNF has been shown to interact with GFRA2 and GDNF family receptor alpha 1. Mutations in this gene may be associated with Hirschsprung’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).The recombinant human G-DNF expressed in E.coli is a disulfide-linked homo-dimer, with an apparent molecular weight of 17 kDa.
-

Gentamicin Sulfate
$100.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsGentamicin Sulfate
-
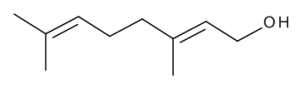
Geraniol
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H18 O
-

Geranyl Linalool
$818.51 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H34O
-
GH, Human
$34.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsGrowth Hormone (GH) is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin family which play an important role in growth control. The human GH cDNA encodes a 217 amino acid (aa), and the first 26 aa is a signal peptide. By alternative splicing, at least four isoforms of GH have been identified. The major role of GH in stimulating body growth is to stimulate the liver and other tissues to secrete IGF-1. GH stimulates both the differentiation and proliferation of myoblasts, and also stimulates amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in muscle and other tissues.
-

GH, Human(CHO-expressed)
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsGrowth Hormone (GH) is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin family which play an important role in growth control. The human GH cDNA encodes a 217 amino acid (aa), and the first 26 aa is a signal peptide. By alternative splicing, at least four isoforms of GH have been identified. The major role of GH in stimulating body growth is to stimulate the liver and other tissues to secrete IGF-1. GH stimulates both the differentiation and proliferation of myoblasts, and also stimulates amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in muscle and other tissues.
-

GH, Mouse
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsGrowth Hormone (GH), is a member of the somatotropin / prolactin family of hormones which play an important role in growth control. The gene, along with four other related genes, is located at the growth hormone locus on chromosome 17 where they are interspersed in the same transcriptional orientation; an arrangement which is thought to have evolved by a series of gene duplications. The five genes share a remarkably high degree of sequence identity. Alternative splicing generates additional isoforms of each of the five growth hormones, leading to further diversity and potential for specialization. This particular family member is expressed in the pituitary but not in placental tissue as is the case for the other four genes in the growth hormone locus. Mutations in or deletions of the gene lead to growth hormone deficiency and short stature.
-

Giemsa Stain
$238.22 Add to cart View Product DetailsGiemsa Stain
-
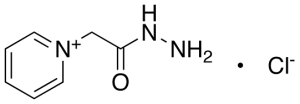
Girard’s Reagent P
$129.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H10N3O • Cl
-
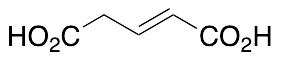
Glutaconic Acid
$573.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H6O4
-
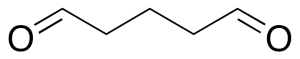
Glutaraldehyde (50% in water)
$169.91 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H8 O2
-
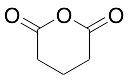
Glutaric Anhydride
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H6O3
-

Glutathione
$125.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H17 N3 O6 S






