10g
Showing 4351–4400 of 4637 results
-

Tetrabutylammonium Periodate
$275.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H36N . IO4
-
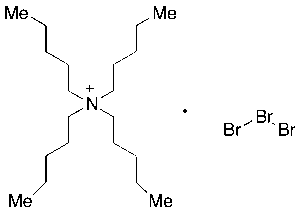
Tetrabutylammonium Tribromide
$50.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H36Br3N
-
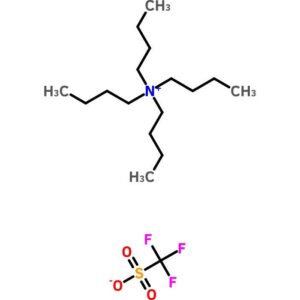
Tetrabutylammonium Trifluoromethanesulfonate
$103.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrabutylammonium Trifluoromethanesulfonate
-
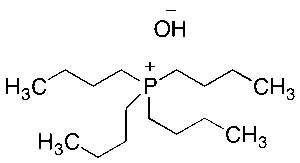
Tetrabutylphosphonium Hydroxide (40% in Water)
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H36 P . H O
-
Tetrabutylstannane
$210.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H36 Sn
-

Tetracaine Hydrochloride
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H24 N2 O2 . Cl H
-
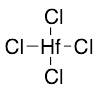
Tetrachlorohafnium
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Cl4Hf
-

Tetracycline
$69.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H24 N2 O8
-
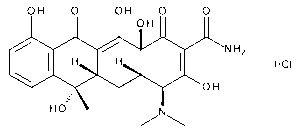
Tetracycline Hydrochloride
$114.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H24 N2 O8 . Cl H
-

Tetradecanamine
$83.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H31 N
-

Tetraethoxymethane
$100.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H20O4
-

Tetraethyl Orthosilicate
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H20O4Si
-
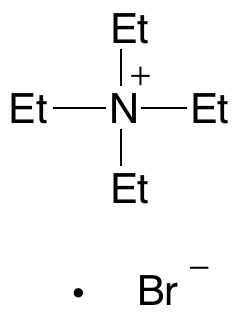
Tetraethylammonium Bromide
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H20BrN
-

Tetraethylammonium Chloride
$124.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H20 N . Cl
-
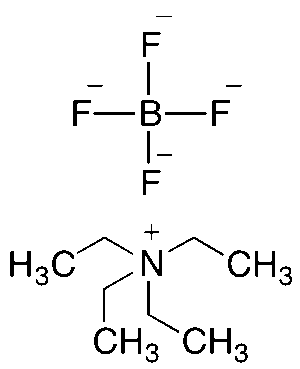
Tetraethylammonium Tetrafluoroborate
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H20 B F4 N3
-

Tetraethylene Glycol
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H18 O5
-

Tetraethylenepentamine Pentahydrochloride
$219.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H28Cl5N5
-

Tetraglyme
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H22 O5
-
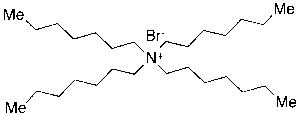
Tetraheptylammonium Bromide
$112.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H60BrN
-
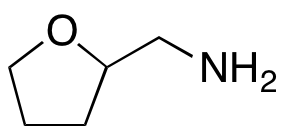
Tetrahydro-2-furanmethanamine
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H11NO
-
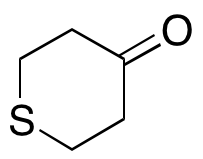
Tetrahydro-4H-thiopyran-4-one
$50.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H8OS
-

Tetrahydronaphthalene
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H12
-
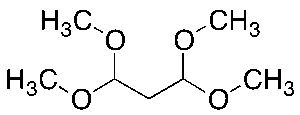
Tetramethoxypropane
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H16O4
-
Tetramethrin
$539.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H25 N O4
-

