1mg
Showing 4751–4800 of 7910 results
-

HIV-1 p24 Antibody (5A4), mAb, Mouse
$382.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman immunodeficiency virus (HIV) belongs to Lentivirus that infects humans through attacking the body’s immune system. The virus can be divided into HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV1 p24 (capsid) protein is critical in HIV-1 viral replication. HIV-1 p24 is a useful biomarker for diagnosing HIV infection.
-

HIV-1 p24 Antibody (M564), mAb, Mouse
$382.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman immunodeficiency virus (HIV) belongs to Lentivirus that infects humans through attacking the body’s immune system. The virus can be divided into HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV1 p24 (capsid) protein is critical in HIV-1 viral replication. HIV-1 p24 is a useful biomarker for diagnosing HIV infection.
-

HIV-1 p24 Antibody (P152), mAb, Mouse
$382.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman immunodeficiency virus (HIV) belongs to Lentivirus that infects humans through attacking the body’s immune system. The virus can be divided into HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV1 p24 (capsid) protein is critical in HIV-1 viral replication. HIV-1 p24 is a useful biomarker for diagnosing HIV infection.
-
HMGB1, His, Human
$1,901.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1), previously known as HMG-1 or amphoterin, is a member of the high mobility group box family of non-histone chromosomal proteins. Human HMGB1 is expressed as a 30 kDa, 215 amino acid (aa) single chain polypeptide containing three domains: two N-terminal globular, 70 aa positively charged DNA-binding domains (HMG boxes A and B), and a negatively charged 30 aa C-terminal region that contains only Asp and Glu.4, 5 Residues 27 – 43 and 178 – 184 contain a NLS. Posttranslational modifications of the molecule have been reported, with acetylation occurring on as many as 17 lysine residues. HMGB1 is expressed at high levels in almost all cells. It was originally discovered as a nuclear protein that could bend DNA. Such bending stabilizes nucleosome formation and regulates the expression of select genes upon recruitment by DNA binding proteins.
-
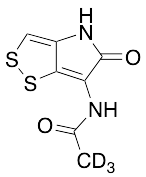
Holomycin-d3
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H3D3N2O2S2
-
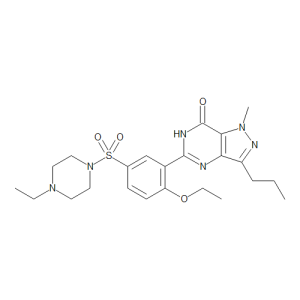
Homo Sildenafil
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H32 N6 O4 S
-
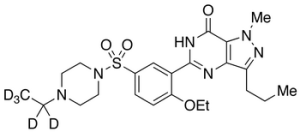
Homo Sildenafil-d5
$169.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H27D5N6O4S
-
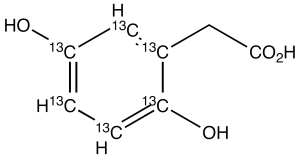
Homogentisic Acid-13C6
$240.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C213C6H8O4
-
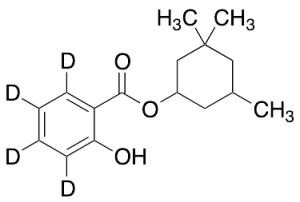
Homosalate-d4
$227.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 D4 H18 O3
-
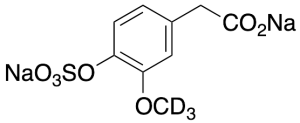
Homovanillic Acid Sulfate Sodium Salt-d3
$213.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H5D3Na2O7S
-
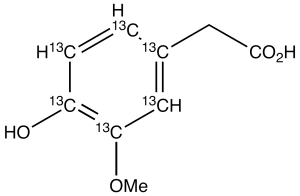
Homovanillic Acid-13C6
$719.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 13C6 C3 H10 O4
-

