1mg
Showing 3101–3150 of 3770 results
-
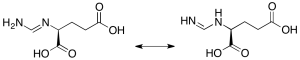
L-Formiminoglutamic Acid
$115.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H10 N2 O
-

LAG-3 (CD223) Fc Chimera, Human
$1,293.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsLymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3), also known as CD223, is a cell-surface 70kDa molecule belong to Ig superfamily with diverse biologic effects on T cell function. LAG-3 is a CD4 homolog originally cloned in 1990. The gene for LAG-3 lies adjacent to the gene for CD4 on human chromosome 12 (12p13) and is approximately 20% identical to the CD4 gene. human LAG-3 shares 70%, 67%, 76%, and 73% aa sequence identity with mouse, rat, porcine, and bovine LAG-3, respectively. LAG-3 is expressed on B cells, NK cells, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, and a subset of T cells. LAG-3 was relatively overexpressed on transgenic T cells rendered anergic in vivo by encounter with cognate self-antigen. LAG-3 negatively regulates murine T cell activation and homeostasis. LAG-3 activates antigen-presenting cells through MHC class II signaling, leading to increased antigen-specific T-cell responses in vivo. Blocking or knocking out LAG-3 in neuronal cultures or in animals mitigated the transmission of α-synuclein between neurons, and dampened accumulation as well as toxic effects of the fibrils on motor function. Anti-LAG3 antibodies are already being tested as cancer treatments, it could also make a useful therapeutic target to treat Parkinson’s and other synucleinopathies.
-

Leptin, Human
$146.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeptin is a cytokine belonging to the Interleukin 6 family, and has a four-helix bundle structure. Leptin is encoded by the ob gene, and produced and secreted by white adipose tissue. The receptors of Leptin are Type I cytokine receptors, which exist in two different forms: a short form expressed in multiple tissues, and a long form expressed exclusively in the central nervous system (CNS). Upon binding to Leptin, the receptors activate the JAK/STAT3 pathway and PI3K, and stimulate transcriptional programs that regulate feeding behavior, metabolic rate, endocrine axes, and glucose fluxes. The deficiency of Leptin in human and mouse causes morbid obesity, diabetes, and neuroendocrine anomalies. Leptin also has effects on reproduction and immunity. In summary, Leptin is a pivotal cytokine controlling energy balance, and as such has profound effects on human health.
-

Leptin, Rat
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeptin is a cytokine belonging to the Interleukin 6 family, and has a four-helix bundle structure. Leptin is encoded by the ob gene, and produced and secreted by white adipose tissue. The receptors of Leptin are Type I cytokine receptors, which exist in two different forms: a short form expressed in multiple tissues, and a long form expressed exclusively in the central nervous system (CNS). Upon binding to Leptin, the receptors activate the JAK/STAT3 pathway and PI3K, and stimulate transcriptional programs that regulate feeding behavior, metabolic rate, endocrine axes, and glucose fluxes. The deficiency of Leptin in human and mouse causes morbid obesity, diabetes, and neuroendocrine anomalies. Leptin also has effects on reproduction and immunity. In summary, Leptin is a pivotal cytokine controlling energy balance, and as such has profound effects on human health.
-
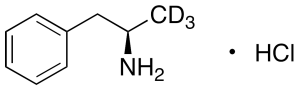
Levamfetamine-d3 Hydrochloride
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H10 D3 N . H Cl
-

LIF, Human
$1,470.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-

LIF, Mouse
$2,117.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-

LIGHT, Human
$1,293.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsLIGHT, also known as tumor-necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily member 14 (TNFSF14), is predominantly expressed on activated immune cells and some tumor cells. LIGHT (homologous to lymphotoxin, exhibits inducible expression and competes with Herpes Simplex Virus glycoprotein D for Herpes Virus Entry Mediator, a receptor expressed by T cells), is a protein primarily expressed on activated T cells, activated Natural Killer (NK) cells, and immature dendritic cells (DC). LIGHT can function as both a soluble and cell surface-bound type II membrane protein and must be in its homotrimeric form to interact with its two primary functional receptors: Herpes Virus Entry Mediator (HVEM) and Lymphotoxin-β Receptor (LTβR). LIGHT signaling through these receptors have distinct functions that are cell-type dependent, but interactions with both types of receptors have immune-related implications in tumor biology.
-

