1mg
Showing 2901–2950 of 7910 results
-

Bamifylline
$87.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H27N5O3
-
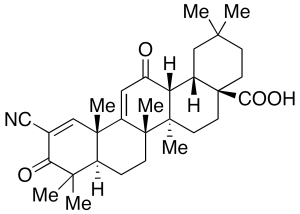
Bardoxolone
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31H41NO4
-
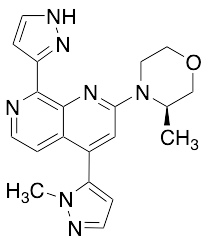
BAY-1895344
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H21N7O
-

BAY-876
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H16F4N6O2
-
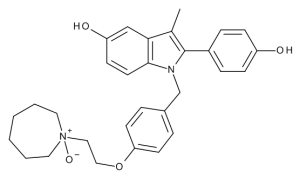
Bazedoxifene N-Oxide
$131.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H34 N2 O4
-
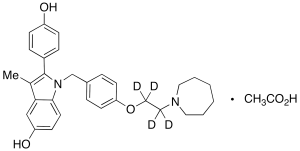
Bazedoxifene-d4
$262.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H30 D4 N2 O3
-
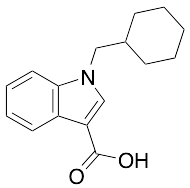
BB-22 3-Carboxyindole Metabolite
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H19NO2
-

BCA-1/CXCL13, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsCXCL13, also known as B-lymphocyte chemoattractant (BLC), is a CXC chemokine that is constitutively expressed in secondary lymphoid organs. BCA-1 cDNA encodes a protein of 109 amino acid residues with a leader sequence of 22 residues. Mature human BCA-1 shares 64% amino acid sequence similarity with the mouse protein and 23 – 34% amino acid sequence identity with other known CXC chemokines. Recombinant or chemically synthesized BCA-1 is a potent chemoattractant for B lymphocytes but not T lymphocytes, monocytes or neutrophils. BLR1, a G protein-coupled receptor originally isolated from Burkitt’s lymphoma cells, has now been shown to be the specific receptor for BCA-1. Among cells of the hematopoietic lineages, the expression of BLR1, now designated CXCR5, is restricted to B lymphocytes and a subpopulation of T helper memory cells. Mice lacking BLR1 have been shown to lack inguinal lymph nodes. These mice were also found to have impaired development of Peyer’s patches and defective formation of primary follicles and germinal centers in the spleen as a result of the inability of B lymphocytes to migrate into B cell areas.
-

BCMA, Human
$3,458.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsBCMA, a member of the TNF receptor superfamily, binds to BAFF and APRIL. BCMA is expressed on mature B-cells and other B-cell lines and plays an important role in B cell development, function and regulation. BCMA also has the capability to activate NF-kappaB and JNK. The human BCMA gene codes for a 184 amino acid type I transmembrane protein, which contains a 54 amino acid extracellular domain, a 23 amino acid transmembrane domain, and a 107 amino acid extracellular domain.
-
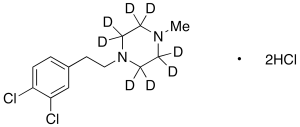
BD 1063-d8 Dihydrochloride
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 D8 H10 Cl2 N2
-

BD-1, Human
$2,238.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsDefensins (alpha and beta) are cationic peptides with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity that comprise an important arm of the innate immune system. The α-defensins are distinguished from the β-defensins by the pairing of their three disulfide bonds. To date, four human β-defensins have been identified; BD-1, BD-2, BD-3 and BD-4. β-defensins are expressed on some leukocytes and at epithelial surfaces. In addition to their direct antimicrobial activities, they are chemoattractant towards immature dendritic cells and memory T cells. The β-defensin proteins are expressed as the C-terminal portion of precursors and are released by proteolytic cleavage of a signal sequence and, in the case of BD-1 (36 a.a.), a propeptide region. β-defensins contain a six-cysteine motif that forms three intra-molecular disulfide bonds. β-Defensins are 3-5 kDa peptides ranging in size from 33-47 amino acid residues.
-

BD-2, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsDefensins (alpha and beta) are cationic peptides with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity that comprise an important arm of the innate immune system. The α-defensins are distinguished from the β-defensins by the pairing of their three disulfide bonds. To date, four human β-defensins have been identified; BD-1, BD-2, BD-3 and BD-4. β-defensins are expressed on some leukocytes and at epithelial surfaces. In addition to their direct antimicrobial activities, they are chemoattractant towards immature dendritic cells and memory T cells. The β-defensin proteins are expressed as the C-terminal portion of precursors and are released by proteolytic cleavage of a signal sequence and, in the case of BD-1 (36 a.a.), a propeptide region. β-defensins contain a six-cysteine motif that forms three intra-molecular disulfide bonds. β-Defensins are 3-5 kDa peptides ranging in size from 33-47 amino acid residues.
-