Tetramethyl Bisphenol A
$1,279.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H24 O2
-
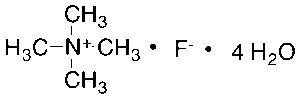
Tetramethylammonium Fluoride Tetrahydrate
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H12FN . 4H2O
-
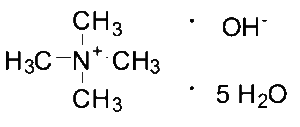
Tetramethylammonium Hydroxide Pentahydrate
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H23NO6
-

Tetramethylol Acetylenediurea
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H14 N4 O6
-

Tetramethylpyrazine
$120.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H12 N2
-
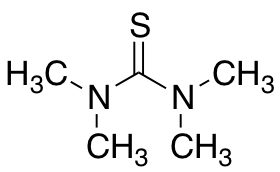
Tetramethylthiourea
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H12N2S
-
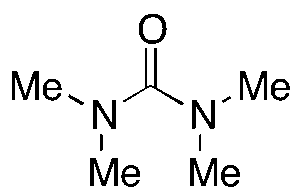
Tetramethylurea
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H12 N2 O
-
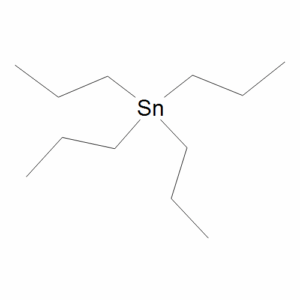
Tetrapropyltin
$1,329.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H28 Sn
-
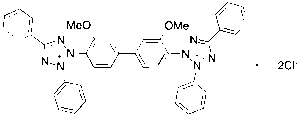
Tetrazolium Blue Chloride (>90%)
$473.51 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C40H32N8O2 . 2Cl
-

TGF-α, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming Growth Factor-alpha (TGF-α) , also known as sarcoma growth factor, TGF-type I and ETGF, is a member of the EGF family of cytokines. It is expressed in monocytes, brain cells, keratinocytes and various tumor cells. TGF-α signals through EGFR and acts synergistically with TGF-beta to promote the proliferation of a wide range of epidermal and epithelial cells. TGF-α is a transforming growth factor that is a ligand for the epidermal growth factor receptor, which activates a signaling pathway for cell proliferation, differentiation and development. This protein may act as either a transmembrane-bound ligand or a soluble ligand. The biological actions of TGF-α and EGF are similar. For instance, TGF-α and EGF bind to the same receptor. When TGF-α binds to EGFR it can initiate multiple cell proliferation events.
-

TGF-β 1, Mouse
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFβ1) is the prototype of a growing superfamily of peptide growth factors and plays a prominent role in a variety of cellular processes, including cell-cycle progression, cell differentiation, reproductive function, development, motility, adhesion, neuronal growth, bone morphogenesis, wound healing, and immune surveillance. TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and TGF-β3 signal via the same heteromeric receptor complex, consisting of a ligand binding TGF-β receptor type II (TβR-II), and a TGF-β receptor type I (TβR-I). Signal transduction from the receptor to the nucleus is mediated via SMADs. TGF-β expression is found in cartilage, bone, teeth, muscle, heart, blood vessels, hematopoietic cells, lung, kidney, gut, liver, eye, ear, skin, and the nervous system.
-

TGF-β 2, Human
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming growth factor beta-2 (TGF-β2) is a secreted protein which belongs to the TGF-beta family. It is known as a cytokine that performs many cellular functions and has a vital role during embryonic development. The precursor is cleaved into mature TGF-beta-2 and LAP, which remains non-covalently linked to mature TGF-beta-2 rendering it inactive. It is an extracellular glycosylated protein. It is known to suppress the effects of interleukin dependent T-cell tumors. Defects in TGFB2 may be a cause of non-syndromic aortic disease (NSAD).
-

