50g
Showing 801–850 of 1859 results
-
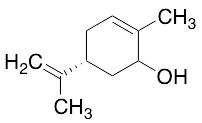
Carveol(Mixture of cis and trans)
$401.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H16 O
-

Cathepsin L, Human
$266.51 Add to cart View Product DetailsCathepsin L is an enzyme. Cathepsin L, a lysosomal endopeptidase expressed in most eukaryotic cells, is a member of the papain-like family of cysteine proteinases. Cathepsin L plays a major role in antigen processing, tumor invasion and metastasis, bone resorption, and turnover of intracellular and secreted proteins involved in growth regulation. Unlike the precursor forms of other papain family members, the 43 kDa pro-cathepsin L itself is secreted from various cells. Pro-cathepsin L is the major excreted protein of malignantly transformed mouse fibroblasts and is also one of the major acidic cysteine proteases in mammalian cells.
-
CD160 Fc Chimera, Human
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD160 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored Ig domain protein that is expressed on almost all intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs), γδ T (gamma delta T) cells, NK (natural killer) cells, and a minor subset of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. In terms of function, work has centered on the role of CD160 in enhancing NK or CD8 T cell activation. Such effects have been attributed to the ability of CD160 to bind classical and nonclassical MHC class I molecules, although with apparent low affinity, requiring clustering of MHC class I molecules or overexpression of CD160 or MHC class I for detection of the interaction.
-
CD19 Fc Chimera, Human
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD19 is a 95 kDa coreceptor, which amplifies the signaling cascade in B cells. On the B cell surface, CD19 associates with CD21, CD81 and Leu-13 to exert its function. The cytoplasmic tail of CD19 has nine conserved tyrosine residues playing critical roles in CD19 mediated function by coupling signaling molecules to the receptor. Mature human CD19 consists of a 272aa extracellular domain (ECD) with two Ig-like domains, a 22aa transmembrane segment, and a 243aa cytoplasmic domain.
-
CD24 Fc Chimera, Human
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsSignal transducer CD24 also known as cluster of differentiation 24 or heat stable antigen CD24 (HSA) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD24 gene. CD24 is a cell adhesion molecule. CD24 is a sialoglycoprotein expressed at the surface of most B lymphocytes and differentiating neuroblasts. It is also expressed on neutrophils and neutrophil precursors from the myelocyte stage onwards. The encoded protein is anchored via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) link to the cell surface. The protein also contributes to a wide range of downstream signaling networks and is crucial for neural development. Cross-linking of CD24 on the surface of neutrophils induces apoptosis, and this appears to be defective in sepsis.
-

CD24 Fc Chimera, Mouse
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsSignal transducer CD24 also known as cluster of differentiation 24 or heat stable antigen CD24 (HSA) is a protein that in mouse is encoded by the CD24 gene. CD24 is a cell adhesion molecule. CD24 is a sialoglycoprotein expressed at the surface of most B lymphocytes and differentiating neuroblasts. It is also expressed on neutrophils and neutrophil precursors from the myelocyte stage onwards. The encoded protein is anchored via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) link to the cell surface. The protein also contributes to a wide range of downstream signaling networks and is crucial for neural development. Cross-linking of CD24 on the surface of neutrophils induces apoptosis, and this appears to be defective in sepsis.
-

CD25/IL-2Rα Fc Chimera, Human
$301.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe IL-2 receptor system consists of three non-covalently linked subunits termed IL-2Rα, IL-2Rβ, and IL-2Rγ. The IL-2Rα is a type I transmembrane protein consisting of a 219 amino acid (a.a.) extracellular domain, a 19 a.a. transmembrane domain and a 13 a.a. intracellular domain, which is not involved in the transduction of IL-2 signal. Activated T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs) and NK cells express high levels of CD25 and expression of the high-affinity IL-2Rα is mostly limited to these cell populations. Signaling via IL-2Rα mediates multiple biological processes in various cell populations, e.g. proliferation and differentiation of B cells and NK cells. A soluble form of IL-2Rα (IL-2Rα) appears in serum, concomitant with its increased expression on cells. The function of the soluble IL-2Rα is unclear. Increased levels of IL-2Rα in biological fluids reportedly correlate with increased T and B cell activation and immune system activation. Increased serum concentration of IL-2Rα has been observed in patients with a variety of inflammatory conditions and in the course of some leukemias and lymphomas.
-

