1mg
Showing 4601–4650 of 7910 results
-
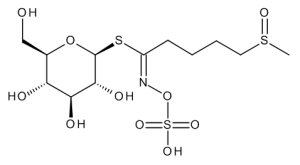
Glucoraphanin
$210.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H23 N O10 S3
-
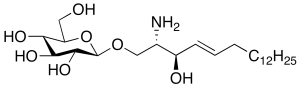
Glucosyl-C18-sphingosine
$236.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H47NO7
-

Glufosinate
$62.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H12 N O4 P
-
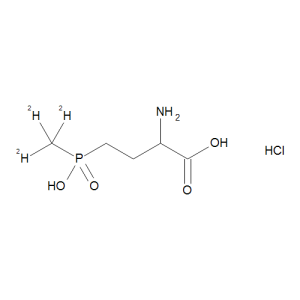
Glufosinate-d3 Hydrochloride
$407.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 2H3 H9 N O4 P . Cl H
-
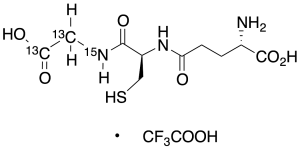
Glutathione (glycine-13C2,15N) Trifluoroacetate Salt
$327.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C813C2H17N215NO6S • C2HF3O2
-

Glutathione Ammonium Salt-d5
$385.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H12D5N3O6S (free acid)
-

Glutathione S-Transferase
$64.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsGlutathione S-Transferase (GST), an antioxidant enzyme, is involved in the primary cellular defense mechanism against reactive oxygen species. GST is soluble in water and has a mass of 26.98 kDa. It occurs as a dimer in all aerobic organisms.
-
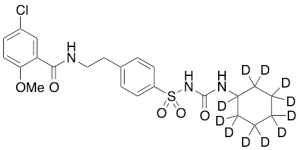
Glyburide-d11
$204.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 D11 H17 Cl N3 O5 S
-
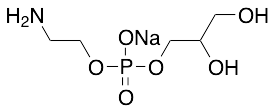
Glycerol 3-Phosphoethanolamine Sodium Salt (>90%)
$188.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H13 N Na O6 P
-

Glycerolkinase
$222.77 Add to cart View Product DetailsGlycerolkinase
-

Glycidyl Behenate-d5
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H43D5O3
-
Glycidyl Caprylate D5
$71.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11H15D5O3
-

Glycidyl Docosahexaenoate-d5
$179.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H31D5O3
-
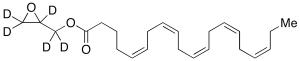
Glycidyl Eicosapentaenoate-d5
$219.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H29D5O3
-
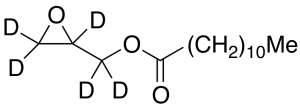
Glycidyl Laurate-d5
$219.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15H23D5O3
-

Glycidyl Linoleate-d5
$89.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 2H5 H31 O3
-
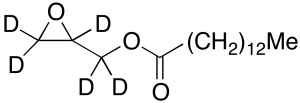
Glycidyl Myristate-d5
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H27D5O3
-

Glycidyl Oleate-13C18
$331.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C18 C3 H38 O3
-

Glycidyl Palmitate-13C16
$218.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H36 O3
-
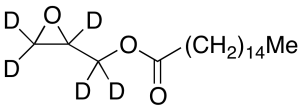
Glycidyl Palmitate-d5
$281.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 D5 H31 O3
-

Glycidyl Palmitoleate-d5 (Technical Grade)
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 D5 H29 O3
-
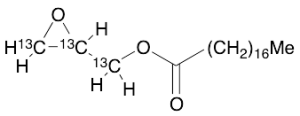
Glycidyl Stearate-13C3
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C1813C3H40O3
-
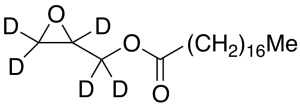
Glycidyl Stearate-d5
$263.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 D5 H35 O3
-
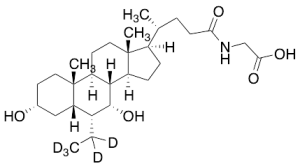
Glycine 6-Ethylchenodeoxycholate-d5
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H42D5NO5
-
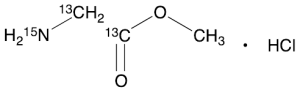
Glycine-13C2,15N Methyl Ester Hydrochloride
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C¹³C2H7¹⁵NO2.HCl
-
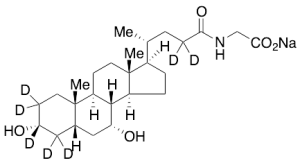
Glycochenodeoxycholic Acid-d7 Sodium Salt (Major)
$215.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H35D7NNaO5
-
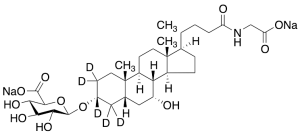
Glycochenodeoxycholic-d5 Acid-3-O-Beta-glucuronide Disodium Salt
$895.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C32H44D5NNa2O11
-
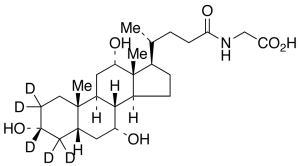
Glycocholic Acid-d5
$243.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H38D5NO6
-

