10g
Showing 3851–3900 of 4637 results
-
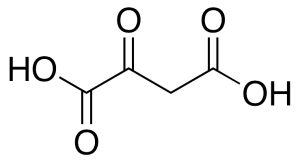
Oxaloacetic Acid
$111.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H4 O5
-
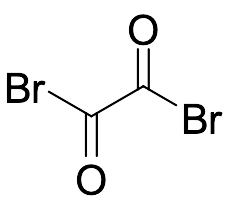
Oxalyl Bromide
$264.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H8 O3
-
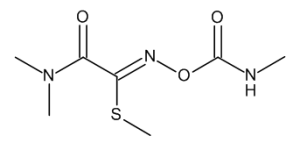
Oxamyl
$365.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H13 N3 O3 S
-

Oxolamine Citrate
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H19 N3 O . C6 H8 O7
-
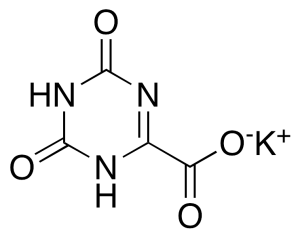
Oxonic Acid Potassium Salt
$55.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H2 N3 O4 . K
-

Oxybenzone
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H12 O3
-

Oxyfluorfen
$545.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H11 Cl F3 N O4
-

Oxyphenisatine
$755.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H15 N O3
-

Oxytetracycline Dihydrate
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H24 N2 O9 . 2 H2 O
-
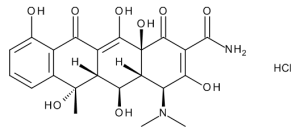
Oxytetracycline Hydrochloride
$1,436.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H24 N2 O9 . Cl H
-

Oxythiamine Hydrochloride
$396.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H15N3O2S . HCl
-
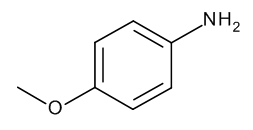
p-Anisidine
$148.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H9 N O
-

p-Chloroacetophenone
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H7ClO
-
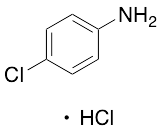
p-Chloroaniline Hydrochloride
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H6 Cl N . Cl H
-
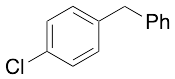
p-Chlorobenzylbenzene
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H11Cl
-
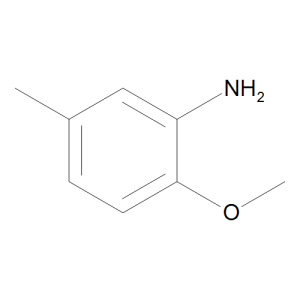
p-Cresidine
$69.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H11 N O
-
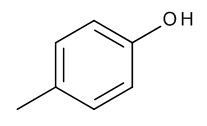
p-Cresol
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H8 O
-
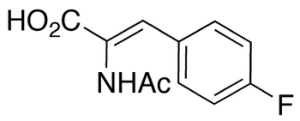
p-Fluoro-Alpha-acetamidocinnamic Acid
$1,356.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H10 F N O3
-
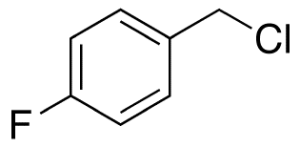
p-Fluorobenzyl Chloride
$136.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H6ClF
-

p-Methylphosphonic Acid
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C H5 O3 P
-

p-Naphtholbenzein
$154.54 Add to cart View Product Detailsp-Naphtholbenzein
-
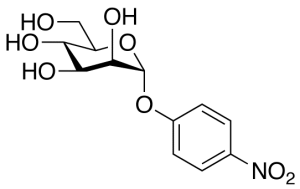
p-Nitrophenyl a-D-Mannopyranoside
$647.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H15 N O8
-
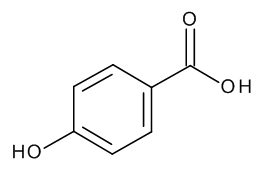
p-Salicylic Acid
$91.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H6 O3
-

p-Sulfamylacetanilide
$1,535.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H10 N2 O3 S
-
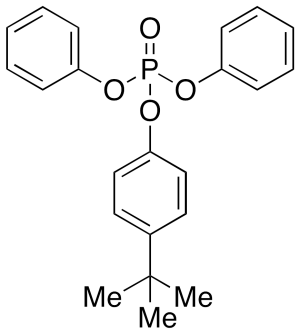
p-t-Butylphenyl Diphenyl Phosphate
$1,683.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H23O4P
-
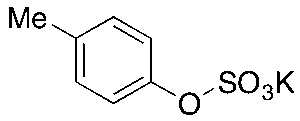
p-Tolyl Sulfate Potassium Salt
$1,699.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H7O4S.K
-

