50g
Showing 1101–1150 of 1859 results
-

GenCRISPR™ Cas12a (Cpf1) Nuclease
$97.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe
clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats, known as CRISPR systems are adaptive immune mechanisms commonly
present in archaea and bacteria. The CRISPR systems enable the host to specifically
target and cleave foreign nucleic acids thus targeting infectiousviruses and
plasmids. Recently, a type V CRISPR system has been identified in several
bacteria, the Cpf1 CRISPR from Prevotella and Francisella 1. In contrast to
Cas9 systems, CRISPR/Cpf1 systems are smaller in size, do not require an
additional trans-activating crRNA (tracrRNA), and allow for targeting of
additional genomic regions by cleaveing the target DNA proceeded by a short
T-rich protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM). On the other hand, the Cas9 system requires
a G-rich PAM following the target DNA. Furthermore, Cas12a/Cpf1 introduces a
staggered DNA double stranded break with a 4 or 5-nt 5’ overhang. Recombinant
Acidaminococcus sp. BV3L6 Cas12a (cpf1) nuclease is expressed in E. coli and
purified. The nuclease contains nuclear localization sequence (NLS) at the
C-terminus and 6× His-tag at the C-terminus. -

Gentian Violet (~90%)
$95.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H30 N3 . Cl
-
GH, Human
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsGrowth Hormone (GH) is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin family which play an important role in growth control. The human GH cDNA encodes a 217 amino acid (aa), and the first 26 aa is a signal peptide. By alternative splicing, at least four isoforms of GH have been identified. The major role of GH in stimulating body growth is to stimulate the liver and other tissues to secrete IGF-1. GH stimulates both the differentiation and proliferation of myoblasts, and also stimulates amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in muscle and other tissues.
-

GH, Human(CHO-expressed)
$314.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsGrowth Hormone (GH) is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin family which play an important role in growth control. The human GH cDNA encodes a 217 amino acid (aa), and the first 26 aa is a signal peptide. By alternative splicing, at least four isoforms of GH have been identified. The major role of GH in stimulating body growth is to stimulate the liver and other tissues to secrete IGF-1. GH stimulates both the differentiation and proliferation of myoblasts, and also stimulates amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in muscle and other tissues.
-

GH, Mouse
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsGrowth Hormone (GH), is a member of the somatotropin / prolactin family of hormones which play an important role in growth control. The gene, along with four other related genes, is located at the growth hormone locus on chromosome 17 where they are interspersed in the same transcriptional orientation; an arrangement which is thought to have evolved by a series of gene duplications. The five genes share a remarkably high degree of sequence identity. Alternative splicing generates additional isoforms of each of the five growth hormones, leading to further diversity and potential for specialization. This particular family member is expressed in the pituitary but not in placental tissue as is the case for the other four genes in the growth hormone locus. Mutations in or deletions of the gene lead to growth hormone deficiency and short stature.
-
Girard’s Reagent T
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H14ClN3O
-
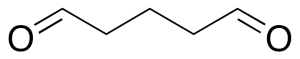
Glutaraldehyde (50% in water)
$530.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H8 O2
-
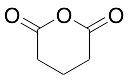
Glutaric Anhydride
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H6O3
-
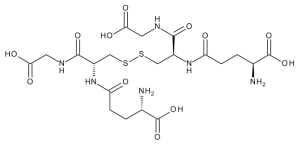
Glutathione Disulfide
$445.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H32 N6 O12 S2
-

Glycochenodeoxycholic Acid Sodium Salt
$5,275.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsGlycochenodeoxycholic Acid Sodium Salt
-
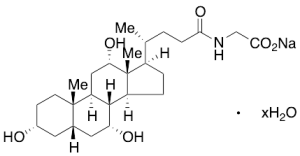
Glycocholic Acid Hydrate Sodium Salt
$2,449.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H42 N O6 . Na . H2 O
-
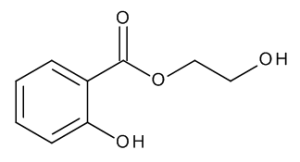
Glycol Salicylate
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H10 O4
-
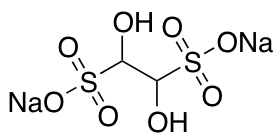
Glyoxal Sodium Bisulfite (contains oligomers)
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H4Na2O8S2
-

GM-CSF, Human
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can induce human endothelial cells to migrate and proliferate. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-
GM-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can induce human endothelial cells to migrate and proliferate. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

GM-CSF, Mouse
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

GM-CSF, Mouse
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

GM-CSF, Rat
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

Griseofulvin
$301.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H17 Cl O6
-
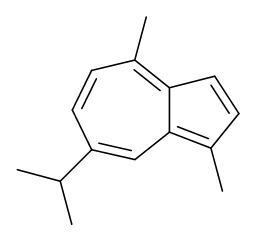
Guaiazulene
$667.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H18
-