Glycodeoxycholic Acid (2,2,4,4-d4)
$218.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 D4 H39 N O5
-
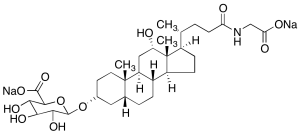
Glycodeoxycholic Acid-3-O-Beta-glucuronide Disodium Salt
$235.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C32H49NNa2O11
-
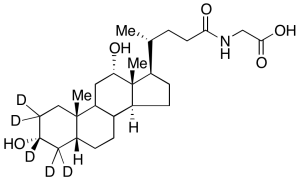
Glycodeoxycholic Acid-D5
$218.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H38D5NO5
-
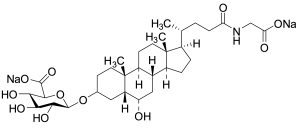
Glycohyodeoxycholic Acid 3-O-Beta-Glucuronide Disodium Salt
$232.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C32H49NNa2O11
-
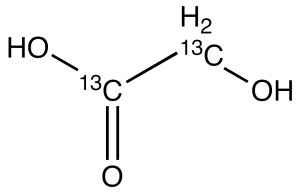
Glycolic Acid-13C2
$194.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C2H4O3
-
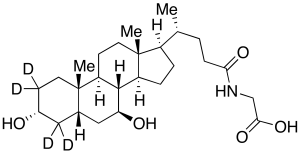
Glycoursodeoxycholic Acid-d4 (Major)
$146.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 D4 H39 N O5
-
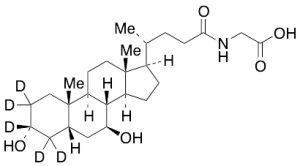
Glycoursodeoxycholic Acid-d5
$255.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H38D5NO5
-
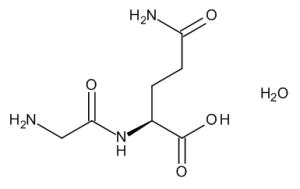
Glycyl-L-Glutamine
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H13 N3 O4 . H2 O
-
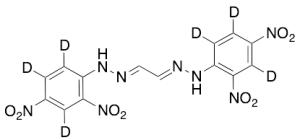
Glyoxal-bis-2,4-DNPH-d6
$242.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 D6 H4 N8 O8
-
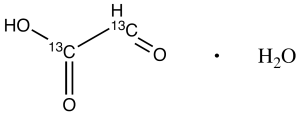
Glyoxylic Acid-13C2 Monohydrate
$257.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C2H4O4
-
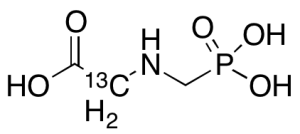
Glyphosate-13C
$119.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C213CH8NO5P
-
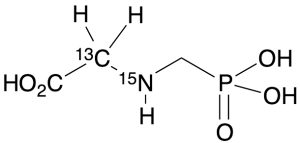
Glyphosate-13C,15N
$215.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C C2 H8 15N O5 P
-
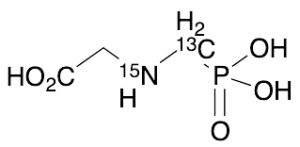
Glyphosate-13C,15N
$267.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C C2 H8 15N O5 P
-
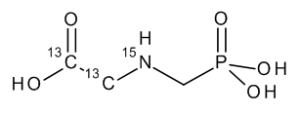
Glyphosate-13C2,15N
$232.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C2 C H8 15N O5 P
-
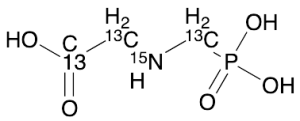
Glyphosate-13C3,15N
$211.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C3 H8 15N O5 P
-
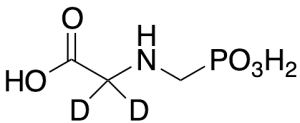
Glyphosate-C2-d2
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H6D2NO5P
-

GM-CSF, Human
$1,923.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can induce human endothelial cells to migrate and proliferate. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

GM-CSF, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can induce human endothelial cells to migrate and proliferate. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

GM-CSF, Human (P. pastoris-expressed)
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can induce human endothelial cells to migrate and proliferate. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-
GM-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can induce human endothelial cells to migrate and proliferate. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

GM-CSF, Mouse
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

GM-CSF, Mouse
$1,470.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.






