1mg
Showing 7301–7350 of 7910 results
-
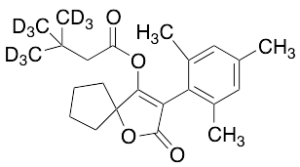
Spiromesifen-d9
$227.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 2H9 H21 O4
-
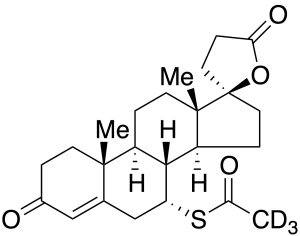
Spironolactone-d3
$225.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H29D3O4S
-
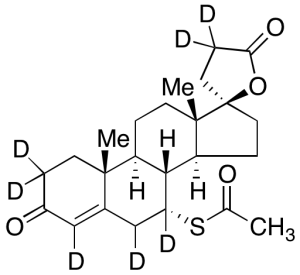
Spironolactone-d7 (Major)
$189.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H25D7O4S
-

Spiroxamine-d4
$229.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H31D4NO2
-
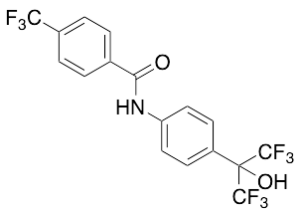
SR 1078
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H21 N O4
-

SR 57227A Hydrochloride
$100.91 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H14ClN3.HCl
-

SRT 1460 TFA Salt
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H29N5O4S • x(C2HF3O2)
-

ST 1936
$112.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H17 Cl N2
-

ST2 (16G5), mAb, Mouse
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsSuppression of Tumorigenicity 2 (ST2), a member of the Interleukin-1 receptor family, has two isoforms, one is soluble form (sST2) and the other one is transmembrane form (ST2L). sST2, lacking the transmembrane and intracellular domains, can prevent the interaction between IL-33 and ST2L. It plays a role in inflammatory and immune processes and is considered as a promising marker for myocardial stress.
-

ST2 (6B3), mAb, Mouse
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsSuppression of Tumorigenicity 2 (ST2), a member of the Interleukin-1 receptor family, has two isoforms, one is soluble form (sST2) and the other one is transmembrane form (ST2L). sST2, lacking the transmembrane and intracellular domains, can prevent the interaction between IL-33 and ST2L. It plays a role in inflammatory and immune processes and is considered as a promising marker for myocardial stress.
-

ST2 (8H6), mAb, Mouse
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsSuppression of Tumorigenicity 2 (ST2), a member of the Interleukin-1 receptor family, has two isoforms, one is soluble form (sST2) and the other one is transmembrane form (ST2L). sST2, lacking the transmembrane and intracellular domains, can prevent the interaction between IL-33 and ST2L. It plays a role in inflammatory and immune processes and is considered as a promising marker for myocardial stress.
-

Staphylokinase
$625.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsStaphylokinase (SAK), a 16kDa profibrinolytic protein from the Staphylococcus aureus, has been demonstrated to induce highly fibrin-specific thrombolysis in both human plasma and in limited clinical trials. Recent studies on the thrombolytic potential of recombinant SAK in achieving early perfusion in myocardial infarction and in the dissolution of platelet-rich clot have clearly established its immense utility in clinical medicine as a thrombolytic agent and suggested that it can be developed as a potent clot-dissolving agent.
-
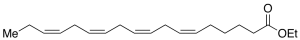
Stearidonic Acid Ethyl Ester
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H32 O2
-

Stearoyl-L-carnitine-13C3 Chloride
$122.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2213C3H50ClNO4
-

Stearoyl-NTA
$145.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H52N2O7
-
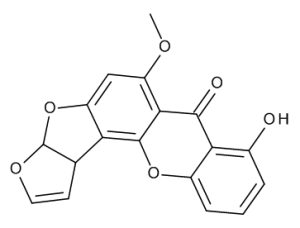
Sterigmatocystin
$114.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H12 O6
-
Steviol Acyl Glucuronide Potassium Salt
$235.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H37KO9
-
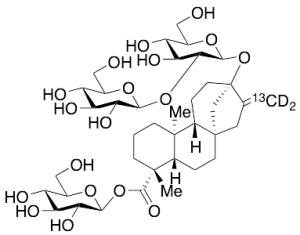
Stevioside-13C,d2 (90%)
$1,527.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C C37 D2 H58 O18
-

Stiripentol-d9
$282.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H9D9O3
-
Streptavidin-HRP
$81.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsStreptavidin is a protein that has similar binding properties to avidin. It is isolated from streptomyces avidinii. Streptavidin has a molecular weight of 60 KD and has 4 subunits. Each subunit can bind one molecule of biotin. Biotin is a 244 da water soluble vitamin. Streptavidin has an extremely high binding affinity (Kd=10 – 15 ) for biotin.
Streptavidin – HRP (M00091) is a HRP conjugated streptavidin and can be used for analysis of biotinylated molecules. -

