50g
Showing 1001–1050 of 1859 results
-
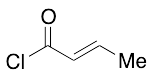
E-Crotonoyl Chloride
$244.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H5ClO
-
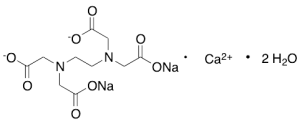
Edetate Calcium Disodium Dihydrate
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H12CaN2O8 . 2H2O . 2Na
-
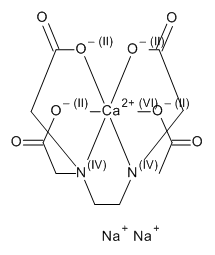
EDTA Calcium Disodium Salt Hydrate
$81.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H12 Ca N2 O8 . 2 Na
-

EGF Fc Chimera, Human
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-

EGF R, His, Human
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsEGF Receptor, also known as ERBB, ERBB1 and HER1, is a type I transmembrane protein belonging to the tyrosine protein kinase family. It belongs to a family of tyrosine kinase receptors including Human EGF Receptors (HER) 2, 3, and 4 which all play important roles in cell growth and differentiation. Their primary ligands are EGF, Heparin-Binding EGF and Transforming Growth Factor α. Upon ligand binding, EGFR undergoes asymmetric dimerization, composed of an “activator” and a “receiver”. EGFR and its family members are disregulated in numerous cancers. In particular, EGFR is overexpressed in many epithelial solid tumors. Evidence suggests EGFR is an excellent target for pharmacologic intervention in Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) due to its high level of expression and prominent role in tumor growth and metastasis.
-
EGF, His, Human
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-
EGF, Human
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-

EGF, Mouse
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-

EGF, Rat (CHO-expressed)
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsEpidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that stimulates the proliferation of various epidermal and epithelial cells. Additionally, EGF has been shown to inhibit gastric secretion, and to be involved in wound healing. EGF signals through the EGF receptor (EGFR) also known as erbB1, is a class I tyrosine kinase receptor. This receptor also binds with TGF-α and VGF (vaccinia virus growth factor). EGF-receptor binding results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide first purified from the mouse submandibular gland, but since then found in many human tissues including submandibular gland, parotid gland. Salivary EGF, which seems also regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of oro-esophageal and gastric tissue integrity. The biological effects of salivary EGF include healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, stimulation of DNA synthesis as well as mucosal protection from intraluminal injurious factors such as gastric acid, bile acids, pepsin, and trypsin and to physical, chemical and bacterial agents.
-
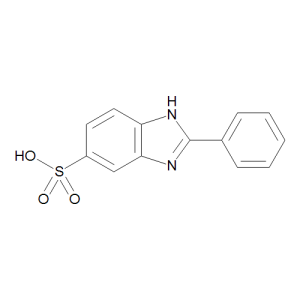
Ensulizole
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H10 N2 O3 S
-
Enterokinase (EK), His, Lyophilized, Bovine
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsEnterokinase (EK) is an enzyme produced by cells of the duodenum and involved in human digestion. It plays a role of turning trypsinogen to its active form trypsin, and indirectly activates the pancreatic digestive enzymes. Enterokinase is a specific protease that cleaves after a lysine preceded by four aspartic acids: Asp-Asp-Asp-Asp-Lys(DDDDK↑). Enterokinase will not work if the recognition site is followed by a proline. rbEKhas the highest activity than EK of other species and is used wildly in biochemical applications. rbEK with 6 × His-tag binds with Ni2+ affinity chromatography and was designed for removing from digestion system.
Recombinant Bovine Enterokinase (His-tagged) (rbEK) as the light chain is a single glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 200 amino acids, 6 × His at C-terminus. A fully biologically active molecule, rbEK has a molecular mass of 40 kDa and is obtained by proprietary chromatographic techniques at GenScript. -
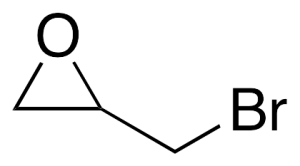
Epibromhydrin
$189.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H5BrO
-
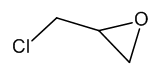
Epichlorohydrin
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H5 Cl O
-

EPO, Human
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsErythropoietin (EPO), a glycoprotein produced primarily by the kidney, is the principal factor that regulates erythropoiesis by stimulating the proliferation and differentiation of erythroid progenitor cells. The production of EPO by kidney cells is increased in response to hypoxia or anemia. Recombinant EPO has been approved for the treatment of anemia associated with chronic renal failure as well as for anemia of AZT treated AIDS patients.The cDNAs for EPO have been cloned from human, mouse, canine, etc. The mature proteins from the various species are highly conserved, exhibiting greater than 80% sequence identity at the amino acid level. Human EPO cDNA encodes a 193 amino acid residue precursor protein that is processed to yield a 165 amino acid residue mature protein. EPO contains one O-linked and three N-linked glycosylation sites. Glycosylation of EPO is required for EPO biological activities in vivo. EPO exhibits structural as well as amino sequence identity to the amino terminal 153 amino acid region of thrombopoietin.
-
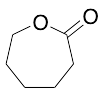
Epsilon-Caprolactone
$225.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H10O2
-
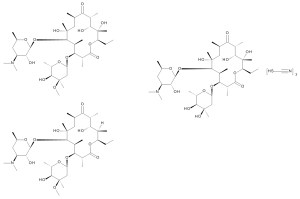
Erythromycin Thiocyanate
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C37H67NO13 • CHNS
-
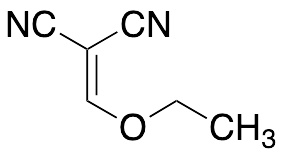
Ethoxymethylene Malononitrile
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H6 N2 O
-

