50g
Showing 851–900 of 1859 results
-

CNTF, Mouse
$293.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsCiliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) is a polypeptide hormone whose actions appear to be restricted to the nervous system where it promotes neurotransmitter synthesis and neurite outgrowth in certain neuronal populations. CNTF was initially identified as a trophic factor for embryonic chick ciliary parasympathetic neurons in culture. Furthermore, the protein is also a potent survival factor for neurons and oligodendrocytes and may be relevant in reducing tissue destruction during inflammatory attacks. In addition, CNTF is useful for treatment of motor neuron disease and it could reduce food intake without causing hunger or stress. Recombinant murine CNTF containing 198 amino acids and it shares 82 % and 95 % a.a. sequence identity with human and rat CNTF.
-

CNTF, Rat
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsCiliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF) is a polypeptide hormone which acts within the nervous system where it promotes neurotransmitter synthesis and neurite outgrowth in certain neuronal populations. CNTF is a potent survival factor for neurons and oligodendrocytes and may play a role in reducing tissue damage during increased inflammation. A mutation in this gene, which results in aberrant splicing, leads to ciliary neurotrophic factor deficiency, however this phenotype is not causally related to neurologic disease.
-
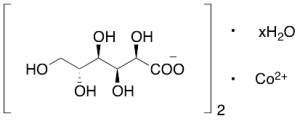
Cobalt(II) Gluconate Hydrate
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H22CoO14. xH2O
-
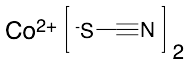
Cobalt(II) Thiocyanate
$599.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Co (S C N)2
-
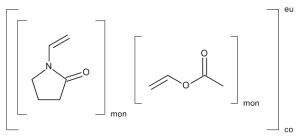
Copovidone (Technical Grade)
$276.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H9NO.C4H6O2
-
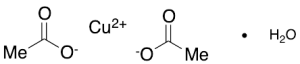
Copper (II) Acetate Monohydrate
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C2 H3 O2 . Cu . H2 O
-

Copper (II) Bromide
$105.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Br2 Cu
-
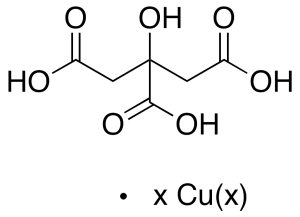
Copper Citrate
$407.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H8O7 xCu
-
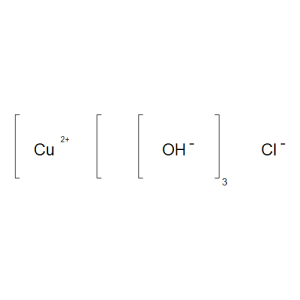
Copper Oxychloride
$71.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Cl Cu2 H3 O3
-

Copper(I) Chloride
$152.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : ClCu
-
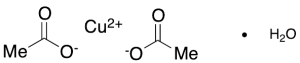
Copper(II) Acetate Monohydrate
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H8O4 .Cu .H2O
-
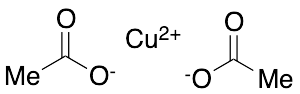
Copper(II) Acetate, Anhydrous
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2(C2H3O2)- . (Cu)2+
-

Copper(II) Nitrate Hemipentahydrate
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Cu(NO3)2 • 2.5[H2O]
-
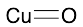
Copper(II) Oxide
$288.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-
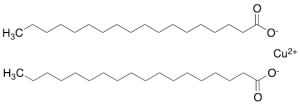
Copper(II) Stearate (contains ~10% inorganics)
$116.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C36H70CuO4
-
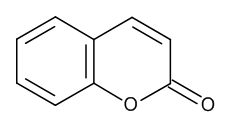
Coumarin
$121.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H6 O2
-
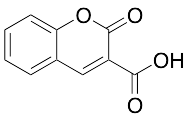
Coumarin-3-carboxylic acid
$152.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H6O4
-
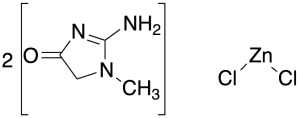
Creatinine Zinc Chloride
$187.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C4 H7 N3 O . Zn . 2 Cl
-
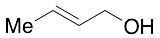
Crotyl Alcohol (cis/trans Mixture)
$324.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H8O
-
CTLA-4 Fc Chimera, Human
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsCytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated molecule-4 (CTLA-4) is a cell surface molecule that is closely related to CD28, and a powerful negative regulator of T cell activation. Structurally, CTLA-4 is a member of the Ig superfamily, having a single extracellular V-like domain , homology with CD28; The overall sequence homology between CD28 and CTLA-4 is about 20%, but they share a 27% (murine) to 31% (human) identity at the amino acid level. Inhibitory receptor acting as a major negative regulator of T-cell responses. The affinity of CTLA-4 for its natural B7 family ligands, CD80 and CD86, is considerably stronger than the affinity of their cognate stimulatory coreceptor CD28.
-

CTLA-4 Fc Chimera, Mouse
$50.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsCTLA-4 (Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4) is also known as CD152, is an Inhibitory receptor acting as a major negative regulator of T-cell responses. CTLA-4 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, which is expressed on the surface of T cells and transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells. CTLA-4 and CD28 are homologous receptors expressed by both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, which mediate opposing functions in T-cell activation. Both receptors share a pair of ligands expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs). The affinity of CTLA-4 for its natural B7 family ligands, CD80 and CD86, is considerably stronger than the affinity of their cognate stimulatory co-receptor CD28.
-