TGF-β 2, Mouse
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming growth factor beta 2 (TGF-β2) is a member of TGF-beta superfamily that shares a characteristic cysteine knot structure. Mice with TGF-β2 gene deletion show defects in development of cardiac, lung, craniofacial, limb, spinal column, eye, inner ear and urogenital systems. All TGF-β isoforms signal via the same heteromeric receptor complex, consisting of a ligand binding TGF-β receptor type II (TβR-II), and a TGF-β receptor type I (TβR-I). Signal transduction from the receptor to the nucleus is mediated via SMADs. TGF-β expression is found in cartilage, bone, teeth, muscle, heart, blood vessels, hematopoietic cells, lung, kidney, gut, liver, eye, ear, skin, and the nervous system.
-

TGF-β 3, Human
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming growth factor beta 3(TGFB3) is a member of a TGF -β superfamily which is defined by their structural and functional similarities. TGFB3 is secreted as a complex with LAP. This latent form of TGFB3 becomes active upon cleavage by plasmin, matrix metalloproteases, thrombospondin -1, and a subset of integrins. It binds with high affinity to TGF- β RII, a type II serine/threonine kinase receptor. TGFB3 is involved in cell differentiation, embryogenesis and development. It is believed to regulate molecules involved in cellular adhesion and extracellular matrix (ECM) formation during the process of palate development. Without TGF-β3, mammals develop a deformity known as a cleft palate.
-
TGF-β1, Human
$146.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsTGF-β1 (transforming growth factor beta 1) is one of three closely related mammalian members of the large TGF-β1 superfamily that share a characteristic cystine knot structure. TGF-β1, -2 and -3 are highly pleiotropic cytokines that act as cellular switches to regulate processes such as immune function, proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Each TGF-β isoform has some non-redundant function; for TGF-β1, mice with targeted deletion show defects in hematopoiesis and endothelial differentiation and died of overwhelming inflammation. TGF-β1 signaling begins with high-affinity binding to a type II ser/thr kinase receptor termed TGF-β RII. This receptor then phosphorylates and activates a second ser/thr kinase receptor, TGF-β RI (also called activin receptor‑like kinase (ALK)-5), or alternatively, ALK-1. This complex phosphorylates and activates Smad proteins that regulate transcription.
-

TGFβ1, Bovine
$142.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsTGF-β1 (transforming growth factor beta 1) is one of three closely related mammalian members of the large TGF-β1 superfamily that share a characteristic cystine knot structure. TGF-β1, -2 and -3 are highly pleiotropic cytokines that act as cellular switches to regulate processes such as immune function, proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Each TGF-β isoform has some non-redundant function; for TGF-β1, mice with targeted deletion show defects in hematopoiesis and endothelial differentiation and died of overwhelming inflammation. TGF-β1 signaling begins with high-affinity binding to a type II ser/thr kinase receptor termed TGF-β RII. This receptor then phosphorylates and activates a second ser/thr kinase receptor, TGF-β RI (also called activin receptor‑like kinase (ALK)-5), or alternatively, ALK-1. This complex phosphorylates and activates Smad proteins that regulate transcription.
-
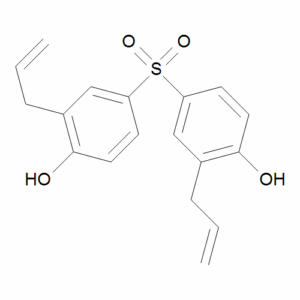
TGSH
$179.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H18O4S
-

Theophylline-7-acetic Acid
$74.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H10 N4 O4
-

Thiamine Hydrochloride
$71.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H17 N4 O S . Cl . Cl H
-

Thiamine Nitrate
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H17 N4 O S . N O3
-
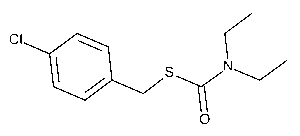
Thiobencarb
$946.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H16 Cl N O S
-

Thiobenzoic Acid (94%)(Benzenecarbothioic Acid)
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H6OS
-

Thiobutabarbital
$1,389.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H16 N2 O2 S
-

Thioglycolic Acid
$95.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2 H4 O2 S
-
Thionaphthenquinone
$614.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H4 O2 S
-

Thionin Acetate
$303.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsThionin Acetate






