1mg
Showing 3501–3550 of 7070 results
-
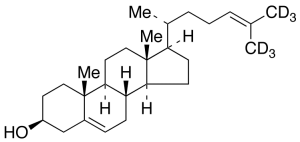
Desmosterol-d6
$280.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 2H6 H38 O
-
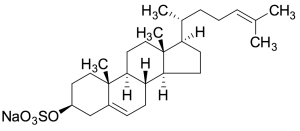
Desmosteryl Sulfate Sodium Salt
$363.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H43 Na O4 S
-
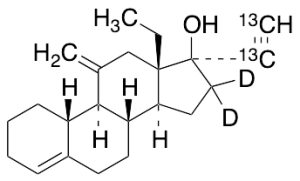
Desogestrel-13C2,d2 (Major)
$332.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2013C2H28D2O
-

Desomorphine-d3
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 2H3 H18 N O2
-

Desonide-13C3
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2113C3H32O6
-
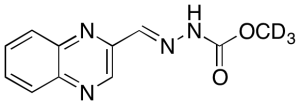
Desoxycarbadox-D3
$363.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 2H3 H7 N4 O2
-
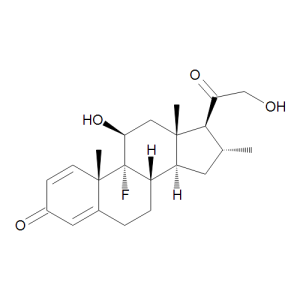
Desoxymetasone
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H29 F O4
-
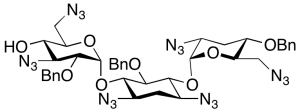
Despentamino Pentazido Tobramycin 6”-Carbamate Tetrabenzyl Ether
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C47H52N16O10
-
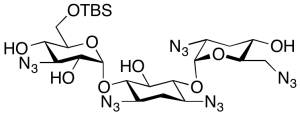
Despentamino Pentazido Tobramycin 6”-tert-Butyldimethysilyl Ether
$122.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H41N15O9Si
-
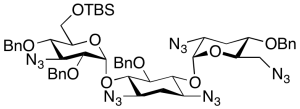
Despentamino Pentazido Tobramycin Tetrabenzyl Ether 6”-tert-Butyldimethysilyl Ether
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C52H65N15O9Si
-
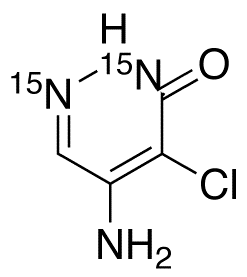
Desphenyl Chloridazon-15N2
$257.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H4 Cl 15N2 N O
-
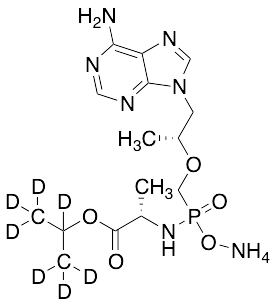
Desphenyl Tenofovir Alafenamide-d7 Ammonium Salt
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15H21D7N7O5P
-
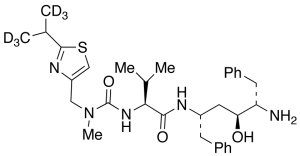
Desthiazolylmethyloxycarbonyl Ritonavir-d6
$169.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C32 D6 H39 N5 O3 S
-
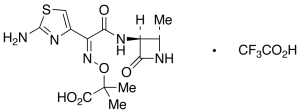
Desulfo Aztreonam Trifluoroacetic Acid Salt (Contains ~20% Unknown Inorganic Salts)
$533.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H18F3N5O7S
-
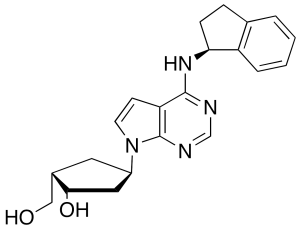
Desulfonamide MLN 4924
$302.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H24N4O2
-