Cumene
$248.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H12
-
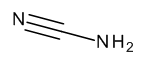
Cyanamide
$113.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C H2 N2
-
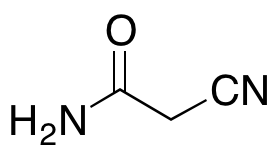
Cyanoacetamide
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H4 N2 O
-
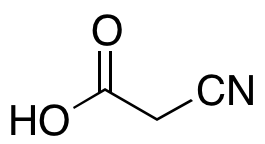
Cyanoacetic Acid
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H3NO2
-

Cyclohexanepropanoic Acid
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H16O2
-
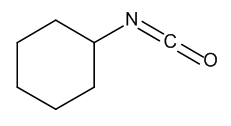
Cyclohexyl Isocyanate
$104.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H11 N O
-
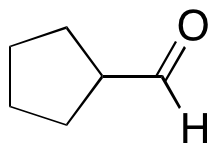
Cyclopentanecarboxaldehyde
$1,022.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H10O
-
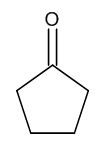
Cyclopentanone
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H8 O
-
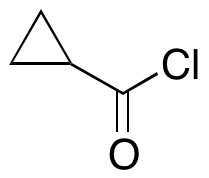
Cyclopropanecarbonyl Chloride
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H5ClO
-
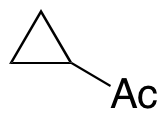
Cyclopropyl Methyl Ketone
$93.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H8O
-
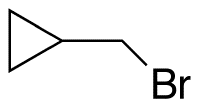
Cyclopropylmethyl Bromide
$100.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H7Br
-
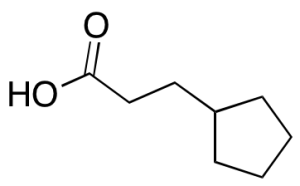
Cypionic Acid
$264.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H14O2
-
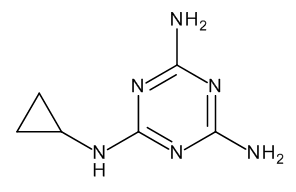
Cyromazine
$1,328.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H10 N6
-
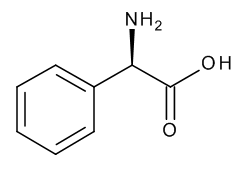
D-(-)-2-Phenylglycine
$544.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H9 N O2
-
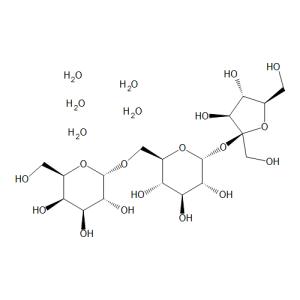
D-(+)-Raffinose Pentahydrate
$71.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H32 O16 . 5 H2 O
-

D-(+)-Trehalose Dihydrate
$419.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H22 O11 . 2 H2 O
-
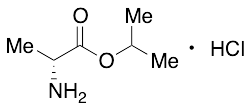
D-Alanine Isopropyl Ester Hydrochloride, ~90%
$468.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H14ClNO2
-
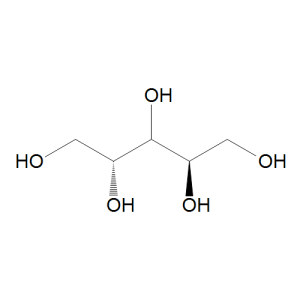
D-Arabinitol
$1,807.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H12 O5
-

D-Arabinose
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H10 O5
-
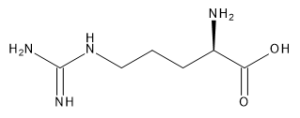
D-Arginine
$232.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H14 N4 O2
-

D-Fructose
$91.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H12O6
-
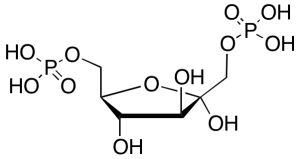
D-Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphate Sodium Salt Hydrate
$163.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H13 O12 P2 . Na . H2 O
-
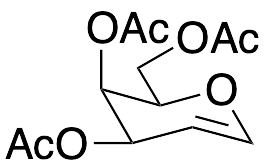
D-Galactal Triacetate
$545.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H16 O7
-

D-Glucose
$125.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H12O6
-

D-Lactose
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H22 O11
-
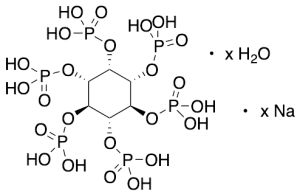
D-myo-Inositol 1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexakisphosphate Sodium Salt Hydrate, Zea mays (>85% purity)
$185.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H18 O24 P6 . Na . H2 O
-
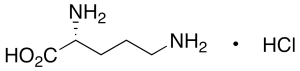
D-Ornithine Hydrochloride
$1,302.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H12 N2 O2 . Cl H
-

D-Panthenol
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H19 N O4
-
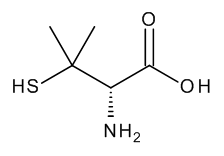
D-Penicillamine
$252.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H11 N O2 S