Homovanillic Acid-d3
$244.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 2H3 H7 O4
-
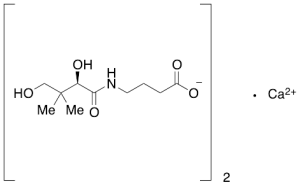
Hopantenate Calcium
$178.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2(C20H19NO5) • Ca
-
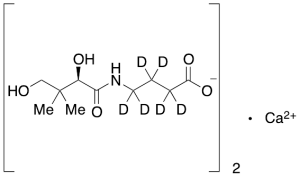
Hopantenate-d6 Calcium
$116.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20H24D12CaN2O10
-
HRP-Protein A
$50.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsStaphylococcal Protein A binds strongly and specifically to the Fc region of immunoglobulin molecules, especially IgG of many species such as Human, Rabbit, Pig, etc. The product contains five high affinity binding sites that are capable of interacting with the Fc region of IgG. HRP-Protein A is produced by covalently linking HRP to Protein A, which can be used in immuno-detection such as immunoblotting (Western or Dot blot), ELISA, and immunohistochemistry.
-

HRP-Protein G
$69.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtein G, a cell surface protein of Group G streptococci, is a Type III Fc receptor that binds to the Fc region of IgG by a non-immune mechanism similar to that of protein A. It contains 3 IgG binding domains and is engineered to delete albumin-binding region. HRP has been covalently coupled to Protein G to produce the HRP-Protein G, which can be used in detection systems such as immunoblotting, ELISA, immunoperoxidase electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry.
-

HRP-Protein L
$87.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtein L is a cell surface protein expressed by Peptostreptoccocus magnus, that binds to the variable light chains (kappa chains) of immunoglobulins without interfering with antigen binding. In contrast to IgG-binding proteins such as protein A and protein G, protein L can be used for the detection and purification of mammalian kappa light chain antibodies of all classes. HRP-Protein L is produced by covalently linking HRP to protein L. The complex can be used in immuno-detection such as immunoblotting (western or dot blot), ELISA, and immunohistochemistry.
-

hsCRP (11C2), mAb, Mouse
$38.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsC-reactive protein (CRP) is synthesized in the liver by macrophage. Its level in blood increases when inflammation occurs. CRP serves as a useful marker for diagnosis of inflammation. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), can serve as a risk marker for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, peripheral vascular disease. Measuring hsCRP in blood is helpful to provide positive treatment of the disease.
-

hsCRP (12D6), mAb, Mouse
$38.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsC-reactive protein (CRP) is synthesized in the liver by macrophage. Its level in blood increases when inflammation occurs. CRP serves as a useful marker for diagnosis of inflammation. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), can serve as a risk marker for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, peripheral vascular disease. Measuring hsCRP in blood is helpful to provide positive treatment of the disease.
-

HT-2 Toxin (>85%)
$257.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H32 O8
-
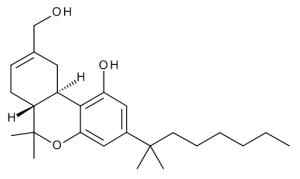
HU 210
$70.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H38 O3
-

Human IgE (RC13), mAb, Mouse
$100.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsIgE is a type of immunoglobulins produced by the immune system. It is composed of two heavy chains and two light chains, like Ig molecules. IgE plays an essential role in various allergic reactions. Its main function is immunity to parasites such as Schistosoma mansoni, Trichinella spiralis, and Fasciola hepatica. It also plays an important role in type I hypersensitivity. Total IgE is considered as a significant marker of allergic state.
-

Human IgE (RC7H), mAb, Mouse
$100.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsIgE is a type of immunoglobulins produced by the immune system. It is composed of two heavy chains and two light chains, like Ig molecules. IgE plays an essential role in various allergic reactions. Its main function is immunity to parasites such as Schistosoma mansoni, Trichinella spiralis, and Fasciola hepatica. It also plays an important role in type I hypersensitivity. Total IgE is considered as a significant marker of allergic state.
-