Desvancosaminyl Vancomycin Hydrate (>90%)
$222.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C59H62Cl2N8O22 • H2O
-
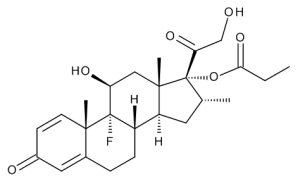
Dexamethasone 17-Propionate
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H33 F O6
-
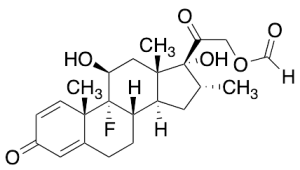
Dexamethasone 21-Formate
$53.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H29 F O6
-
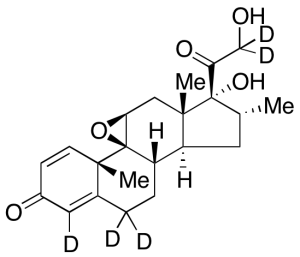
Dexamethasone 9,11-Epoxide-d5
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H23D5O5
-
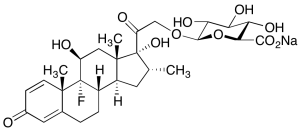
Dexamethasone Beta-D-Glucuronide Sodium Salt
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28 H36 F Na O11
-
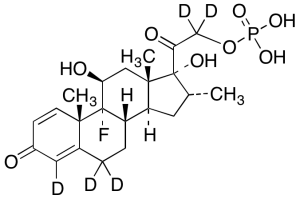
Dexamethasone Phosphate-D5 (Major)
$745.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 2H5 H25 F O8 P
-
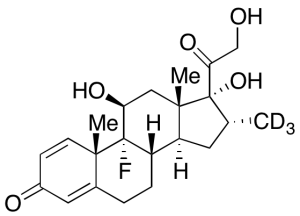
Dexamethasone-d3
$292.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H26D3FO5
-
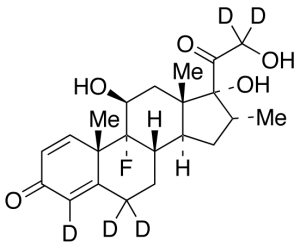
Dexamethasone-D5
$361.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 2H5 H24 F O5
-
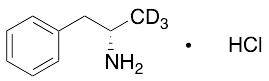
Dexamfetamine-d3 Hydrochloride
$219.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H11D3ClN
-
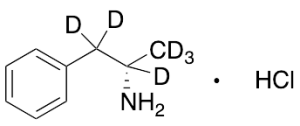
Dexamfetamine-D6 Hydrochloride (~94 : 6 e.r.)
$183.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H7D6N • HCl
-
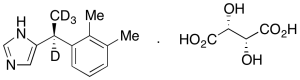
Dexmedetomidine-d4 L-Tartrate (d4-Major)
$356.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H12D4N2 • C4H6O6
-

Dextromoramide
$138.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H32 N2 O2
-
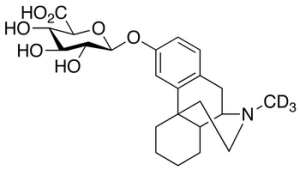
Dextrorphan-d3 Beta-D-O-Glucuronide
$264.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 2H3 H28 N O7
-

Dezocine
$421.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H23NO
-
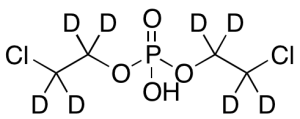
Di-beta,beta’-Chloroethylphosphoric Acid-d8
$243.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4HD8Cl2O4P
-
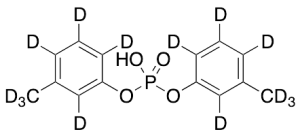
Di-m-tolyl Phosphate-d14(>85%)
$215.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14HD14O4P
-
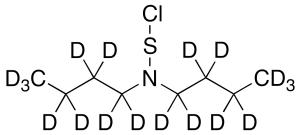
Di-N-butyl Amidosulfenyl Chloride-d18
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8D18ClNS
-