LIX/CXCL5 (92aa), Mouse
$2,242.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe mouse homolog of ENA-78 is called LIX. ENA-78/LIX is a CXC chemokine that signals through the CXCR2 receptor. It is expressed in monocytes, platelets, endothelial cells, and mast cells. ENA-78/LIX is a chemoattractant for neutrophils. The three naturally occurring variants of human ENA-78; ENA 5-78, ENA 9-78 and ENA 10-78, contain 74, 70, and 69 amino acid residues, respectively, and possess the same biological activity. ENA-78/LIX contains the four conserved cysteine residues present in CXC chemokines, and also contains the ‘ELR’ motif common to CXC chemokine that bind to the CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptors.
-

Lp-PLA2 (10D46), mAb, Mouse
$190.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsLipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (LpPLA2) is an enzyme which participates in proinflammatory process. High concentration of LpPLA2 in serum indicates risk of heart attack and stroke. LpPLA2 is considered as specific coronary marker for diagnosing cardiovascular heart disease.
-

Lp-PLA2 (9C42), mAb, Mouse
$190.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsLipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (LpPLA2) is an enzyme which participates in proinflammatory process. High concentration of LpPLA2 in serum indicates risk of heart attack and stroke. LpPLA2 is considered as specific coronary marker for diagnosing cardiovascular heart disease.
-
LR3-IGF-I (Receptor Grade), Human
$159.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsIGF-1 is a well-characterized basic peptide secreted by the liver that circulates in the blood. It has growth-regulating, insulin-like, mitogenic activities. IGF-1 is a growth factor that has a major, but not absolute, dependence on somatotropin. It is believed to be mainly active in adults in contrast to IGF-2, which is also a major fetal growth factor. Human Long R3 Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (rhLR3IGF-1) contains an 83 amino acid analog of human IGF-I. Compared to the complete human IGF-I sequence, an addition of the rhLR3IGF-1 includes the substitution of an Arg for the Glu at position 3 (hence R3)and a13 amino acid extension peptide at the N-terminus. An enhanced potency is due to the markedly decreased binding of human Long-R3-IGF-I to IGF binding proteins which normally inhibit the biological actions of IGFs.
-
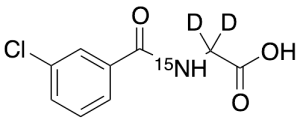
m-Chloro Hippuric Acid-d2,15N
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 D2 H6 Cl 15N O3
-

M-CSF, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-
M-CSF, Mouse
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Rat
$2,307.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

m-nitro-(R,R)-threo-Chloramphenicol
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H12 Cl2 N2 O5
-

Magnamycin B (>80%)
$242.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C42H67NO15
-

Maspin, Human
$2,238.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMammary serine protease inhibitor (Maspin), also known as serpin B5 is a non-inhibitory serpin that is encoded by the SERPINB5 gene in humans. The protein is expressed predominantly in normal mammary epithelial cells but at significantly reduced levels or absent in most breast carcinomas. As it does not undergo the S (stressed) to R (relaxed) conformational transition characteristic of active serpins, it exhibits no serine protease inhibitory activity. The maspin functions as tumor suppressor, blocking the growth, invasion, and metastatic properties of mammary tumors. This anti-tumor activity is achieved, in part, by the ability of maspin to inhibit angiogenesis and to preferentially promote apoptosis of tumor cells.
-

MCP-1/CCL2, Human
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsCCL2, also known as monocyte chemotactic and activating factor (MCAF), was initially purified independently by two groups based on its ability to chemoattract monocytes. Subsequent to its cloning and sequencing, it became evident that this protein is also identical to the product of the human JE gene. The JE gene, originally identified in mouse fibroblasts, is a plateletderived growth factor (PDGF)inducible gene. The human CCL2 cDNA encodes a 99 amino acid residue precursor protein with a 23 residue hydrophobic signal peptide that is cleaved to generate the 76 residue mature protein. Natural CCL2 is heterogeneous in size due to the addition of Olinked carbohydrates and sialic acid residues. In addition to fibroblasts; tumor cells, smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and mononuclear phagocytes can also produce CCL2 either constitutively or upon stimulation by various stimuli. CCL2 is a member of the β (CC) subfamily of chemokines. Recently, the existence of MCP2 and MCP3 with 62% and 73% amino acid identity respectively, to CCL2 have been reported.
-

