1mg
Showing 3601–3650 of 6728 results
-
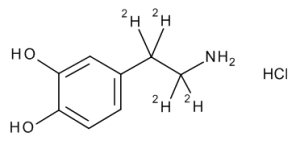
Dopamine-d4 Hydrochloride
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 2H4 H7 N O2 . Cl H
-
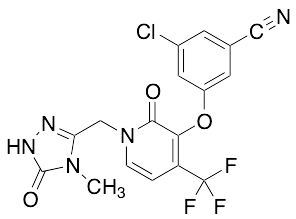
Doravirine
$56.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H11 Cl F3 N5 O3
-
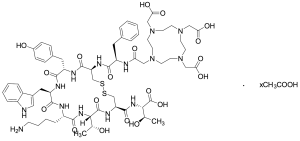
DOTA-(Tyr3)-octreotate Acetate Salt
$263.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C65H90N14O19S2.xCH3COOH
-
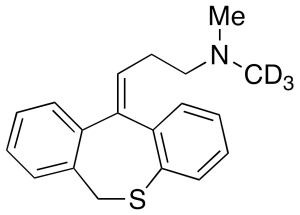
Dothiepin-D3
$216.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19H18D3NS
-

Dowex AG 50W-X8
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-
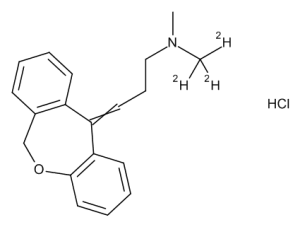
Doxepin-d3 Hydrochloride
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 2H3 H18 N O . Cl H
-
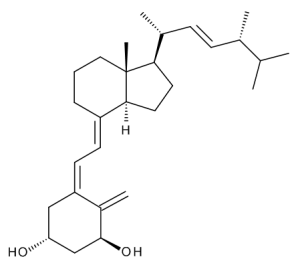
Doxercalciferol
$60.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28 H44 O2
-
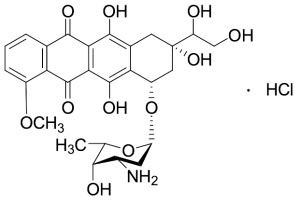
Doxorubicinol Hydrochloride (>90%) (Mixture of diastereomers)
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27H31NO11 • HCl
-

Doxycycline Hydrate (>90%)
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H24N2O8 . x(H2O)
-
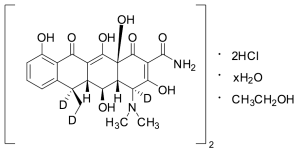
Doxycycline-d3 Hyclate (Major)
$292.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2(C22H21D3N2O8) • 2HCl • xH2O • C2H6O
-
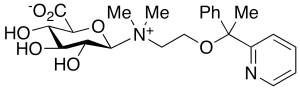
Doxylamine Beta-D-Glucuronide (Mixture of diastereomers)
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H30N2O7
-
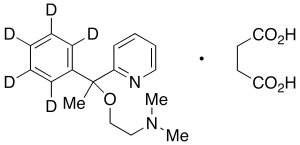
Doxylamine-d5 Succinate
$177.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 2H5 H17 N2 O . C4 H6 O4
-
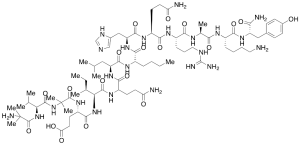
DPC AJ1951, xTFA
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C76 H127 N23 O19 . x[C2 H F3 O2]
-
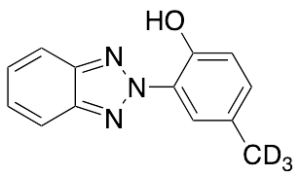
Drometrizole-d3
$188.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H8D3N3O
-
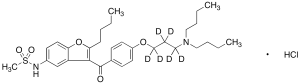
Dronedarone-d6 Hydrochloride
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31H39D6ClN2O5S
-
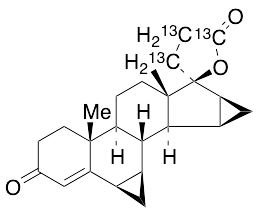
Drospirenone-13C3
$223.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2113C3H30O3
-
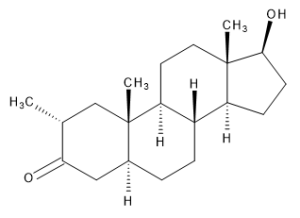
Drostanolone
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H32 O2
-
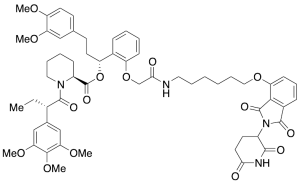
dTAG-13
$357.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C57H68N4O15
-
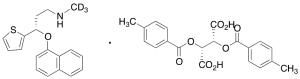
Duloxetine-d3 Di-p-toluoyl-L-tartaric Acid Salt
$232.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C38H34D3NO9S
-