BD-3, Human
$2,190.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsDefensins (alpha and beta) are cationic peptides with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity that comprise an important arm of the innate immune system. The α-defensins are distinguished from the β-defensins by the pairing of their three disulfide bonds. To date, four human β-defensins have been identified; BD-1, BD-2, BD-3 and BD-4. β-defensins are expressed on some leukocytes and at epithelial surfaces. In addition to their direct antimicrobial activities, they are chemoattractant towards immature dendritic cells and memory T cells. The β-defensin proteins are expressed as the C-terminal portion of precursors and are released by proteolytic cleavage of a signal sequence and, in the case of BD-1 (36 a.a.), a propeptide region. β-defensins contain a six-cysteine motif that forms three intra-molecular disulfide bonds. β-Defensins are 3-5 kDa peptides ranging in size from 33-47 amino acid residues.
-
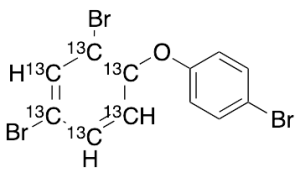
BDE 28-13C6
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 13C6 H7 Br3 O
-
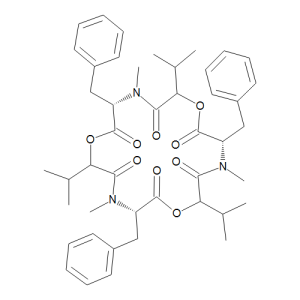
Beauvericin
$188.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C45 H57 N3 O9
-
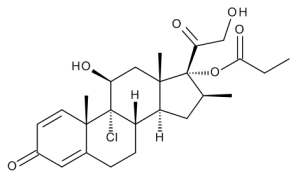
Beclomethasone 17-propionate
$125.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H33 Cl O6
-
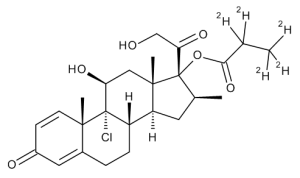
Beclomethasone 17-propionate-D5
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H28D5ClO6
-
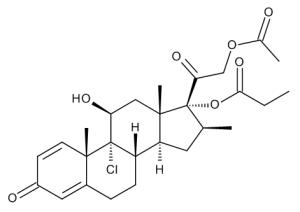
Beclomethasone 21-Acetate 17-Propionate
$253.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H35 Cl O7
-
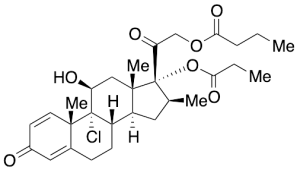
Beclomethasone 21-Butyrate 17-Propionate
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H39ClO7
-
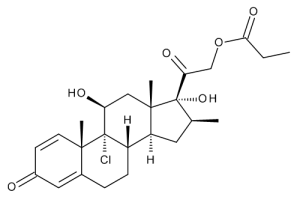
Beclomethasone 21-Propionate
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H33 Cl O6
-
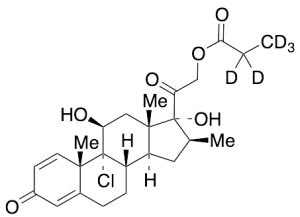
Beclomethasone 21-Propionate-d5
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H28D5ClO6
-
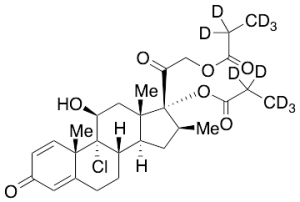
Beclomethasone Dipropionate-d10
$230.29 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28D10H27ClO7
-
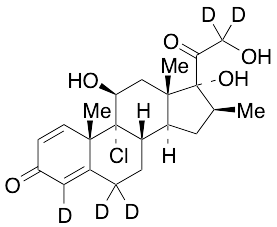
Beclomethasone-d5
$288.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H24D5ClO5
-

