1mg
Showing 2851–2900 of 7910 results
-

Atractyloside Calcium Salt
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30H43Ca1.5O16S2
-
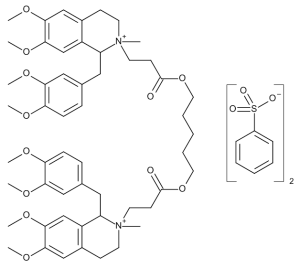
Atracurium Besylate (cis-Monoquatenary)
$253.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C53 H72 N2 O12 . 2 C6 H5 O3 S
-
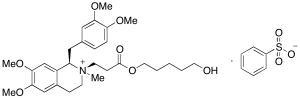
Atracurium Besylate (cis-Quaternary Alcohol)
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29 H42 N O7 . C6 H5 O3 S
-
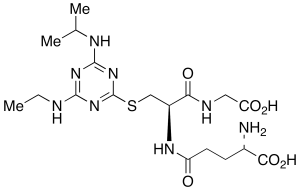
Atrazine Glutathione Adduct
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H30N8O6S
-
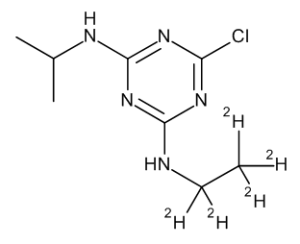
Atrazine-d5
$177.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 2H5 H9 Cl N5
-

Auristatin F TFA Salt
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C40H67N5O8 • x(C2HF3O2)
-
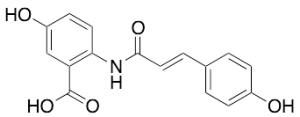
Avenanthramide A
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H13NO5
-

Avenanthramide C
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H13NO6
-
Avermectin A1a (>90%)
$213.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C49H74O14
-
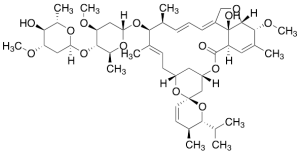
Avermectin A1b (>85%)
$643.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C48H72O14
-

Avibactam Sodium Salt
$42.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H10 N3 O6 S . Na
-
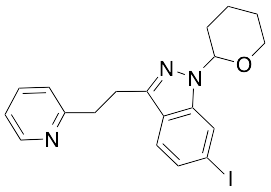
Axitinib Iodo Tetrahydropyran
$199.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H20 I N3 O
-
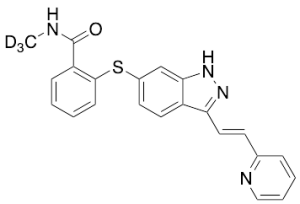
Axitinib-d3
$1,423.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 D3 H15 N4 O S
-
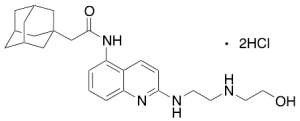
AZ 10606120 Dihydrochloride (~90%)
$100.91 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H34N4O2 • 2(HCl)
-

AZ 5104 Hydrochloride
$79.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27H31N7O2 . HCl
-
Azadirachtin B
$169.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C33 H42 O14
-
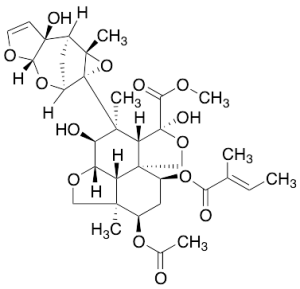
Azadirachtin D
$163.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H44O14
-
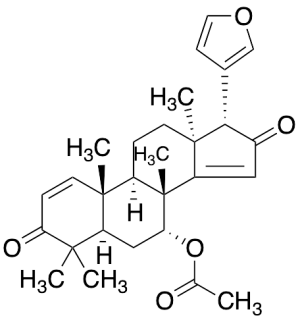
Azadiradione (~90%)
$227.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28 H34 O5
-
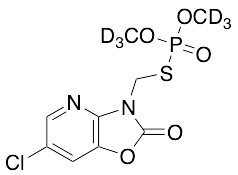
Azamethiphos-d6
$227.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 D6 H4 Cl N2 O5 P S
-

Azapropazone
$524.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H20 N4 O2
-
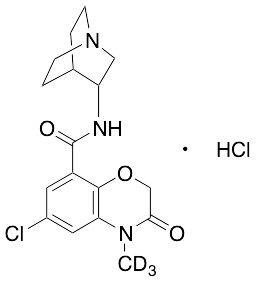
Azasetron-D3 Hydrochloride
$258.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 2H3 H17 Cl N3 O3 . Cl H
-