MCP-1/CCL2, Mouse
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsChemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) is also referred to as monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP1) and small inducible cytokine A2. CCL2 is a small cytokine that belongs to the CC chemokine family. CCL2 recruits monocytes, memory T cells, and dendritic cells to the sites of inflammation produced by either tissue injury or infection. CCL2 is implicated in the pathogeneses of several types of disease characterized by monocytic infiltrates, such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis. CCL2 is anchored in the plasma membrane of endothelial cells by glycosaminoglycan side chains of proteoglycans. CCL2 is primarily secreted by monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells. CCL2 can signal through the CCR2 receptor.
-
MCP‑3/CCL7, Human(CHO-expressed)
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsChemokine (C-C motif) ligand 7 (CCL7) is a small cytokine that was previously called monocyte-specific chemokine 3 (MCP-3). Due to CCL7 possessing two adjacent N-terminal cysteine residues in its mature form, it is classified within the subfamily of chemokines known as CC chemokines. CCL7 specifically attracts monocytes, and regulates macrophage function. It is produced by certain tumor cell lines and by macrophages. This chemokine is located on chromosome 17 in humans, within a large cluster containing many other CC chemokines and is most closely related to CCL2. CCL7 can signal through the CCR1, CCR2 and CCR3 receptors.
-

Mesothelin, hFc, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsMesothelin, also known as MSLN, is a 40 kDa protein that is expressed in mesothelial cells. It has been reported that this protein is over expressed in several human tumors, including mesothelioma, ovarian cancer, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, and cholangiocarcinoma. Mesothelin can bind MUC16 (also known as CA125), indicating that the interaction of mesothelin and MUC16 may contribute to the implantation and peritoneal spread of tumors by cell adhesion. Since mesothelin is overexpressed in several cancers and is immunogenic, the protein could be exploited as tumor marker or as the antigenic target of a therapeutic cancer vaccine.
-

Mesothelin, His, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsMesothelin, also known as MSLN, is a 40 kDa protein that is expressed in mesothelial cells. It has been reported that this protein is over expressed in several human tumors, including mesothelioma, ovarian cancer, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, and cholangiocarcinoma. Mesothelin can bind MUC16 (also known as CA125), indicating that the interaction of mesothelin and MUC16 may contribute to the implantation and peritoneal spread of tumors by cell adhesion. Since mesothelin is overexpressed in several cancers and is immunogenic, the protein could be exploited as tumor marker or as the antigenic target of a therapeutic cancer vaccine.
-

MIF, Human
$1,177.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine, existing as a homotrimer in vivo. MIF was originally identified as a T cell derived factor responsible for the inhibition of macrophage migration. However, recently MIF has received much more attention because of its possible roles in angiogenesis and cancer development. MIF is over-expressed in various cancers, including pancreatic, breast, colon, brain, prostate, skin, and lung. The intratumoral expression of MIF is strongly correlated with angiogenic growth factor expression, such as the expression of Interleukin 8 (IL-8) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), and with risk of recurrence after resection.
-

MIF, Mouse
$2,518.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF or MMIF), also named as glycosylation-inhibiting factor (GIF), L-dopachrome isomerase, or phenylpyruvate tautomerase, is a protein encoded by the MIF gene. It is released from white blood cells by bacterial antigen stimulation to trigger an acute immune response, or by glucocorticoids to counter-act the inhibitory effects of glucocorticoids on immune system. MIF is a homotrimer of which each subunit contains 115 amino acids. As mentioned above, MIF is involved in the innate immune response to bacterial pathogens and counter-acts the anti-inflammatory activity of glucocorticoids. Furthermore, it also plays a role as mediator in regulating the function of macrophages in host defense and has phenylpyruvate tautomerase and dopachrome tautomerase activity in vitro. Mouse MIF is active on human cells, while human MIF is active on mouse cells. Mouse MIF is 99 %, 84 %, 90 %, and 90 % a.a. identical to rat, porcine, bovine and human MIF, respectively.
-

MIG/CXCL9, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsChemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9 (CXCL9), also known as monokine induced by interferon gamma (MIG), is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family. The CXCL9 gene is induced in macrophages and in primary glial cells of the central nervous system specifically in response to IFNγ. CXCL9 has been shown to be a chemoattractant for activated T-lymphocytes and TIL but not for neutrophils or monocytes. The human CXCL9 cDNA encodes a 125 amino acid residue precursor protein with a 22 amino acid residue signal peptide that is cleaved to yield a 103 amino acid residue mature protein. CXCL9 has an extended carboxy-terminus containing greater than 50% basic amino acid residues and is larger than most other chemokines. A chemokine receptor (CXCR3) specific for CXCL9 and IP-10 has recently been cloned and shown to be highly expressed in IL-2-activated T-lymphocytes.
-
MIG/CXCL9, Mouse
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsChemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9 (CXCL9), also known as monokine induced by interferon gamma (MIG), is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family.The CXCL9 gene is induced in macrophages and in primary glialcells of the central nervous systemin response to IFNγ. CXCL9 has been shown to be achemo attractant for activated Th1lymphocytes and tumor-infiltrating leukocytes (TILs) but not for neutrophils or monocytes. CXCL is also involved in other cellular activities including inhibition of tumor growth, angiogenesis, and inhibition of colony formation of hematopoietic progenitors. CXCL9 is closely related to two other CXC chemokines, CXCL10 and CXCL11.CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 all elicit their chemotactic functions by interacting with the chemokine receptor CXCR3.
-