Ethoxyoxalyl Chloride
$65.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H5ClO3
-
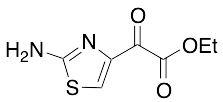
Ethyl 2-(2-Aminothiazol-4-yl)glyoxylate
$199.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H8N2O3S
-

Ethyl 2-Mercaptoacetate
$232.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H8O2S
-
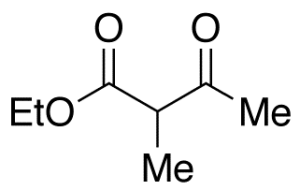
Ethyl 2-Methylacetoacetate
$97.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H12O3
-
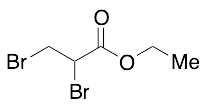
Ethyl 2,3-Dibromopropanoate
$65.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H8Br2O2
-
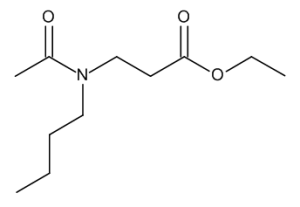
Ethyl 3-(N-Butylacetamido)propanoate
$175.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H21 N O3
-

Ethyl 3-Aminobenzoate Methanesulfonate
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H11 N O2 . C H4 O3 S
-
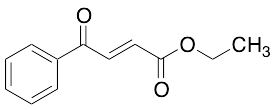
Ethyl 3-Benzoylacrylate
$109.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H12O3
-
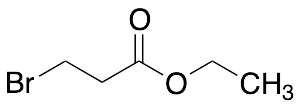
Ethyl 3-Bromopropionate
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H9BrO2
-

Ethyl 3-cyclopropyl-3-oxopropanoate
$77.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H12O3
-
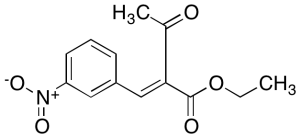
Ethyl 3-Nitrobenzylideneacetoacetate
$217.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H13NO5
-
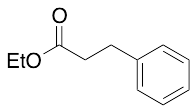
Ethyl 3-Phenylpropionate
$124.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H14 O2
-

Ethyl 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoate
$138.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H10O4
-
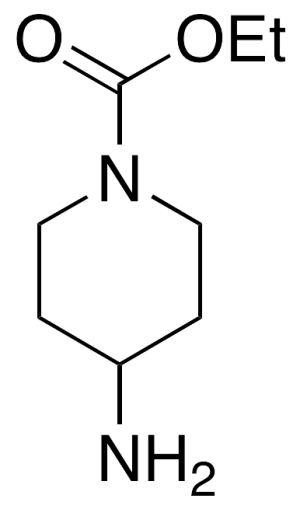
Ethyl 4-Aminopiperidine-1-carboxylate
$174.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H16N2O2
-
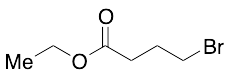
Ethyl 4-Bromobutanoate
$60.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H11BrO2
-
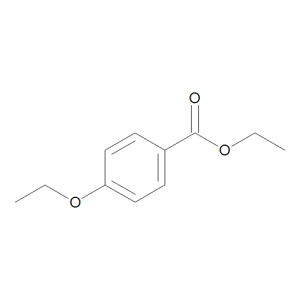
Ethyl 4-Ethoxybenzoate
$170.78 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H14 O3
-
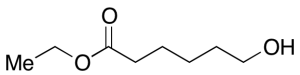
Ethyl 6-Hydroxyhexanoate
$232.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H16O3
-

Ethyl Acetoacetate
$131.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H10O3
-
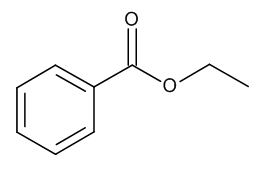
Ethyl Benzoate
$217.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H10 O2
-
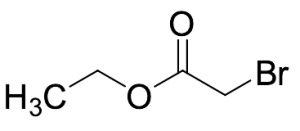
Ethyl Bromoacetate
$69.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H7BrO2
-
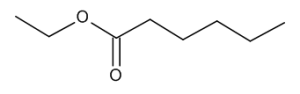
Ethyl Caproate
$217.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H16 O2
-

Ethyl Carbazate
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H8N2O2
-
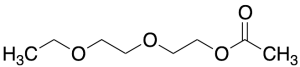
Ethyl Carbitol Acetate
$87.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H16 O4
-

Ethyl Chrysanthemate
$232.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H20O2
-
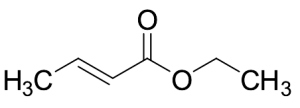
Ethyl Crotonate
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H10O2
-

Ethyl Cyano(hydroxyimino)acetate
$122.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H6N2O3
-
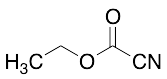
Ethyl Cyanoformate
$253.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H5 N O2
-
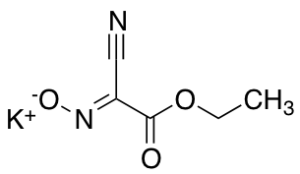
Ethyl Cyanoglyxylate-2-oxyme Potassium Salt
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H6N2O3K
-
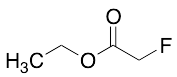
Ethyl fluoroacetate
$189.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H7FO2
-
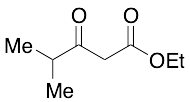
Ethyl Isobutyrylacetate
$169.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H14O3
-

Ethyl Isodehydroacetate
$375.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H12O4
-
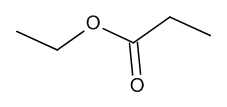
Ethyl Propionate(Propionic Acid Ethyl Ester)
$276.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H10 O2
-
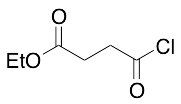
Ethyl Succinoyl Chloride
$109.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H9ClO3