HB-EGF, Human
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsProheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF), also known as DTR, DTS and HEGFL, is a member of the EGF family of mitogens. It is expressed in macrophages, monocytes, endothelial cells and muscle cells. HB-EGF signals through the EGF receptor to stimulate the proliferation of smooth muscle cells, epithelial cells and keratinocytes. Compared to EGF, HB-EGF binds to the EGF receptor with a higher affinity and has been shown to bemore mitogenic, likely due to its ability to bind to heparin and heparin sulfate proteoglycans. HB-EGF has also been reported to act as a diphtheria toxin receptor, mediating endocytosis of the bound toxin. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor has been shown to interact with NRD1, Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 and BAG1.
-

HB-EGF, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsProheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF), also known as DTR, DTS and HEGFL, is a member of the EGF family of mitogens. It is expressed in macrophages, monocytes, endothelial cells and muscle cells. HB-EGF signals through the EGF receptor to stimulate the proliferation of smooth muscle cells, epithelial cells and keratinocytes. Compared to EGF, HB-EGF binds to the EGF receptor with a higher affinity and has been shown to bemore mitogenic, likely due to its ability to bind to heparin and heparin sulfate proteoglycans. HB-EGF has also been reported to act as a diphtheria toxin receptor, mediating endocytosis of the bound toxin. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor has been shown to interact with NRD1, Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 and BAG1.
-

HB-EGF, Mouse
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsHeparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) is a member of the EGF family of proteins. HB-EGF-like growth factor is synthesized as a membrane-anchored mitogenic and chemotactic glycoprotein. An epidermal growth factor produced by monocytes and macrophages, due to an affinity for heparin is termed HB-EGF. It has been shown to play a role in wound healing, cardiac hypertrophy and heart development and function. The transmembrane form of HB-EGF is the unique receptor for diptheria toxin and functions in juxtacrine signaling in cells. Both forms of HB-EGF participate in normal physiological processes and in pathological processes including tumor progression and metastasis, organ hyperplasia, and atherosclerotic disease. HB-EGF can bind two locations on cell surfaces, heparan sulfate proteoglycans and EGF-receptor effecting cell to cell interactions.
-
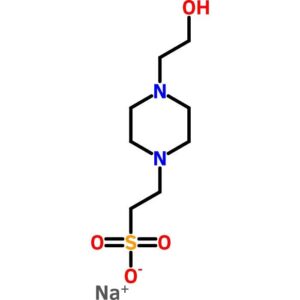
HEPES Sodium Salt
$57.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsHEPES Sodium Salt
-

Heregulin β-1, Human
$107.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsNeuregulins or neuroregulins are a family of four structurally related proteins (NRG1, NRG2, NRG3 and NRG4) that are members of the EGF family of proteins. Studies indicate neuregulins function in nervous system development with essential roles in vertebrate embryogenesis including: cardiac development, Schwann cell and oligodendrocyte differentiation, certain aspects of neuronal development, and the formation of neuromuscular synapses. Neuregulin 1 is essential for the normal development of the nervous system and the heart. It is produced in numerous isoforms by alternative splicing, allowing it to perform a variety of functions. All NRG1 isoforms contain an EGF-like domain that is required for direct binding to ErbB3 or ErbB4 receptor tyrosine kinases. The transmembrane NRG1 isoforms contain an extracellular domain that can be proteolytically cleaved to release soluble growth factors.
-
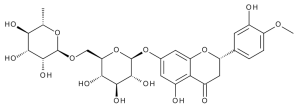
Hesperidine
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28 H34 O15
-
Hetastarch, Technical Grade
$150.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-
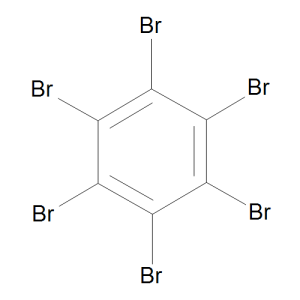
Hexabromobenzene
$93.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 Br6
-

Hexadecyltrimethylammonium Bromide
$93.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H42 N . Br
-

Hexadimethrine Bromide
$663.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsHexadimethrine Bromide
-
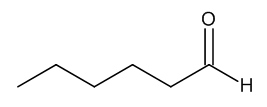
Hexanal
$145.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H12 O
-
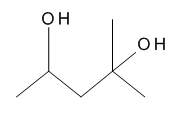
Hexylene Glycol
$81.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H14 O2
-

HGF, Human
$314.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsHepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF),also known as hepatopoietin-A and scatter factor, is a pleiotropic mitogen belonging to the peptidase S1 family (plasminogen subfamily). It is produced by mesenchymal cells and acts on epithelial cells, endothelial cells and haemopoietic progenitor cells. HGF binds to the proto-oncogenic c-Met receptor to activate a tyrosine kinase signaling cascade. It regulates cell growth, motility and morphogenesis, thus it plays a pivotal role in angiogenesis, tumorogenesis and tissue regeneration.
-