MIP-1α/CCL3, Human
$2,238.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 3 (CCL3) is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family. CCL3 is primarily expressed in T cells, B cells, and monocytes after antigen or mitogen stimulation. CCL3 exhibits chemoattractive and adhesive effects on lymphocytes. CCL3 exerts multiple effects on hematopoietic precursor cells and inhibits the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells in vitro as well as in vivo. CCR1 and CCR5 have been identified as functional receptors for CCL3.
-
MIP-2/CXCL2, Mouse
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsChemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 (CXCL2) is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family that is also referred to as macrophage inflammatory protein 2-alpha (MIP2-alpha), Growth-regulated protein beta (Gro-beta) and Gro oncogene-2 (Gro-2). CXCL2 is secreted by monocytes and macrophages and is chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes and hematopoietic stem cells. CXCL2’s amino acid sequence is 90% identical to the amino acid sequence of related chemokine, CXCL1. CXCL2 signals through the CXCR2 receptor.
-

MIP-3α/CCL20, Human
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage Inflammatory Protein-3 (MIP-3α), also known as chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20 (CCL20) or liver activation regulated chemokine (LARC), is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family. MIP-3α is expressed in the liver, lymph nodes, appendix, PBL and lung and can signal through the CCR6 receptor. It is strongly chemotactic for lymphocytes and weakly attracts neutrophils. MIP-3α is implicated in the formation and function of mucosal lymphoid tissues via chemoattraction of lymphocytes and dendritic cells toward the epithelial cells surrounding these tissues. Additionally, it promotes the adhesion of memory CD4+ T cells and inhibits colony formation of bone marrow myeloid immature progenitors.
-

MIP-3α/CCL20, Human(CHO-expressed)
$1,177.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage Inflammatory Protein-3 (MIP-3α), also known as chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20 (CCL20) or liver activation regulated chemokine (LARC), is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family. MIP-3α is expressed in the liver, lymph nodes, appendix, PBL and lung and can signal through the CCR6 receptor. It is strongly chemotactic for lymphocytes and weakly attracts neutrophils. MIP-3α is implicated in the formation and function of mucosal lymphoid tissues via chemoattraction of lymphocytes and dendritic cells toward the epithelial cells surrounding these tissues. Additionally, it promotes the adhesion of memory CD4+ T cells and inhibits colony formation of bone marrow myeloid immature progenitors.
-

MIP-3α/CCL20, Mouse
$2,264.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage Inflammatory Protein-3 (MIP-3α), also known as chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20 (CCL20) or liver activation regulated chemokine (LARC), is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family. MIP-3α is expressed in the liver, lymph nodes, appendix, PBL and lung and can signal through the CCR6 receptor. It is strongly chemotactic for lymphocytes and weakly attracts neutrophils. MIP-3α is implicated in the formation and function of mucosal lymphoid tissues via chemoattraction of lymphocytes and dendritic cells toward the epithelial cells surrounding these tissues. Additionally, it promotes the adhesion of memory CD4+ T cells and inhibits colony formation of bone marrow myeloid immature progenitors.
-

MIP-4/CCL18, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsCCL18, is a novel CC chemokine that is highly homologous to MIP-1α (61% amino acid sequence identity). CCL18 cDNA encodes an 89 aa residue precursor protein with a 20 aa putative signal peptide that is cleaved to generate a 69 aa residue mature protein which lacks potential glycosylation sites. In vitro, CCL18 mRNA expression is induced in alternatively activated macrophages by Th2 cytokines such as IL-4, IL-10 and IL-13, and inhibited by IFN-γ. CCL18 mRNA is also expressed by GM-CSF/IL-4-induced monocyte-derived dendritic cells. In vivo, CCL18 is highly expressed in lung and placenta but is not expressed in epidermal Langerhans cells. Recombinant CCL18 has been shown to chemoattract naive T cells, but not monocytes or neutrophils.
-
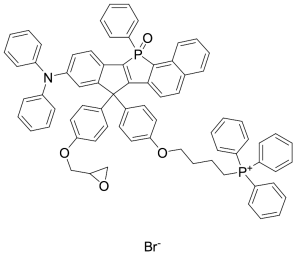
MitoPB Yellow
$571.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C74H60NO4P2 • Br
-