Di-n-butyl Phthalate-d22
$62.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 D22 O4
-
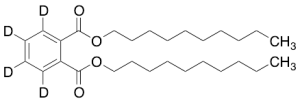
Di-n-decyl Phthalate-3,4,5,6-d4
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28 2H4 H42 O4
-
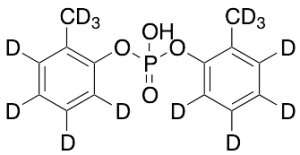
Di-o-tolyl-phosphate-d14
$227.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14HD14O4P
-

Di-p-tolyl Phosphorochloridate-d14
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 D14 Cl O3 P
-
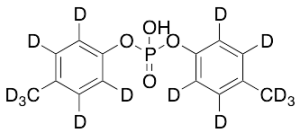
Di-p-tolyl-phosphate-d14
$227.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 D14 H O4 P
-
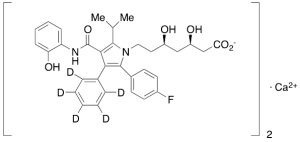
di(2-Hydroxy Atorvastatin-d5) Calcium Salt
$329.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C66H58D10CaF2N4O12
-

Diacetoxyscirpenol
$163.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H26 O7
-
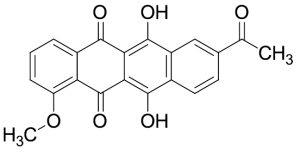
Dianhydrodaunomycinone
$163.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H14 O6
-
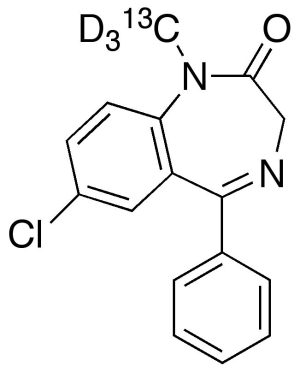
Diazepam-13C,d3
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C1513CH10D3ClN2O
-
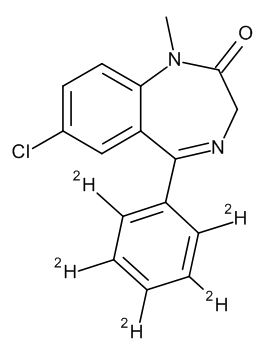
Diazepam-d5
$124.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 2H5 H8 Cl N2 O
-
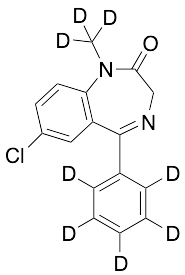
Diazepam-d8
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 2H8 H5 Cl N2 O
-
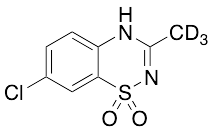
Diazoxide-d3
$223.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H4D3ClN2O2S
-
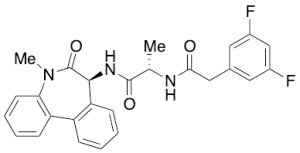
Dibenzazepine (Deshydroxy LY 411575)
$49.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H23 F2 N3 O3
-

Dibenzepin-d3
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 D3 H18 N3 O
-
![Dibenzo[de,qr]naphthacene-9,14-dione](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimagesh3chf810622786797598D417495.png)
Dibenzo[de,qr]naphthacene-9,14-dione
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H12O2
-
![Dibenzo[def,p]chrysene-d14 (Major)](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimagesh06h0e10690432368670D416948.png)
Dibenzo[def,p]chrysene-d14 (Major)
$291.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24D14
-
![Dibenzo[def,p]chrysene-d8 (Major)](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimageshd6h1410690432565278D416947-300x273.png)
Dibenzo[def,p]chrysene-d8 (Major)
$867.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H6D8
-
![Dibenzyl [2-Methyl-4-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-4-yl]methyl-d4 Phosphate](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/sys-masterimagesh0bh7b10690420801566D417892-300x133.png)
Dibenzyl [2-Methyl-4-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-4-yl]methyl-d4 Phosphate
$232.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 D4 H42 N O5 P






