20L
Showing 301–350 of 445 results
-
Polysorbate 20, NF
$1,061.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolysorbate 20, NF
-

Polysorbate 40, NF
$1,520.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolysorbate 40, NF
-

Polysorbate 60
$456.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolysorbate 60
-

Polysorbate 60, NF
$1,221.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolysorbate 60, NF
-

Polysorbate 80, FCC
$586.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolysorbate 80, FCC
-

Polysorbate 80, NF
$1,061.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolysorbate 80, NF
-

Polysorbate 85
$592.27 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolysorbate 85
-

Potassium Dichromate, 0.25 N Solution, For COD, APHA
$336.67 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Dichromate, 0.25 N Solution, For COD, APHA
-

Potassium Fluoride, 50 Percent (w/v) Solution
$2,068.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Fluoride, 50 Percent (w/v) Solution
-

Potassium Fluoride, 50 Percent (w/v) Solution
$870.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Fluoride, 50 Percent (w/v) Solution
-

Potassium Hydroxide, 0.1 N Aqueous Solution
$310.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Hydroxide, 0.1 N Aqueous Solution
-

Potassium Hydroxide, 0.1 N Solution
$209.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Hydroxide, 0.1 N Solution
-

Potassium Hydroxide, 0.5 N Solution
$143.77 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Hydroxide, 0.5 N Solution
-

Potassium Hydroxide, 0.5 N Solution
$312.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Hydroxide, 0.5 N Solution
-

Potassium Hydroxide, 1.0N (1.0M)
$362.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Hydroxide, 1.0N (1.0M)
-

Potassium Hydroxide, 10 Percent (w/v), Solution
$442.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Hydroxide, 10 Percent (w/v), Solution
-

Potassium Hydroxide, 45 Percent (w/w) Aqueous Solution
$634.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Hydroxide, 45 Percent (w/w) Aqueous Solution
-

Potassium Hydroxide, 45 Percent (w/w) Aqueous Solution, Reagent
$662.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Hydroxide, 45 Percent (w/w) Aqueous Solution, Reagent
-

Potassium Iodide, 10 Percent (w/v) Aqueous Solution
$973.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Iodide, 10 Percent (w/v) Aqueous Solution
-

Potassium Iodide, 20 Percent (w/v) Aqueous Solution
$1,137.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Iodide, 20 Percent (w/v) Aqueous Solution
-

Potassium Iodide, 20 Percent (w/v) Aqueous Solution
$1,943.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsPotassium Iodide, 20 Percent (w/v) Aqueous Solution
-
Propionaldehyde
$674.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropionaldehyde
-
Propylene Glycol Methyl Ether
$1,183.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropylene Glycol Methyl Ether
-
Propylene Glycol Methyl Ether Acetate
$703.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropylene Glycol Methyl Ether Acetate
-
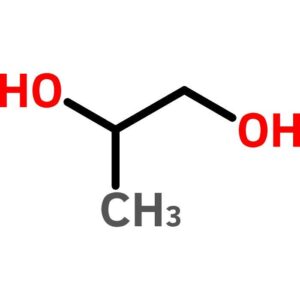
Propylene Glycol, FCC
$808.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropylene Glycol, FCC
-

Propylene Glycol, USP
$1,234.72 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropylene Glycol, USP
-

Propylene Glycol, USP, EP, BP, JP
$1,463.02 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropylene Glycol, USP, EP, BP, JP
-

Propylene Phenoxytol, Reagent
$2,509.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsPropylene Phenoxytol, Reagent
-

PUREGRIP® Rhino Safety Coated Glass Bottles, Amber, 20L, with GL45 VersaCap
$1,198.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsPUREGRIP® Rhino Safety Coated Glass Bottles, Amber, 20L, with GL45 VersaCap
-

PUREGRIP® Rhino Safety Coated Glass Bottles, Clear, 20L, with GL45 VersaCap
$992.52 Add to cart View Product DetailsPUREGRIP® Rhino Safety Coated Glass Bottles, Clear, 20L, with GL45 VersaCap
-

PUREGRIP® Rhino Safety Coated Glass Carboy, Clear, 20L, with 83B VersaCap
$1,307.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsPUREGRIP® Rhino Safety Coated Glass Carboy, Clear, 20L, with 83B VersaCap
-

Purified Water, Meets USP Specifications
$148.78 Add to cart View Product DetailsPurified Water, Meets USP Specifications
-
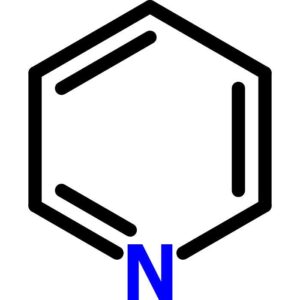
Pyridine, Reagent, ACS
$1,481.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridine, Reagent, ACS
-