p-Trifluoromethylphenol
$162.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H5 F3 O
-
P,P’-[(1,2-Phenylene)bis(methylene)]bisphosphonic Acid P,P,P’,P’-tetraethyl ester
$1,471.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H28O6P2
-
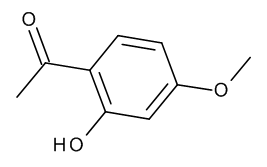
Paeonol
$95.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H10 O3
-
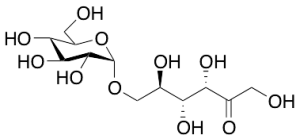
Palatinose
$85.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H22 O11
-
Palladium (5% on Barium Sulfate)
$319.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Pd
-

Palladium Hydroxide (20% on Carbon) (~50% water by weight)
$526.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : H2O2Pd
-

Palladium on Charcoal, 5 Percent, Catalyst, Powder
$346.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsPalladium on Charcoal, 5 Percent, Catalyst, Powder
-

Palmatine Chloride
$631.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H22 N O4 . Cl
-
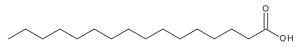
Palmitic Acid
$54.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H32 O2
-
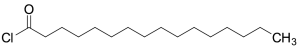
Palmitoyl Chloride
$396.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H31ClO
-
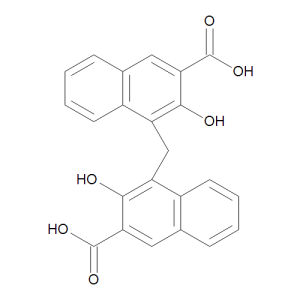
Pamoic Acid
$1,278.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H16 O6
-
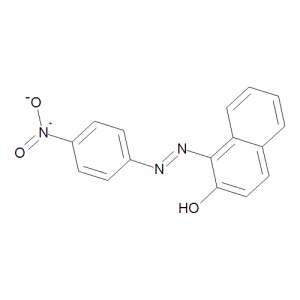
Para Red
$83.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H11 N3 O3
-
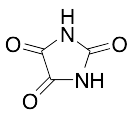
Parabanic Acid
$242.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H2 N2 O3
-
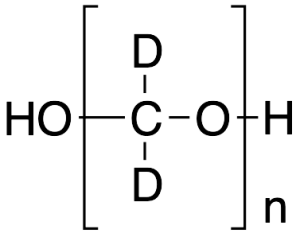
Paraformaldehyde-D2
$1,407.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : (C 2H2 O)n
-

Paraquat Dichloride (42% w/w in Water)
$280.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H14 N2 . 2 Cl
-
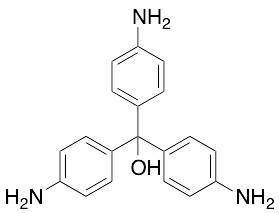
Pararosaniline Base
$95.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H19 N3 O
-

PD-L1 Fc Chimera, Mouse
$34.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsProgrammed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) also known as cluster of differentiation 274 (CD274) or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD274 gene. PD-L1 is a 40 kDa type 1 transmembrane protein that has been speculated to play a major role in suppressing the immune system during particular events such as pregnancy, tissue allografts, autoimmune disease and other disease states such as hepatitis. Normally the immune system reacts to foreign antigens where there is some accumulation in the lymph nodes or spleen which triggers a proliferation of antigen-specific CD8+ T cell. The formation of PD-1 receptor / PD-L1 or B7.1 receptor /PD-L1 ligand complex transmits an inhibitory signal which reduces the proliferation of these CD8+ T cells at the lymph nodes and supplementary to that PD-1 is also able to control the accumulation of foreign antigen specific T cells in the lymph nodes through apoptosis which is further mediated by a lower regulation of the gene Bcl-2. PD-L1 binds to its receptor, PD-1, found on activated T cells, B cells, and myeloid cells, to modulate activation or inhibition.
-
PDGF-AA, Mouse
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-Derived Growth Factor-AA (PDGF-AA) is one of five dimers (PDGF-AA, AB, BB, CC, and DD) formed by 4 different PDGF subunits. In chemical terms, platelet-derived growth factor is a dimeric glycoprotein composed of two A (-AA) or two B (-BB) chains or a combination of the two (-AB). The dimeric isoforms PDGFAA, AB and BB are differentially expressed in various cell types, and their effects are mediated through two distinct receptors termed α and β. Differences exist in isoform binding to each receptor. Ingeneral, PDGF isoforms are potent mitogens for connective tissue cells including dermal fibroblasts, glial cells, arterial smooth muscle cells and some epithelial andendothelial cells. In addition to its activity as a mitogen, PDGF is chemotactic for fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, neutrophils and mononuclear cells. PDGF-AA plays a significant role in blood vessel formation (angiogenesis).
-