Human Kappa Light Chain (2F1C1), mAb, Mouse
$326.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsImmunoglobulins (Ig) and free light chains (FLC) is involved in humoral immune response. Ig is composed of two identical light chains and two identical heavy chains. FLC contains two types: kappa free light chain (KFLC) and lambda free light chain (LFLC). The expression of Kappa or Lambda is greatly increased in multiple myeloma or other B cell malignancies. It is useful for the identification of certain non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, leukemias and plasmacytomas. Immunohistochemistry is commonly applied for the detection of free light chains.
-

Human Lambda Light Chain (2D54), mAb, Mouse
$326.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsImmunoglobulins (Ig) and free light chains (FLC) is involved in humoral immune response. Ig is composed of two identical light chains and two identical heavy chains. FLC contains two types: kappa free light chain (KFLC) and lambda free light chain (LFLC). The expression of Kappa or Lambda is greatly increased in multiple myeloma or other B cell malignancies. It is useful for the identification of certain non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, leukemias and plasmacytomas. Immunohistochemistry is commonly applied for the detection of free light chains.
-

HVEM-Fc, Human
$439.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsHerpes Virus Entry Mediator (HVEM) is a transmembrane protein that is the receptor for TNFSF14 (also known as LIGHT) and is therefore referred to asTNFRSF14. HVEM is expressed broadly on immune cells such as T cells, natural killer (NK) cells and monocytes. The interaction of 3 molecules of LIGHT with three molecules of HVEM forms a hexameric complex that leads to the recruitment and retention of effector cells and activates NK cells to produce large amounts of IFN-γ and GM-CSF. In addition to the canonical binding partner LIGHT, HVEM can also bind to the inhibitory signaling protein, B- and T- lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), which suppresses immune responses. Therefore, the HVEM network plays an important role in regulating immunity and the behavior of lymphocytes.
-
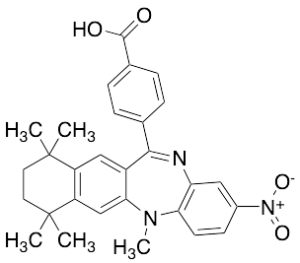
HX 531
$127.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H29N3O4
-
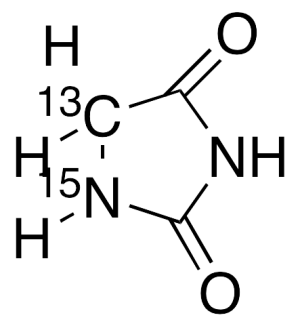
Hydantoin-5-13C,1-15N
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C213CH4N15NO2
-
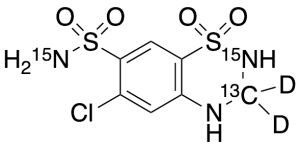
Hydrochlorothiazide-13C,15N2,d2
$244.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C613CH6D2ClN15N2O4S2
-
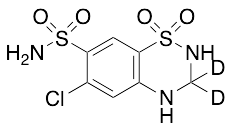
Hydrochlorothiazide-d2
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 2H2 H6 Cl N3 O4 S2
-
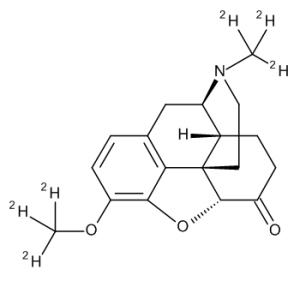
Hydrocodone-d6
$277.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 2H6 H15 N O3
-
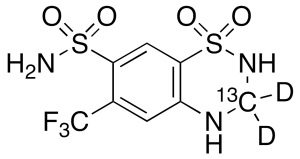
Hydroflumethiazide-13CD2
$165.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C713CH6D2F3N3O4S2
-
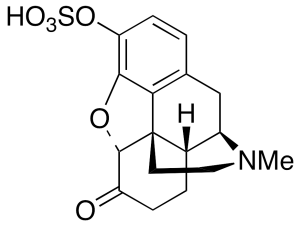
Hydromorphone 3-Sulfate
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H19NO6S
-
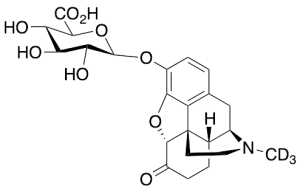
Hydromorphone-3-glucuronide-d3
$307.91 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H24D3NO9
-
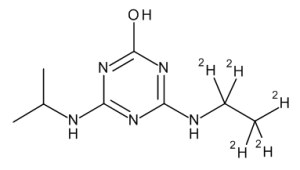
Hydroxy Atrazine-d5
$218.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 2H5 H10 N5 O
-
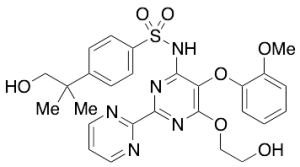
Hydroxy Bosentan
$250.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H29 N5 O7 S
-
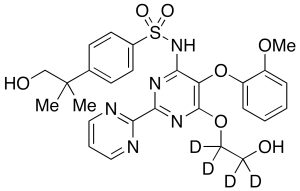
Hydroxy Bosentan-d4
$244.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 2H4 H25 N5 O7 S
-
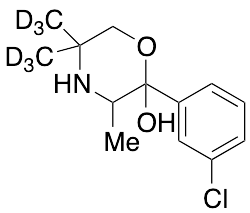
Hydroxy Bupropion-d6
$218.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H12D6ClNO2
-
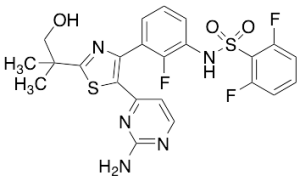
Hydroxy Dabrafenib
$200.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H20 F3 N5 O3 S2
-
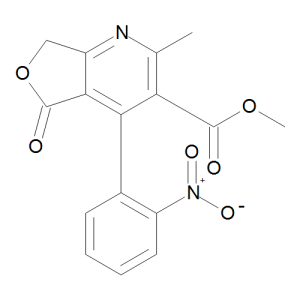
Hydroxy Dehydro Nifedipine Lactone
$286.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H12 N2 O6
-