Monkeypox A29L protein, His Tag
$1,630.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe A29L protein from Monkeypox binds to cell surface heparin to promote fusion of viral membrane with host plasma membrane, it is a potential target for developing diagnosis and vaccine.
-

Monkeypox L1R protein, His Tag
$1,630.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe L1R protein from Monkeypox is crucial for viral growth and virion morphogenesis, it is a potential target for developing diagnosis and vaccine.
-
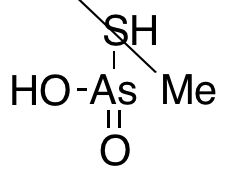
Monomethyl Arsonothioic Acid (80%)
$219.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CH5AsO2S
-

MonoRab™ Anti-Mouse IgG (H&L) (76F10), mAb, Rabbit
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsRabbit anti-mouse monoclonal antibody is a secondary antibody which recognizes mouse immunoglobulins with high affinity. It is a useful tool for the detection, sorting, capture or purification of its specified target. It can be used in several analysis systems such as ELISA or Western Blot (WB), Immunohistochemistry (IHC), Flow Cytometry (FACS) and Time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay (TRFIA). It also can be used to develop secondary antibody-coupled magnetic beads for immunoprecipitation (IP), Co-IP, and isolation of cells.
-

MonoRab™ Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) antibody (103D6), mAb, Rabbit
$261.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsAnti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) is a glycoprotein dimer. It is a member of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily. AMH is a hormone produced by small follicles in the ovary. It is a novel fertility marker to assess ovarian reserve levels.
-

MonoRab™ Biotin Antibody (53C8), mAb, Rabbit
$38.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsBiotin is widely conjugated to proteins and antibodies for biochemical assays. Avidin (streptavidin)-biotin system is commonly used for many immunoassays such as ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Immunofluorescence, In Situ Hybridization, and Immunohistochemistry. Anti-Biotin mAb is a better alternative to avidins to minimize background and maximize signal intensity.
-

MonoRab™ FITC Antibody (F11), mAb, Rabbit
$38.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsFluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) is a derivative of fluorescein used in wide-ranging applications including flow cytometry. It is the original fluorescein molecule functionalized with an isothiocyanate reactive group (-N=C=S), replacing a hydrogen atom on the bottom ring of the structure. This derivative is reactive towards nucleophiles including amine and sulfhydryl groups on proteins.
-

MonoRab™ IL6 (125B3), mAb, Rabbit
$172.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-6 (IL6) is a multi-functional cytokine, produced by variety of cells including T-cells, B-cells, monocytes, fibroblasts, keratinocytes, endothelial cells, mesangial cells, astrocytes and bone marrow stroma cells. It is involved in the induction of B-cell differentiation, growth promotion of myeloma cells and proliferation and differentiation of T cells. IL6 can regulate immune responses, acute phase reactions and hematopoiesis.
-

MonoRabᵀᴹ MSH6 (3B6), mAb, Rabbit
$1,374.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMSH6, also known as MutS protein homolog 6, is a member of the Mutator S (MutS) family of proteins. It functions to repair mutations during DNA replication. MSH6 is a useful in diagnostics of gastrointestinal tract cancer.
-

MonoRab™ NT-proBNP (10B11), mAb, Rabbit
$196.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsBNP and NT-proBNP are separated from precursor molecule proBNP via proteolytic processing. The BNP and NT-proBNP level in blood are proportional to the severity of cardiac dysfunction. They can be used for diagnosis of congestive heart failure (CHF).
-

MonoRab™ NT-proBNP (22B11), mAb, Rabbit
$196.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsBNP and NT-proBNP are separated from precursor molecule proBNP via proteolytic processing. The BNP and NT-proBNP level in blood are proportional to the severity of cardiac dysfunction. They can be used for diagnosis of congestive heart failure (CHF).
-

MonoRabᵀᴹ PD-L1 (1H3), mAb, Rabbit
$1,374.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsIt is type I transmembrane glycoprotein that belongs to the B7 family. PD-L1 is expressed on T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, IFN-γ activated endothelial cells, and monocytes. It plays a role in regulating T cell responses. The interaction of PD-L1 with PD-1 inhibits T cell proliferation and cytokine production.
-

MonoRabᵀᴹ PD-L1 (2B3), mAb, Rabbit
$1,374.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsIt is type I transmembrane glycoprotein that belongs to the B7 family. PD-L1 is expressed on T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, IFN-γ activated endothelial cells, and monocytes. It plays a role in regulating T cell responses. The interaction of PD-L1 with PD-1 inhibits T cell proliferation and cytokine production.
-

MonoRab™ SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody (12D3), mAb, Rabbit
$2,587.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe product is specific for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 subunit and its RBD domain.