Azathioprine-d3
$231.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H4D3N7O2S
-

AZD5363
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H25 Cl N6 O2
-

AZD6738
$53.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H24N6O2S
-
Azelastine-13C,d3
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-
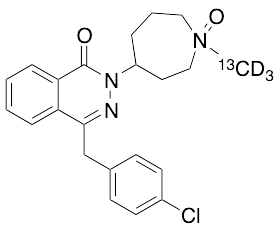
Azelastine-13C,d3 N-Oxide (Mixture of Diastereomers)
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2113CH21D3ClN3O2
-
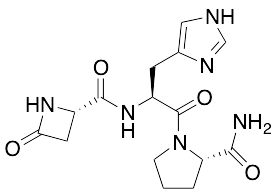
Azetirelin (~85%)
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15H20N6O4
-

Azido-erythro-sphingosine
$131.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H35 N3 O2
-
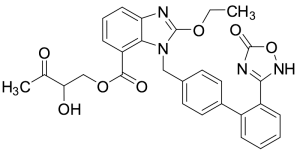
Azilsartan-2-hydroxy-3-oxobutyl acetate
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29 H26 N4 O7
-
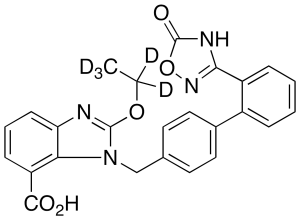
Azilsartan-d5
$269.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H15 D5 N4 O5
-

Azilsartan-d5 Methyl Ester
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H17D5N4O5
-
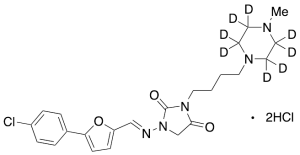
Azimilide-d8 Dihydrochloride
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H22D8Cl3N5O3
-
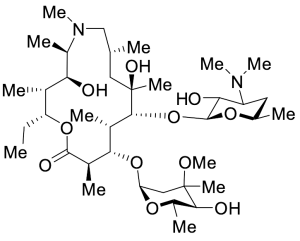
Azithromycin B
$390.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C38H72N2O11
-
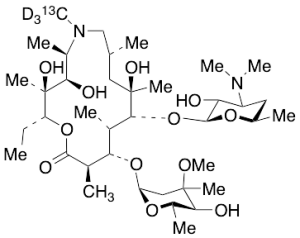
Azithromycin-13CD3
$303.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3713CH69D3N2O12
-

Azithromycin-d3
$190.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C38 2H3 H69 N2 O12
-

Azithromycin-d5
$292.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C38H67D5N2O12
-

Azoxystrobin-d4
$552.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 2H4 H13 N3 O5
-

b-Cembrenediol
$112.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H34O2
-
B-D-Threo-thymidylyl-(3’→5′)-B-D-threo-thymidine-13C2 Ammonia Salt
$213.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18¹³C2H27N4O12P.NH3
-
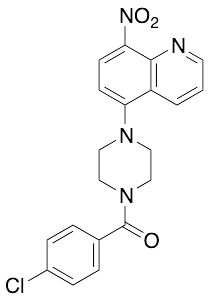
B2
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H17ClN4O3
-

B7-1(CD80) Fc Chimera, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsB7-1/CD80 and B7-2/CD86, together with their receptors CD28 and CTLA-4, constitute one of the dominant co-stimulatory pathways that regulate T- and B-cell responses. Although both CTLA-4 and CD28 can bind to the same ligands, CTLA-4 binds to B7-1 and B7-2 with a 20-100 fold higher affinity than CD28 and is involved in the down-regulation of the immune response. Mature human B7-1 consists of a 208 amino acid extracellular domain (ECD) with two immunoglobulin-like domains, a 21 amino acid transmembrane domain, and a 25 amino acid cytoplasmic domain. Both human and mouse B7-1 and B7-2 can bind to either human or mouse CD28 and sCTLA-4. B7-1 is expressed on activated B cells, activated T cells, and macrophages. B7-2 is constitutively expressed on interdigitating dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, peripheral blood dendritic cells, memory B cells, and germinal center B cells.
-
B7-2/CD86 Fc Chimera, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsB7-1 and B7-2 are homologous costimulatory ligands expressed on the surface of antigen presenting cells (APCs), both are type 1 transmembrane proteins with a membrane distal IgV and a membrane proximal IgC domain. They share ~25% sequence homology and interact with the same receptors, CD28 and CTLA-4.Binding of these molecules to the T cell costimulatory receptors, CD28 and CTLA-4, is essential for the activation and regulation of T cell immunity. T cell activation requires engagement of the T cell receptor (TCR) with the peptide–MHC complex presented on the cell surface of antigen presenting cells (APCs). In addition to this antigen-specific interaction, a second interaction involving costimulatory receptors (CD28, ICOS) on T cells and their respective ligands (B7-1/B7-2, ICOS-L) on APCs is required for optimal T cell activation. B7-1 and B7-2 may also function to deliver signal into dendritic cells. While B7-1 favors binding to CTLA-4, B7-2 shows a preference for CD28.
-