Pyridine, Technical
$2,156.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyridine, Technical
-
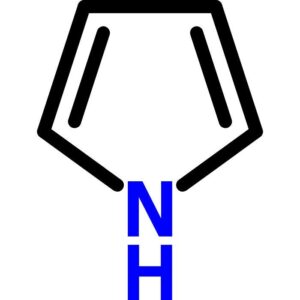
Pyrrole, Reagent
$16,066.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsPyrrole, Reagent
-

Reagent Alcohol
$321.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsReagent Alcohol
-

Red-Four(R) Buffer Solution, pH 4.01
$198.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsRed-Four(R) Buffer Solution, pH 4.01
-

Red-Four(TM) Buffer Solution, pH 4.01 +/- 0.01 @ 25 DEG C, Color-coded RED, Reference Standard
$170.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsRed-Four(TM) Buffer Solution, pH 4.01 +/- 0.01 @ 25 DEG C, Color-coded RED, Reference Standard
-

Safflower Oil, USP
$942.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsSafflower Oil, USP
-

SARS-CoV-2 (Omicron) Neutralizing Antibody Standard
$560.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe product is specific for SARS-CoV-2 RBD domain. The product can neutralize Wild-Type SARS-CoV-2 and Variants of Concern (VOC) including Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Omicron BA.1, Omicron BA.2 and Omicron BA.4/BA.5.
-

SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Standard
$560.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe product is specific for SARS-CoV-2 RBD domain.The product can neutralize Wild-Type SARS-CoV-2 and Variants of Concern (VOC) including Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, but can’t neutralize Omicron BA.1, Omicron BA.2 and Omicron BA.4/BA.5.
-

SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein (RBD, Avi & His Tag)-HRP
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsSevere acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 also known as 2019-nCoV, is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus and is believed to have zoonotic origins and has close genetic similarity to bat coronaviruses. The receptor binding domain (RBD) of spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus binds Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) to invade the host cells. Based on structural biology studies, the RBD can be oriented either in the up/standing or down/lying state with the up/standing state associated with higher pathogenicity.
-

SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein (RBD, L452R, T478K, Avi & His Tag)-HRP
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsSARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2) also known as 2019-nCoV (2019 Novel Coronavirus) is a virus that causes illnesses ranging from the common cold to severe diseases. As of May 2021, three sublineages have been found. Despite its name, B.1.617.3 was the first sublineage of this variant to be detected, in October 2020 in India. This sublineage has remained relatively uncommon compared to the two other sublineages, B.1.617.1 (also known as variant Kappa) and B.1.617.2 (also known as variant Delta), both of which were first detected in December 2020. This variant has the double mutations E484Q and L452R in the spike proteins. Emerging research suggests the variant may be more transmissible than previously evolved ones. Whether the effectiveness of currently-deployed vaccines is affected remains under investigation. Moreover, the sublineage B.1.617.2 has been redesignated as “variant of concern” (VOC-21APR-02) in May 2021, which spreads more quickly than the original version of the virus.
-

SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein RBD-HRP, BA.2 variant, His Tag
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsBA.2 differs from BA.1 in its genetic sequence, including some amino acid differences in the spike protein and other proteins. Studies have shown that BA.2 has a growth advantage over BA.1. Studies are ongoing to understand the reasons for this growth advantage, but initial data suggest that BA.2 appears inherently more transmissible than BA.1, which currently remains the most common Omicron sublineage reported. This difference in transmissibility appears to be much smaller than, for example, the difference between BA.1 and Delta. Further, although BA.2 sequences are increasing in proportion relative to other Omicron sublineages (BA.1 and BA.1.1), there is still a reported decline in overall cases globally.
-

SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein RBD-HRP, Omicron Variant, His Tag
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsSARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory
Syndrome Coronavirus 2) also known as 2019-nCoV (2019 Novel Coronavirus) is a virus that causes illnesses ranging from the common cold to severe diseases. Recently, the new B.1.1.529 variant was confirmed in South Africa and preliminary evidence suggests an increased risk of reinfection with this variant. The B.1.1.529 variant was first reported to WHO on 24 November 2021 and WHO has designated this variant as a VOC (Variant of Concern), named Omicron. There are more than 30 mutations in the spike protein. -
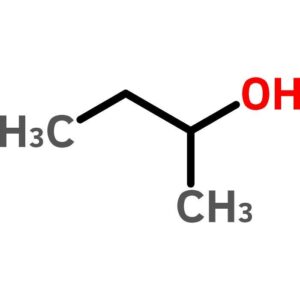
sec-Butyl Alcohol
$476.51 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-Butyl Alcohol
-

Sesame Oil, NF
$1,696.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsSesame Oil, NF
-

Silver Nitrate, 0.050 N Solution
$1,131.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsSilver Nitrate, 0.050 N Solution
-

Silver Nitrate, 0.171 N Standardized Solution
$4,522.78 Add to cart View Product DetailsSilver Nitrate, 0.171 N Standardized Solution
-

Silver Nitrate, 0.171 N Standardized Solution
$2,468.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsSilver Nitrate, 0.171 N Standardized Solution






