10g
Showing 3301–3350 of 4637 results
-
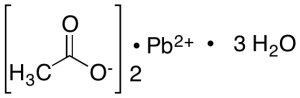
Lead Acetate Trihydrate
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H6O4Pb . 3H2O
-
Lead Powder, -200 mesh
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Pb
-

Lead Titanium Zirconium Oxide (~30% by weight)
$413.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : O3 Pb Ti(x) Zr(y)
-
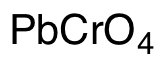
Lead(II) Chromate
$108.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CrO4Pb
-
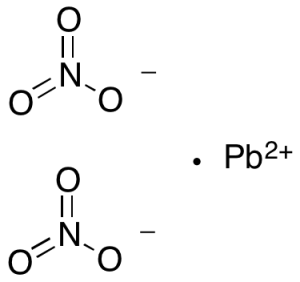
Lead(II) Nitrate
$55.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 N O3 . Pb
-

Lead(II) Oxide
$116.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : PbO
-

Lead(IV) Acetate, Stabilized
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H12 O8 Pb
-
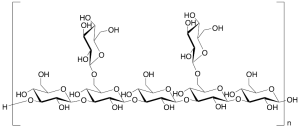
Lentinan (Technical Grade)
$99.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : (C42H70O35)nH2O
-
Leucomycins (>85%)
$97.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-
Levamisole Hydrochloride
$74.42 Add to cart View Product DetailsLevamisole Hydrochloride
-
Lidocaine
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H22 N2 O
-

Lidocaine Hydrochloride Monohydrate
$81.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H22 N2 O . Cl H . H2 O
-

LIF, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-

LIF, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-

Light Green SF Yellowish
$52.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Green SF Yellowish
-
Linalool
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H18 O
-
Lindane
$208.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H6 Cl6
-
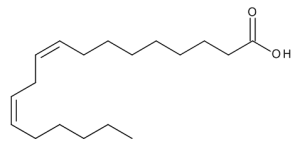
Linoleic Acid
$168.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H32 O2
-

Linoleic Acid
$189.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsLinoleic Acid
-
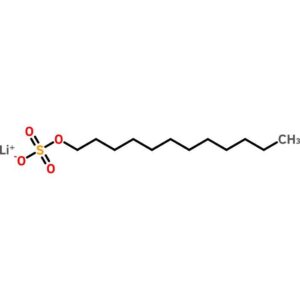
Lithium Dodecyl Sulfate
$74.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsLithium Dodecyl Sulfate
-
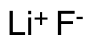
Lithium Fluoride
$83.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : LiF
-
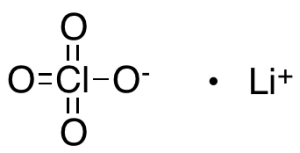
Lithium Perchlorate
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : ClO4 .Li
-
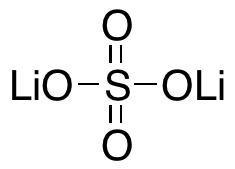
Lithium sulfate, anhydrous
$70.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Li2SO4
-
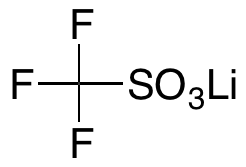
Lithium Trifluoromethylsulfonate
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CF3LiO3S
-

LIX/CXCL5 (74aa), Mouse
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMouse LIX (C-X-C motif chemokine 5) is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family that is cleaved into the following 2 chains [GCP-2(1-78) and GCP-2(9-78)]. Mouse LIX plays a role in reducing sensitivity to sunburn pain in some subjects, and is a potential target which could be used to understand more about pain in other inflammatory conditions. It is most closely related to two highly homologous human neutrophil chemoattractants GCP-2 and ENA-78. The first 78 amino acid residues within the predicted mature mouse LIX shares approximately 61% and 55% amino acid identity with human GCP-2 and ENA-78. This chemokine stimulates the chemotaxis of neutrophils possessing angiogenic properties. It elicits these effects by interacting with the cell surface chemokine receptor CXCR2.
-

Longifolene (>75%)
$411.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H24
-
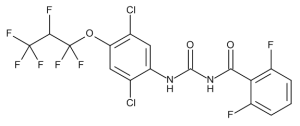
Lufenuron
$1,345.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H8 Cl2 F8 N2 O3
-
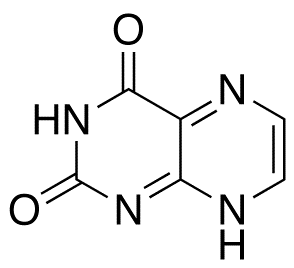
Lumazine
$990.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H4 N4 O2
-
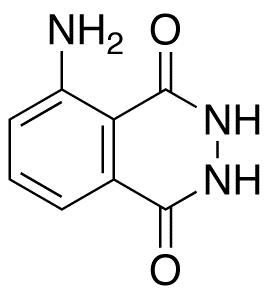
Luminol
$71.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H7 N3 O2
-
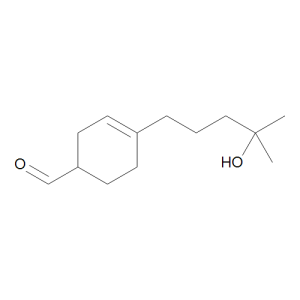
Lyral, mixture of isomers
$435.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H22 O2
-

m-Aminophenyl Tosylate
$1,443.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H13NO3S
-
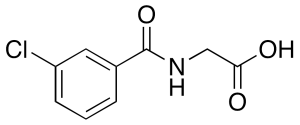
m-Chloro Hippuric Acid
$1,527.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H8ClNO3
-

m-Cresol Purple
$138.61 Add to cart View Product Detailsm-Cresol Purple
-
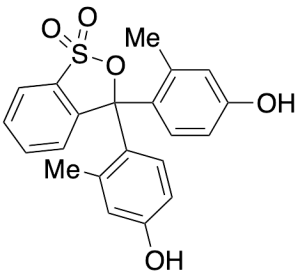
m-Cresol Purple
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H18O5S
-

M-CSF, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Rat
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-
m-Nitrobenzoic Acid
$122.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H5 N O4
-
m-Toluoyl Chloride
$105.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H7ClO
-

m-Toluquinoline
$225.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H9 N
-

Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate
$1,923.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMagnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate
-
Magnesium Carbonate
$145.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C O3 . Mg
-
Magnesium Citrate xHydrate
$111.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H8O7.3/2Mg.XH2O
-
Magnesium Oxide (Technical Grade)
$83.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Mg O
-
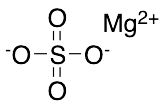
Magnesium Sulfate
$81.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : MgSO4
-
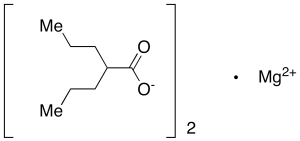
Magnesium Valproate
$1,612.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H30 Mg O4
-
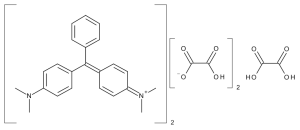
Malachite Green Oxalate
$1,262.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C23 H25 N2 . C2 H2 O4 . 2 C2 H O4
-

Malachite Green Oxalate
$85.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMalachite Green Oxalate






