1mg
Showing 5051–5100 of 7910 results
-
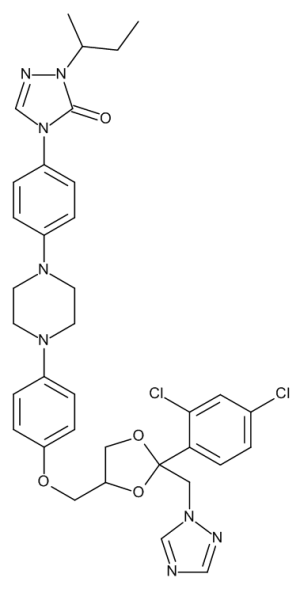
Itraconazole-d3
$200.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 2H3 H35 Cl2 N8 O4
-
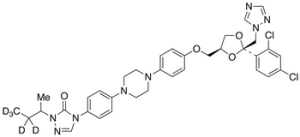
Itraconazole-d5 (major)
$234.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 2H5 H33 Cl2 N8 O4
-
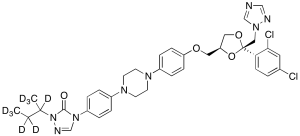
Itraconazole-d9
$261.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35H29D9Cl2N8O4
-
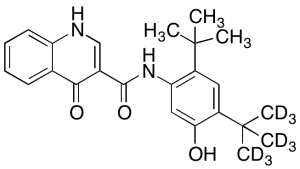
Ivacaftor (4-tertbutyl-d9) (Major)
$336.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H19D9N2O3
-
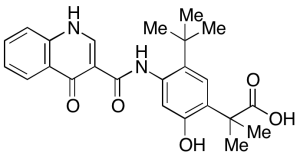
Ivacaftor Carboxylic Acid
$218.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24 H26 N2 O5
-
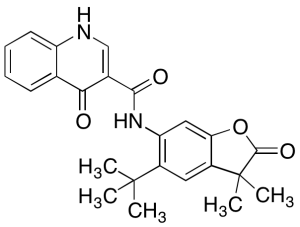
Ivacaftor Carboxylic Acid Lactone
$149.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H24N2O4
-
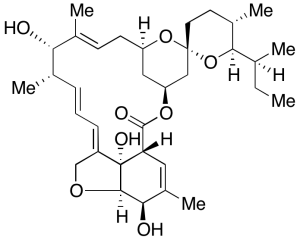
Ivermectin B1 Aglycon
$152.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H50 O8
-
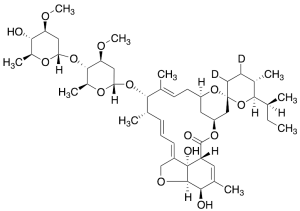
Ivermectin B1a-D2
$150.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C48H72D2O14
-

Ivermectin B1b
$654.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C47 H72 O14
-
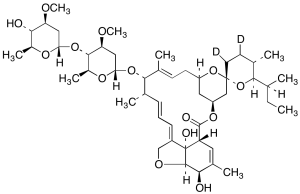
Ivermectin-d2
$183.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C48H72D2O14
-

IWP-3
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H17FN4O2S3
-

Ixabepilone- d3
$2,258.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27H39N2D3O5S
-
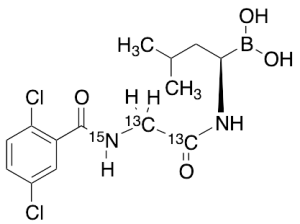
Ixazomib-13C2,15N
$225.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C1213C2H19BCl2N15NO4
-
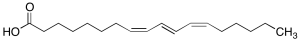
Jacaric Acid (10mg/mL in Ethanol)
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H30O2
-
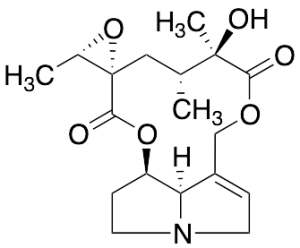
Jacobine
$765.90 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H25 N O6
-
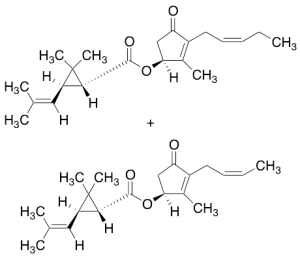
Jasmolin I
$150.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H30O3
-
Jasmolin I + Cinerin I (Mixture)
$295.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H30O3
-
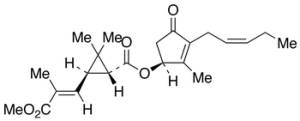
Jasmolin II
$211.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H30O5
-
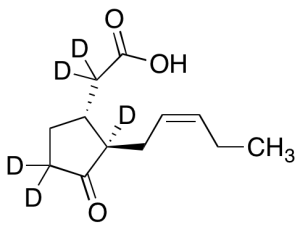
Jasmonic Acid-d5 (Mixture of Diastereomers, (-)-trans major)
$332.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 D5 H13 O3
-