B7-H3 Fc Chimera, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3), a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is also known CD276, which contains two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains and two Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains. B7-H3 may participate in the regulation of T-cell-mediated immune response. B7-H3 also plays a protective role in tumor cells by inhibiting natural-killer mediated cell lysis as well as a role of marker for detection of neuroblastoma cells. Furthermore, B7-H3 is involved in the development of acute and chronic transplant rejection and in the regulation of lymphocytic activity at mucosal surfaces. Human B7-H3 does not bind any known members of the CD28 family of immunoreceptor. However, B7-H3 has been shown to bind an unidentified counter-receptor on activated T cells to co-stimulate the proliferation of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells. B7-H3 has also been found to enhance the induction of primary cytotoxic T lymphocytes and stimulate IFN-gamma production.
-

B7-H3, His, Human
$1,293.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3), a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is also known CD276, which contains two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains and two Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains. B7-H3 may participate in the regulation of T-cell-mediated immune response. B7-H3 also plays a protective role in tumor cells by inhibiting natural-killer mediated cell lysis as well as a role of marker for detection of neuroblastoma cells. Furthermore, B7-H3 is involved in the development of acute and chronic transplant rejection and in the regulation of lymphocytic activity at mucosal surfaces. Human B7-H3 does not bind any known members of the CD28 family of immunoreceptor. However, B7-H3 has been shown to bind an unidentified counter-receptor on activated T cells to costimulate the proliferation of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells. B7-H3 has also been found to enhance the induction of primary cytotoxic T lymphocytes and stimulate IFN-gamma production.
-

Baclofen-d4
$332.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 2H4 H8 Cl N O2
-
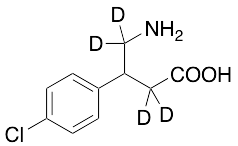
Baclofen-d4 (Major)
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 2H4 H8 Cl N O2
-

BAFF-R, Human
$1,086.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsBAFF Receptor (BAFF-R), a member of the TNFR superfamily, is highly expressed in spleen, lymph node, and resting B cells and to some extent in activated B cells, resting CD4+ cells and peripheral blood leukocytes. BAFF-R is a type III transmembrane protein that binds with high specificity to BAFF (TNFSF13B). BAFF-R/BAFF signaling plays a critical role in B cell survival and maturation.
-

BAFF, Human
$1,651.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsB-cell activating factor, also known as BAFF, TALL-1, TNAK, and zTNF4, is a member of theTNF ligand superfamily designated TNFSF13B. Produced by macrophages, dendritic cells, and T lymphocytes, BAFF promotes the survival of B cells and is essential for B cell maturation. BAFF binds to three TNF receptor superfamily members: B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA/TNFRSF17), transmembrane activator and calcium-modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI/TNFRSF13B) and BAFF receptor (BAFF R/BR3/TNFRSF 13C). These receptors are type III transmembrane proteins lacking a signal peptide. Whereas TACI and BCMA bind BAFF and another TNF superfamily ligand, APRIL(a proliferation-inducing ligand), BAFF R selectively binds BAFF. The BAFF R extracellular domain lacks the TNF receptor canonical cysteine-rich domain (CRD) and contains only a partial CRD with four cysteine residues. Human and mouse BAFF R share 56% aa sequence identity. BAFF R is highly expressed in spleen, lymph node and resting B cells. It is also expressed at lower levels in activated B cell, resting CD4+ T cells, thymus and peripheral blood leukocytes.
-
Bafilomycin A1
$299.29 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35H58O9
-
Bafilomycin B1
$156.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C44H65NO13