CD38, Human
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD38 (also referred to as T10 antigen) is a nonlineage-restricted type II transmembrane glycoprotein that has emerged as an intracellular calcium ion mobilizing messenger. It can serve as an ectoenzyme that catalyzes the synthesis and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose. The enzymatic functions of CD38 probably contribute to an array of its immunoregulatory functions. It has been found on the surface of many immune cells (white blood cells), including CD4+, CD8+, B lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Soluble CD38 and the ability of membrane-bound CD38 to become internalized in response to appropriate stimuli suggest that extracellular and intracellular roles for this protein are equally plausible.
-

CD40L/CD154/TRAP, Human
$159.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD40 Ligand (CD40L/CD154/TRAP) is a membrane glycoprotein and differentiation antigen expressed on the surface of T-cells. The CD40 ligand stimulates B-cell proliferation and secretion of all immunoglobulin isotypes in the presence of cytokines. It also costimulates proliferation of activated T-cell and this is accompanied by the production of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL2. CD40 ligand has been shown to induce cytokine production and tumoricidal activity in peripheral blood monocytes.
-
CD96, His, Human
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD96 (Cluster of Differentiation 96), also known as Tactile (T cell activation, increased late expression), is a receptor protein which is expressed on T cells and NK cells and shares sequence similarity with CD226 (also known as DNAM-1). The main ligand of CD96 is CD155 and CD96 competes with CD226 for binding to CD155. This protein belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and may play a role in the adhesive interactions of activated T and NK cells during the late phase of the immune response. It may also promote NK cell-target adhesion by interacting with PVR present on target cells and function in antigen presentation.
-

CEA Fc chimera, Human
$138.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsCarcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) also known as Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 (CEACAM5), CD antigen CD66e, Meconium antigen 100, is an oncofetal glycoprotein that is normally expressed by mucosal cells. CEA is a member of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily of proteins. CEA is a glycophosphatidylinositol- (GPI-) linked membrane-anchoring protein that is exposed to the cell surface that faces the extracellular matrix. The membrane-anchoring region of CEA can be cleaved by phospholipase C and phospholipase D. The cleaved products are soluble and circulating through blood vessels. Thus, CEA can be present as secreted and cell surface-anchored forms. CEA is functionally associated with cellular interaction, cell adhesion, immune response, anoikis resistance, and promotion of liver metastasis. CEA overexpression is associated with many types of cancers including gastrointestinal, respiratory, and genitourinary system and breast cancers.
-

CEA, His, Human
$138.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsCarcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) also known as Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 (CEACAM5), CD antigen CD66e, Meconium antigen 100, is an oncofetal glycoprotein that is normally expressed by mucosal cells. CEA is a member of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily of proteins. CEA is a glycophosphatidylinositol- (GPI-) linked membrane-anchoring protein that is exposed to the cell surface that faces the extracellular matrix. The membrane-anchoring region of CEA can be cleaved by phospholipase C and phospholipase D. The cleaved products are soluble and circulating through blood vessels. Thus, CEA can be present as secreted and cell surface-anchored forms. CEA is functionally associated with cellular interaction, cell adhesion, immune response, anoikis resistance, and promotion of liver metastasis. CEA overexpression is associated with many types of cancers including gastrointestinal, respiratory, and genitourinary system and breast cancers.
-
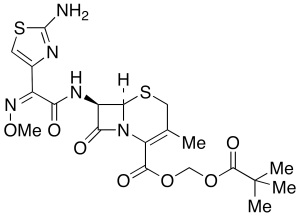
Cefetamet Pivoxil
$672.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H25 N5 O7 S2
-
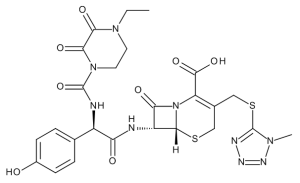
Cefoperazone Acid
$772.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H27 N9 O8 S2
-
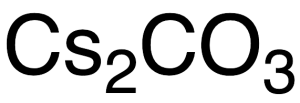
Cesium Carbonate
$112.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Cs2CO3
-
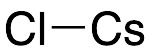
Cesium Chloride
$149.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Cl . Cs
-
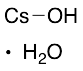
Cesium Hydroxide Monohydrate
$260.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CsHO . H2O
-
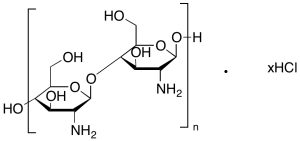
Chitosan Oligosaccharide Hydrochloride Salt (Technical Grade)
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : (C12H24N2O9)n • xHCl
-