Hydroxy Dimetridazole-d3
$110.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 2H3 H4 N3 O3
-
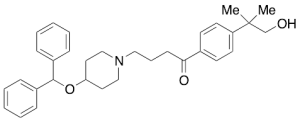
Hydroxy Ebastine
$222.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C32 H39 N O3
-
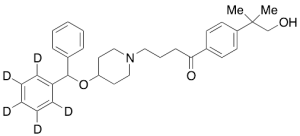
Hydroxy Ebastine-d5
$316.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C32H34D5NO3
-
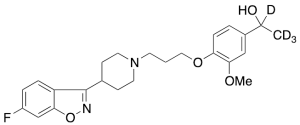
Hydroxy Iloperidone-d4
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H25D4FN2O4
-
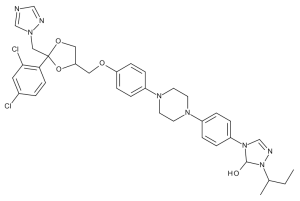
Hydroxy Itraconazole
$219.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 H40 Cl2 N8 O4
-

Hydroxy Itraconazole-d5
$438.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 D5 H33 Cl2 N8 O5
-
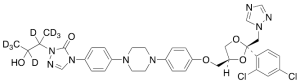
Hydroxy Itraconazole-d8
$369.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 D8 H30 Cl2 N8 O5
-
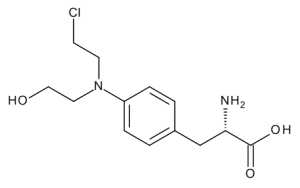
Hydroxy Melphalan (>90%)
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H19 Cl N2 O3
-
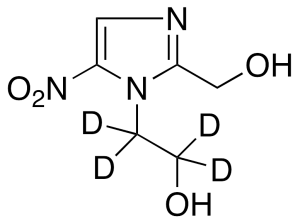
Hydroxy Metronidazole-d4
$213.90 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 2H4 H5 N3 O4
-

Hydroxy Nefazodone Dihydrochloride
$165.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H34Cl3N5O3