Jervine
$108.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H39 N O3
-
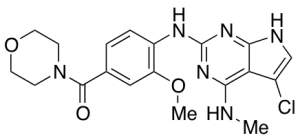
JH-II-127
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19H21ClN6O3
-
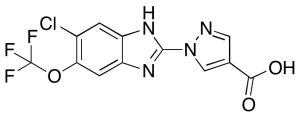
JNJ 42041935
$73.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H6 Cl F3 N4 O3
-
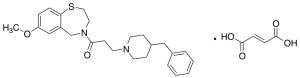
JTV 519 Fumarate
$93.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H32N2O2 • (C4H4O4)
-
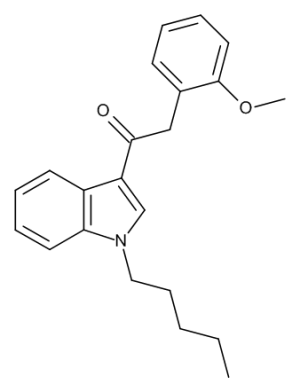
JWH 250
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H25 N O2
-
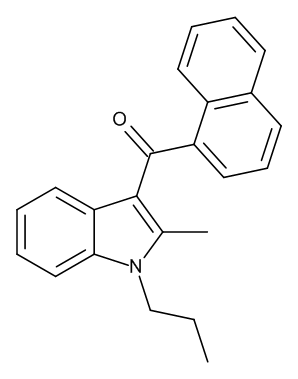
JWH-015
$81.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H21 N O
-
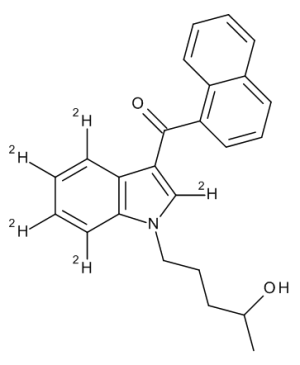
JWH-018 (Indole-d5) 4-Hydroxypentyl
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H18D5NO2
-
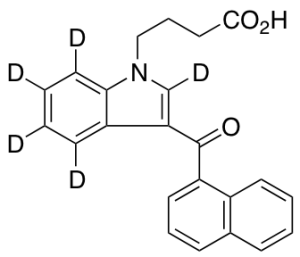
JWH-073 (Indole-d5) Butanoic Acid
$179.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H14D5NO3
-
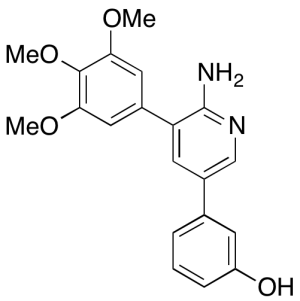
K02288
$55.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H20N2O4
-

KAD-1229-d8 Calcium Hydrate
$324.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19H19D8NO4•1/2Ca
-
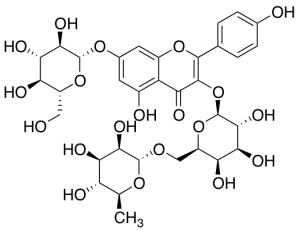
Kaempferol-3-O-robinoside-7-O-glucoside
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C33H40O20
-
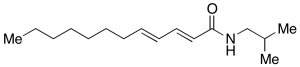
Kalecide
$77.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H29 N O
-
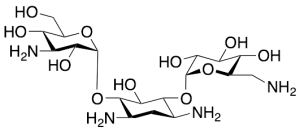
Kanamycin A Deuterated (>90%)
$206.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H36N4O11 for undeuterated
-
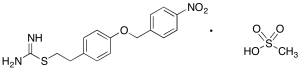
KB-R7943 Mesylate
$50.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H17N3O3S . (CH4O3S)
-
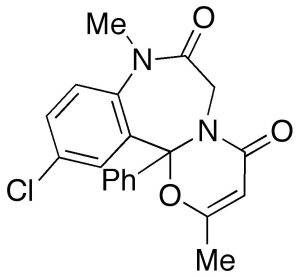
Ketazolam
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H17 Cl N2 O3
-