Duloxetine-d3 Maleate
$283.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 D3 H16 N O S . C4 H4 O4
-
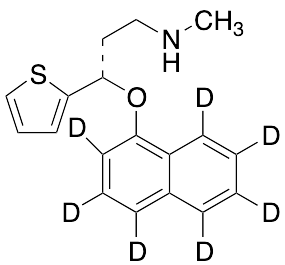
Duloxetine-d7
$261.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H12D7NOS
-
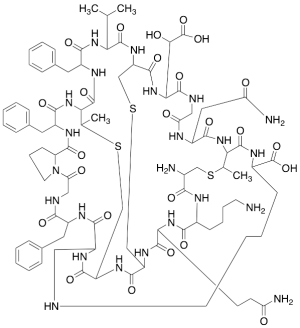
Duramycin (~90%)
$272.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C89H125N23O25S3
-
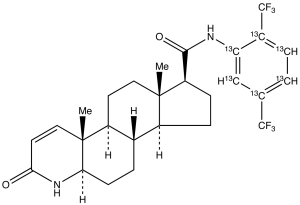
Dutasteride-13C6
$2,464.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2113C6H30F6N2O2
-
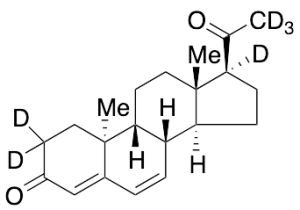
Dydrogesterone-d6 (Major)
$1,133.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H22D6O2
-
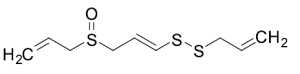
E- Ajoene (~20% in Ethyl Acetate)
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H14OS3
-
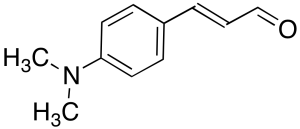
E-4-(Dimethylamino)cinnamaldehyde
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11H13NO
-
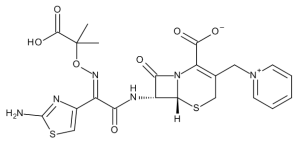
E-Ceftazidime
$266.51 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H22N6O7S2
-
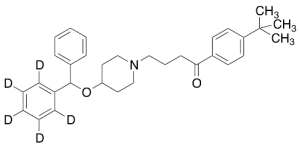
Ebastine-d5
$211.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C32H34D5NO2
-
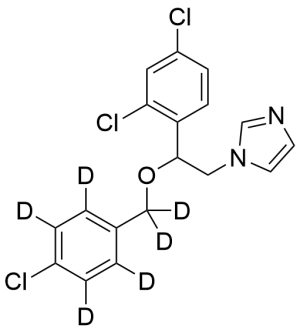
Econazole-d6
$179.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H9 D6 Cl3 N2 O
-
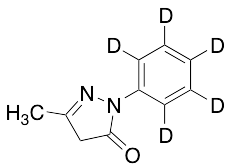
Edaravone D5
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 D5 H5 N2 O
-
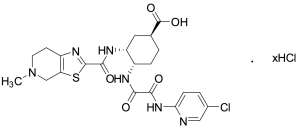
Edoxaban 4-Carboxylic Acid Hydrochloride
$156.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H25ClN6O5S . xHCl
-
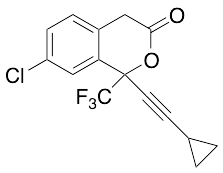
Efavirenz 1-Desamine
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H37 Cl O6
-
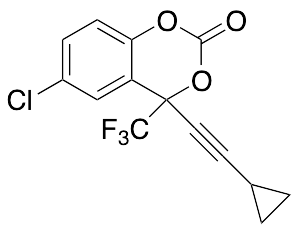
Efavirenz 1-Desamine-1-oxy
$116.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H8ClF3O3
-
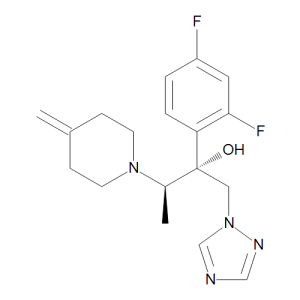
Efinaconazole
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H22 F2 N4 O
-