PDGF-BB, Bovine
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) presenting in serum but absent from plasma was first discovered in an animal study by Lynch and co-workers in the late 1980s. It is a disulfide-linked dimer consisting of two peptides-chain A and chain B. PDGF has three subforms: PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB, and PDGF-AB. It is involved in many biological processes, including hyperplasia, embryonic neuron development, chemotaxis, and respiratory tubule epithelial cell development. The function of PDGF is mediated by two receptors (PDGFR-α and PDGFR-β).
-

PDGF-BB, Human
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) presenting in serum but absent from plasma was first discovered in animal study by Lynch and co-workers in the late 1980s. It is a disulfide-linked dimer consisting of two peptides-chain A and chain B. PDGF has three subforms: PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB, PDGF-AB. It is involved in a number of biological processes, including hyperplasia, embryonic neuron development, chemotaxis, and respiratory tubule epithelial cell development. The function of PDGF is mediated by two receptors (PDGFR-α and PDGFR-β).
-

PDGF-BB, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB (PDGF-BB) is one of five dimers (PDGF-AA, AB, BB, CC, and DD) formed by 4 different PDGF subunits. In vivo, PDGF-BB is mainly produced in heart and placenta, and predominantly expressed by osteoblasts, fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and glial cells. An inactive precursor of PDGF-BB is produced in the endoplasmic reticulum and then activated by a proprotein convertase after secretion. PDGF-BB functions in a paracrine manner and promotes organogenesis, human skeletal development, and wound healing. PDGF-BB also promotes angiogenesis, particularly in the presence of Fibroblast Growth Factor basic. Therefore, PDGF-BB and its related pathways are potential pharmacological targets.
-

PDGF-BB, Human (P. pastoris-expressed)
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB (PDGF-BB) is one of five dimers (PDGF-AA, AB, BB, CC, and DD) formed by 4 different PDGF subunits. In vivo, PDGF-BB is mainly produced in heart and placenta, and predominantly expressed by osteoblasts, fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and glial cells. An inactive precursor of PDGF-BB is produced in the endoplasmic reticulum and then activated by a proprotein convertase after secretion. PDGF-BB functions in a paracrine manner and promotes organogenesis, human skeletal development, and wound healing. PDGF-BB also promotes angiogenesis, particularly in the presence of Fibroblast Growth Factor basic. Therefore, PDGF-BB and its related pathways are potential pharmacological targets.
-

PDGF-BB, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB (PDGF-BB) is one of five dimers (PDGF-AA, AB, BB, CC, and DD) formed by 4 different PDGF subunits. In vivo, PDGF-BB is mainly produced in heart and placenta, and predominantly expressed by osteoblasts, fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and glial cells. An inactive precursor of PDGF-BB is produced in the endoplasmic reticulum and then activated by a proprotein convertase after secretion. PDGF-BB functions in a paracrine manner and promotes organogenesis, human skeletal development, and wound healing. PDGF-BB also promotes angiogenesis, particularly in the presence of Fibroblast Growth Factor basic. Therefore, PDGF-BB and its related pathways are potential pharmacological targets.
-

PDGF-BB, Rat
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB (PDGF-BB) is one of five dimers (PDGF-AA, AB, BB, CC, and DD) formed by 4 different PDGF subunits. In vivo, PDGF-BB is mainly produced in heart and placenta, and predominantly expressed by osteoblasts, fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and glial cells. An inactive precursor of PDGF-BB is produced in the endoplasmic reticulum and then activated by a proprotein convertase after secretion. PDGF-BB functions in a paracrine manner and promotes organogenesis, human skeletal development, and wound healing. PDGF-BB also promotes angiogenesis, particularly in the presence of Fibroblast Growth Factor basic. Therefore, PDGF-BB and its related pathways are potential pharmacological targets.