Ketazolam-13C,d3
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C1913CH14D3ClN2O3
-
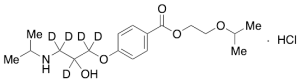
Keto Bisoprolol-d5 Hydrochloride
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 D5 H24 N O5 . H Cl
-
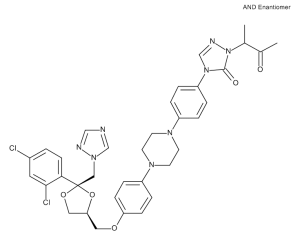
Keto Itraconazole
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 H36 Cl2 N8 O5
-
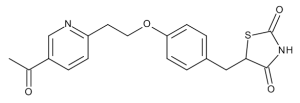
Keto Pioglitazone (M-III)
$219.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H18 N2 O4 S
-
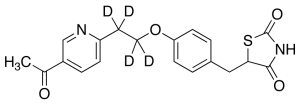
Keto Pioglitazone-d4 (M-III-d4)
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19H14D4N2O4S
-
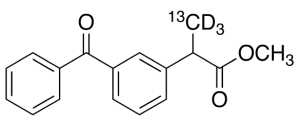
Ketoprofen-13CD3 Methyl Ester
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C1613CH13D3O3
-
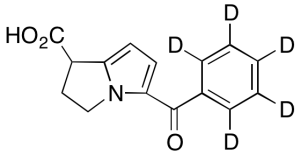
Ketorolac-d5
$251.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15H8D5NO3
-

KGF/FGF-7, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsKeratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF) is a highly specific epithelial mitogen produced by fibroblasts and mesenchymal stem cells. KGF belongs to the heparin binding Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) family, and is known as FGF-7. However, in contrast to the FGF-1, which binds to all known FGF receptors with high affinity, KGF only binds to a splice variant of an FGF receptor, FGFR2-IIIb. FGFR2-IIIb is produced by most of the epithelial cells, indicating that KGF plays roles as a paracrine mediator. KGF induces the differen-tiation and proliferation of various epithelial cells, including keratinocytes in the epidermis, hair follicles and sebaceous glands, and is responsible for the wound repairs of various tissues, including lung, bladder, and kidney.
-

KGF/FGF-7, Mouse
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsKeratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF) is a highly specific epithelial mitogen produced by fibroblasts and mesenchymal stem cells. KGF belongs to the heparin binding Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) family, and is known as FGF-7. However, in contrast to FGF-1, which binds to all known FGF receptors with high affinity, KGF only binds to a splice variant of the FGF receptor, FGFR2-IIIb. FGFR2-IIIb is expressedby most epithelial cells, indicating KGF’s roleas a paracrine mediator. KGF induces the differentiation and proliferation of various epithelial cells such as keratinocytes in the epidermis, hair follicles and sebaceous glands., KGF is also responsible for wound repair of various tissuesincluding lung, bladder, and kidney.
-

Kifunensine
$74.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H12 N2 O6
-

KRAS, His, Human (G12C)
$1,293.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe KRAS gene provides instructions for making a protein called K-Ras, part of the RAS/MAPK pathway. The protein relays signals from outside the cell to the cell’s nucleus. These signals instruct the cell to grow and divide (proliferate) or to mature and take on specialized functions (differentiate). The K-Ras protein is a GTPase, which means it converts a molecule called GTP into another molecule called GDP. In this way the K-Ras protein acts like a switch that is turned on and off by the GTP and GDP molecules. KRAS is usually tethered to cell membranes because of the presence of an isoprene group on its C-terminus. There are two protein products of the KRAS gene in mammalian cells that result from the use of alternative exon 4 (exon 4A and 4B respectively): K-Ras4A and K-Ras4B, these proteins have different structure in their C-terminal region and use different mechanisms to localize to cellular membranes including the plasma membrane.
-

KRAS, His, Human (G12D)
$1,293.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe KRAS gene provides instructions for making a protein called K-Ras, part of the RAS/MAPK pathway. The protein relays signals from outside the cell to the cell’s nucleus. These signals instruct the cell to grow and divide (proliferate) or to mature and take on specialized functions (differentiate). The K-Ras protein is a GTPase, which means it converts a molecule called GTP into another molecule called GDP. In this way the K-Ras protein acts like a switch that is turned on and off by the GTP and GDP molecules. KRAS is usually tethered to cell membranes because of the presence of an isoprene group on its C-terminus. There are two protein products of the KRAS gene in mammalian cells that result from the use of alternative exon 4 (exon 4A and 4B respectively): K-Ras4A and K-Ras4B, these proteins have different structure in their C-terminal region and use different mechanisms to localize to cellular membranes including the plasma membrane.
-
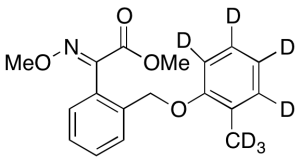
Kresoxim-methyl-d7
$266.51 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H12D7NO4
-

KRN7000
$313.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C50 H99 N O9
-
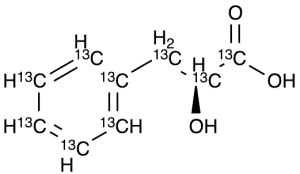
L-(-)-3-Phenyllactic Acid-13C9
$184.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C9 H10 O3
-
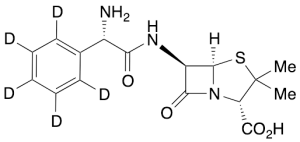
L-(+)-Ampicillin-d5
$258.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H14D5N3O4S