EGF Fc Chimera, Human
$125.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-

EGF R, His, Human
$1,470.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsEGF Receptor, also known as ERBB, ERBB1 and HER1, is a type I transmembrane protein belonging to the tyrosine protein kinase family. It belongs to a family of tyrosine kinase receptors including Human EGF Receptors (HER) 2, 3, and 4 which all play important roles in cell growth and differentiation. Their primary ligands are EGF, Heparin-Binding EGF and Transforming Growth Factor α. Upon ligand binding, EGFR undergoes asymmetric dimerization, composed of an “activator” and a “receiver”. EGFR and its family members are disregulated in numerous cancers. In particular, EGFR is overexpressed in many epithelial solid tumors. Evidence suggests EGFR is an excellent target for pharmacologic intervention in Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) due to its high level of expression and prominent role in tumor growth and metastasis.
-
EGF, His, Human
$125.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-
EGF, Human
$168.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-

EGF, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-

EGF, Mouse
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-

EGF, Rat
$836.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) was originally discovered in crude preparations of nerve growth factor prepared from mouse submaxillary glands as an activity that induced early eyelid opening, incisor eruption, hair growth inhibition, and stunting of growth when injected into newborn mice. It is prototypic of a family of growth factors that are derived from membrane-anchored precursors. All members of this family are characterized by the presence of at least one EGF structural unit (defined by the presence of a conserved 6 cysteine motif that forms three disulfide bonds) in their extracellular domain. EGF is initially synthesized as a 130 kDa precursor transmembrane protein containing 9 EGF units. The mature soluble EGF sequence corresponds to the EGF unit located proximal to the transmembrane domain. The membrane EGF precursor is capable of binding to the EGF receptor and was reported to be biologically active. Mature rat EGF shares 70 % a.a. sequence identity with mature human EGF.
-

EGF, Rat (CHO-expressed)
$521.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-
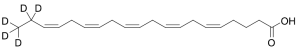
Eicosapentaenoic Acid-d5 (Technical)
$323.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 2H5 H25 O2
-
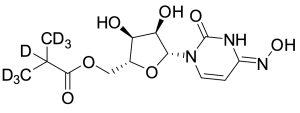
EIDD 2801-D7
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 D7 H12 N3 O7
-
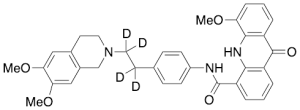
Elacridar-d4 (Major)
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H29D4N3O5
-
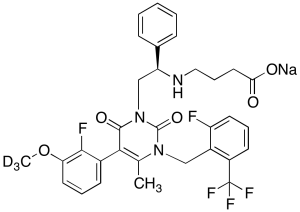
Elagolix Methoxy-d3 Sodium Salt
$257.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C32H26D3F5N3NaO5
-
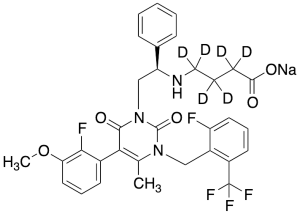
Elagolix-d6 Sodium Salt (Major)
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C32H23D6F5N3NaO5
-
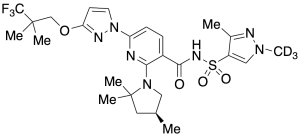
Elexacaftor-D3
$692.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 D3 H31 F3 N7 O4 S
-
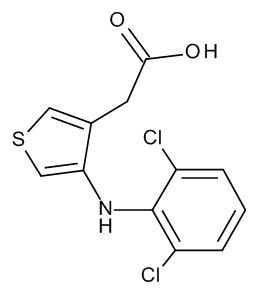
Eltenac
$257.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H9 Cl2 N O2 S
-

Eltenac-13C,d3
$240.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H9 Cl2 N O2 S