Strigolactone GR24
$188.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H14 O5
-
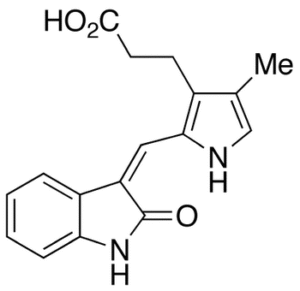
SU 5402
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H16 N2 O3
-
SU11652
$93.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H27ClN4O2
-
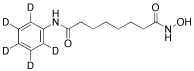
Suberoylanilide-d5 Hydroxamic Acid
$218.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H15D5N2O3
-
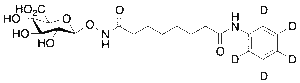
Suberoylanilide-d5 Hydroxamic Acid Beta-D-Glucuronide
$324.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H23D5N2O9
-
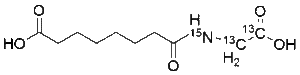
Suberyl Glycine-13C2,15N
$278.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C2 C8 H17 15N O5
-

Suberyl Glycine-d4
$281.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 D4 H13 N O5
-
Suberyl-CoA Sodium Salt
$363.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H48N7O19P3S • xNa
-
Succinyl-L-carnitine-13C3 Chloride
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C3 C8 H20 N O6 . Cl
-
Sucralose-d6
$352.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H13D6Cl3O8
-
Sufentanil-d3 Citrate
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H35D3N2O9S
-
Sulcotrione-d7
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 D7 H6 Cl O5 S
-

Sulfacetamide-d4
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H6D4N2O3S
-
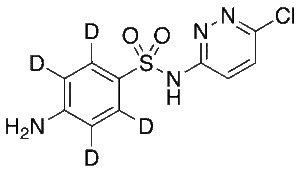
Sulfachlorpyridazine-d4
$185.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H5D4ClN4O2S
-

Sulfadiazine-13C6
$202.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C6 C4 H10 N4 O2 S
-

Sulfadiazine-d4
$216.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 D4 H6 N4 O2 S
-
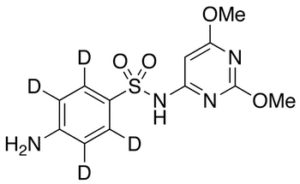
Sulfadimethoxine-d4
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H10D4N4O4S
-
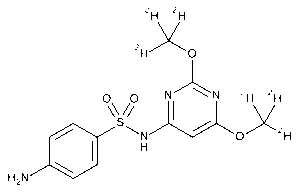
Sulfadimethoxine-d6
$190.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 2H6 H8 N4 O4 S
-

Sulfadoxine-d4
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 D4 H10 N4 O4 S
-
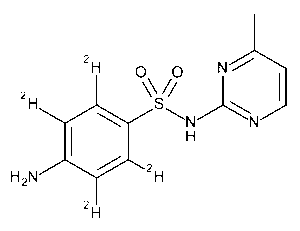
Sulfamerazine-d4
$239.78 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 2H4 H8 N4 O2 S
-
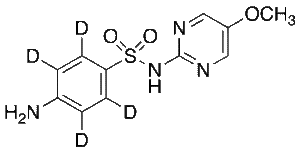
Sulfameter-d4
$213.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11H8D4N4O3S
-
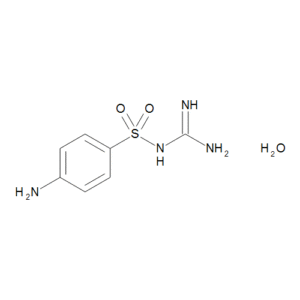
Sulfamethazine Related Compound A
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H10 N4 O2 S . H2 O
-

Sulfamethazine-13C6
$142.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C6 C6 H14 N4 O2 S
-

Sulfamethazine-d4
$131.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 2H4 H10 N4 O2 S
-
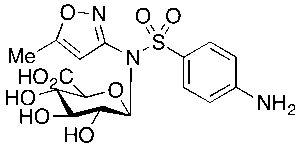
Sulfamethoxazole beta-D Glucuronide
$213.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H19 N3 O9 S
-

Sulfamethoxazole-13C6
$226.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C6 C4 H11 N3 O3 S
-
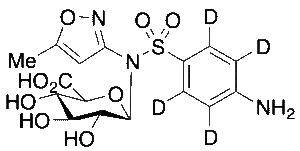
Sulfamethoxazole-d4 Beta-D-Glucuronide
$219.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H15D4N3O9S
-

Sulfamonomethoxine-d3
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 D3 H9 N4 O3 S
-
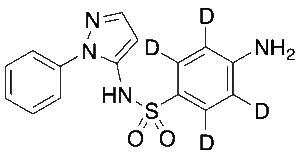
Sulfaphenazole-d4
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15H10D4N4O2S
-

Sulfapyridine-d4
$276.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 2H4 H7 N3 O2 S