Bedaquiline-d6 (Mixture of Diastereomers)
$338.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C32 2H6 H25 Br N2 O2
-
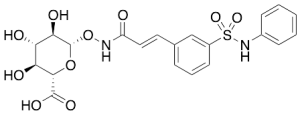
Belinostat Glucuronide
$206.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H22N2O10S
-
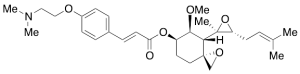
Beloranib
$708.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H41NO6
-
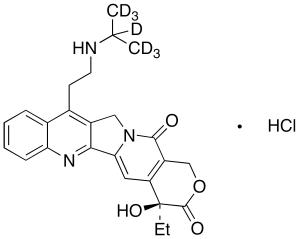
Belotecan-d7 Hydrochloride
$170.78 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H21D7ClN3O4
-
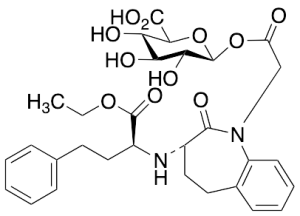
Benazepril Acyl-Beta-D-glucuronide
$233.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30H36N2O11
-
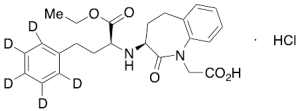
Benazepril-d5 Hydrochloride
$210.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H24D5ClN2O5
-
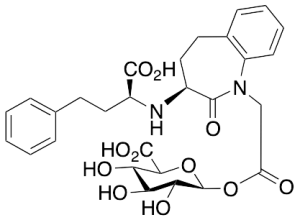
Benazeprilat Acyl-Beta-D-glucuronide
$1,153.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H32N2O11
-
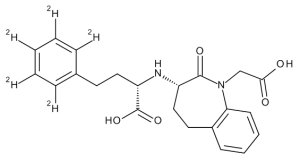
Benazeprilat-d5
$227.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H19D5N2O5
-
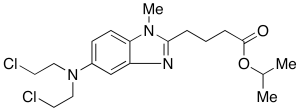
Bendamustine Isopropyl Ester
$302.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H27 Cl2 N3 O2
-
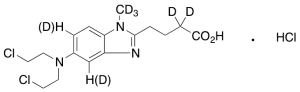
Bendamustine-d6 (major) Hydrochloride
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H16D6Cl3N3O2
-
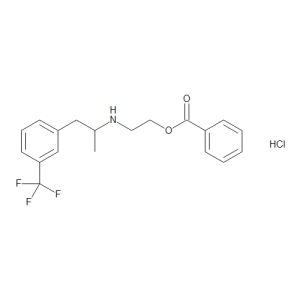
Benfluorex Hydrochloride
$84.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19H21ClF3NO2
-
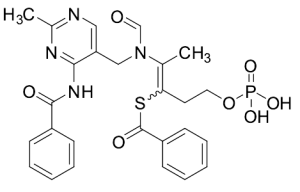
Benfotiamine-Amide
$150.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H27N4O7PS
-
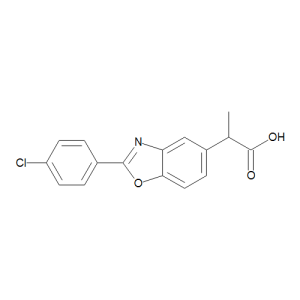
Benoxaprofen
$217.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H12 Cl N O3
-
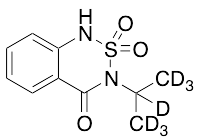
Bentazon-d7
$113.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 D7 H5 N2 O3 S
-
![Benz[a]anthracen-3-ol-d11 (Major)](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimagesh92h5010690570747934B120587-300x213.png)
Benz[a]anthracen-3-ol-d11 (Major)
$223.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18D11HO
-
![Benz[a]anthracene-7,12-dione-D4](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimageshd6h8810692890263582B197942.png)
Benz[a]anthracene-7,12-dione-D4
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 D4 H6 O2
-
![Benz[j]aceanthrylen-2(1H)-one13C2,d2 and Benz[e]aceanthrylen-6(5H)-one13C2,d2](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimagesh3dhb910690540929054B183543-300x115.png)
Benz[j]aceanthrylen-2(1H)-one13C2,d2 and Benz[e]aceanthrylen-6(5H)-one13C2,d2
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C2 C18 D2 H10 O . 13C2 C18 D2 H9 O
-
![Benz[j]aceanthrylene and Benz[e]aceanthrylene (70:30 Mixture)](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimagesh91h4f10680691523614B197910-300x117.png)
Benz[j]aceanthrylene and Benz[e]aceanthrylene (70:30 Mixture)
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C20 H12
-
![Benz[j]aceanthrylene-13C2,d2 and Benz[e]aceanthrylene-13C2,d2](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimageshafh1510690571632670B197912-300x121.png)
Benz[j]aceanthrylene-13C2,d2 and Benz[e]aceanthrylene-13C2,d2
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 13C2 C18 D2 H10
-
Benz[l]aceanthrylen-1(2H)-one
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H12O
-

Benzidine-d8
$118.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 2H8 H4 N2
-
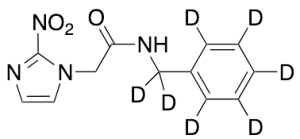
Benznidazole-D7
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H5D7N4O3
-
![Benzo[a]pyrene-3,6-quinone](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimagesh78hf110622113447966B205865.png)
Benzo[a]pyrene-3,6-quinone
$95.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H10 O2
-
![Benzo[a]pyrene-6,12-quinone](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimageshb3hf910680699781150B205870.png)
Benzo[a]pyrene-6,12-quinone
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H10 O2
-
![Benzo[ghi]perylene-d12](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimagesh74h601069290019228613269-300x300.png)
Benzo[ghi]perylene-d12
$230.29 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 2H12
-
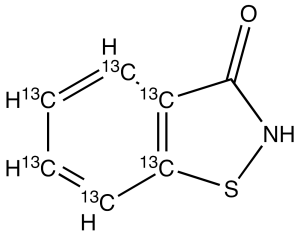
Benzoisothiazol-3-one-13C6
$887.51 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C6 C H5 N O S
-
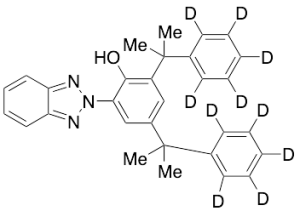
Benzotriazole BT-d10
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 D10 H19 N3 O