Chloramphenicol
$129.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsChloramphenicol
-

Chlorhexidine Digluconate (In 20% solution)
$188.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H30 Cl2 N10 . 2 C6 H12 O7
-

Chloroacetyl Chloride
$69.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H2Cl2O
-
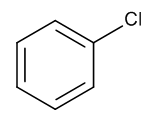
Chlorobenzene
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H5 Cl
-
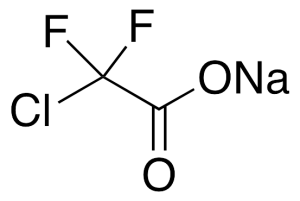
Chlorodifluoro-acetic Acid Sodium Salt
$109.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2ClF2NaO2
-
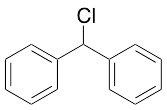
Chlorodiphenylmethane
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H11Cl
-
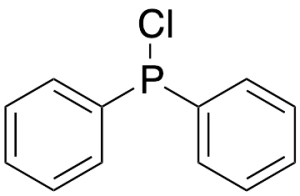
Chlorodiphenylphosphine
$138.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H10ClP
-
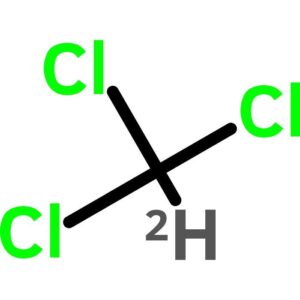
Chloroform-d, 99.8 Atom Percent D
$102.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsChloroform-d, 99.8 Atom Percent D
-

Chloroform-d, 99.8 Atom Percent D, Contains 0.05 Percent (v/v) Tetramethylsilane
$107.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsChloroform-d, 99.8 Atom Percent D, Contains 0.05 Percent (v/v) Tetramethylsilane
-
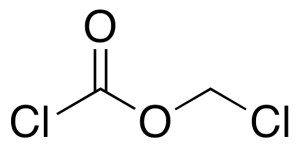
Chloroformic Acid Chloromethyl Ester
$319.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H2Cl2O2
-
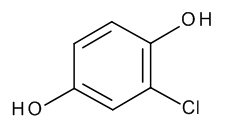
Chlorohydroquinone (Technical Grade, ~90%)
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H5 Cl O2
-
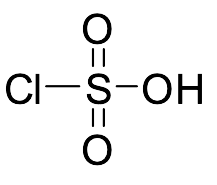
Chlorosulfonic Acid
$152.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : ClHO3S
-

Chlorothiazide
$265.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsChlorothiazide
-

Chloroxylenol
$81.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H9 Cl O
-
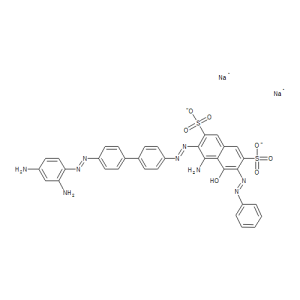
Chlorozol Black E (Technical Grade)
$93.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H25 N9 O7 S2 . 2 Na
-
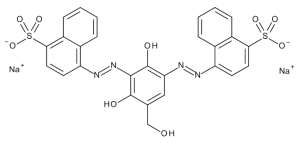
Chocolate Brown HT (Technical Grade)
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H18 N4 O9 S2 . 2 Na
-

Cholesteryl N-Butyrate
$233.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31H52O2
-
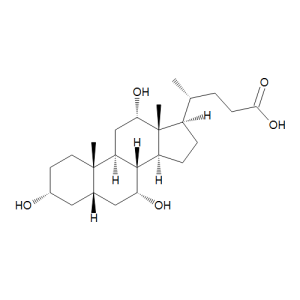
Cholic Acid
$106.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24 H40 O5
-
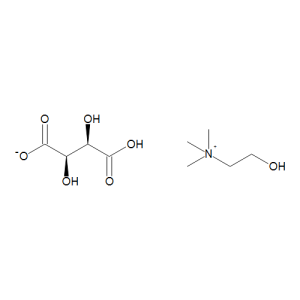
Choline Bitartrate
$117.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H14 N O . C4 H5 O6
-
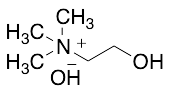
Choline Hydroxide in Methanol Solution (~45% w/w, stabilized with 0.5% Paraformaldehyde)
$113.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H15NO2
-
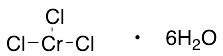
Chromium(III) Chloride Hexahydrate
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Cl3CrH12O6
-
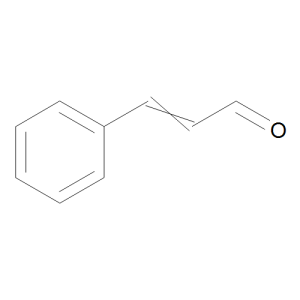
Cinnamaldehyde
$279.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H8 O
-
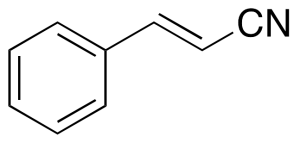
Cinnamonitrile
$1,229.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H7N
-
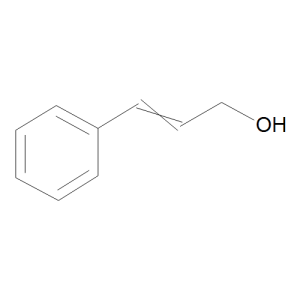
Cinnamyl Alcohol
$223.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H10 O
-

cis-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydrophthalic Anhydride
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H8 O3
-
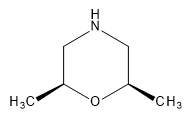
cis-2,6-Dimethylmorpholine
$174.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H13NO
-
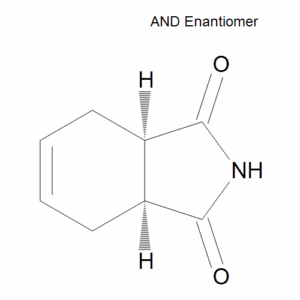
cis-Tetrahydrophthalimide
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H9 N O2
-
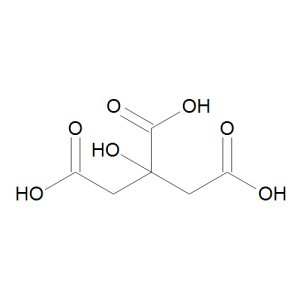
Citric Acid
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H8 O7
-
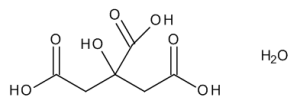
Citric Acid Monohydrate
$79.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H8 O7 . H2 O
-
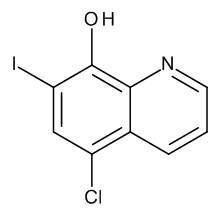
Clioquinol
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H5 Cl I N O
-
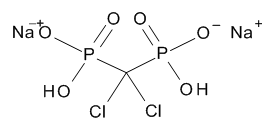
Clodronic Acid Disodium Salt Hydrate
$2,157.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C H2 Cl2 O6 P2 . 2 Na
-

CNTF, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsCiliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF) is a cytokine belonging to the Interleukin 6 (IL-6) family, which also includes IL-6, Oncostatin M, Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF), and Cardiotrophin-1. Structurally, CNTF resembles a four-helix bundle composition, similar to the other members of the IL-6 family. The receptor for CNTF is composed of three parts: a gp130-like subunit common in the IL-6 receptor family, a LIF Receptor β subunit, and a CNTF specific α receptor subunit. Upon binding to the CNTF, the β subunit of the CNTF receptor will undergo tyrosine phosphorylation, and activate the intracellular JAK/STAT pathway. The main function of CNTF in vivo is to promote the differentiation and survival of a variety of neurons and glial cells, including sympathetic precursor cells and spinal motor neurons.