HMGB1, His, Human
$146.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1), previously known as HMG-1 or amphoterin, is a member of the high mobility group box family of non-histone chromosomal proteins. Human HMGB1 is expressed as a 30 kDa, 215 amino acid (aa) single chain polypeptide containing three domains: two N-terminal globular, 70 aa positively charged DNA-binding domains (HMG boxes A and B), and a negatively charged 30 aa C-terminal region that contains only Asp and Glu.4, 5 Residues 27 – 43 and 178 – 184 contain a NLS. Posttranslational modifications of the molecule have been reported, with acetylation occurring on as many as 17 lysine residues. HMGB1 is expressed at high levels in almost all cells. It was originally discovered as a nuclear protein that could bend DNA. Such bending stabilizes nucleosome formation and regulates the expression of select genes upon recruitment by DNA binding proteins.
-
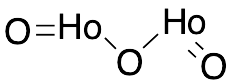
Holmium(III) Oxide
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Ho2O3
-

Homoveratrylamine
$156.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H15 N O2
-
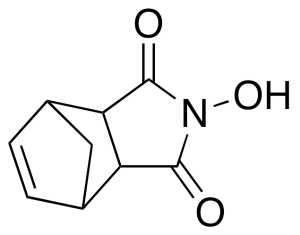
HONB
$97.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H9NO3
-

HRG1-β1, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsHeregulin1-Beta1(HRG1-Beta1) is one of the isoforms encoded by Neuregulin (NRG) genes. NRGs are synthesized as large transmembrane precursor proteins, and the NRG family has 4 members and 26 isoforms. These isoforms provide large diversities, including different tissue distribution, variable potencies, and different biological functions. HRG1-β1 belongs to Type I HRG1, and is expressed in neural tissue, respiratory epithelia, and heart. In vivo, HRG1 binds and activates both ErbB3 and ErbB4, the transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase, and is involved in the proliferation, differentiation, and survival of cells. Aberrantly produced HRG1 could be used in the constitute activation of the ErbB receptors; therefore, the upregulation of HRG1 contributes to the development of tumors, including breast cancer.
-

HVEM-Fc, Human
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsHerpes Virus Entry Mediator (HVEM) is a transmembrane protein that is the receptor for TNFSF14 (also known as LIGHT) and is therefore referred to asTNFRSF14. HVEM is expressed broadly on immune cells such as T cells, natural killer (NK) cells and monocytes. The interaction of 3 molecules of LIGHT with three molecules of HVEM forms a hexameric complex that leads to the recruitment and retention of effector cells and activates NK cells to produce large amounts of IFN-γ and GM-CSF. In addition to the canonical binding partner LIGHT, HVEM can also bind to the inhibitory signaling protein, B- and T- lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), which suppresses immune responses. Therefore, the HVEM network plays an important role in regulating immunity and the behavior of lymphocytes.
-
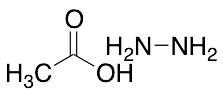
Hydrazine Acetate
$346.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H8N2O2
-
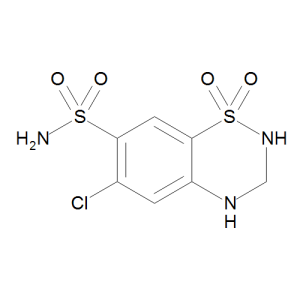
Hydrochlorothiazide
$213.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H8 Cl N3 O4 S2
-
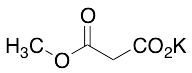
Hydrogen Methyl Malonate Potassium Salt
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H5 O4 . K
-
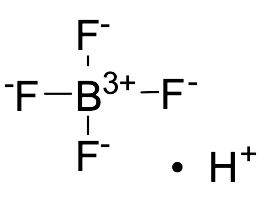
Hydrogen Tetrafluoroborate(1-) (48% solution in H2O)
$142.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : BF4 . H
-

Hydrotalcite, synthetic
$99.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CO3 . 6Mg . 4HO . 4H2O . 2AlH6O6
-

Hydroxy Naphthol Blue
$405.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydroxy Naphthol Blue
-
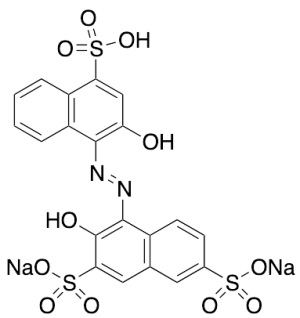
Hydroxy Naphthol Blue Disodium Salt (Technical Grade)
$324.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H12 N2 O11 S3 . 2Na
-

Hydroxylamine Sulfate
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : H8N2O6S
-
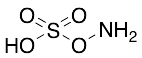
Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic Acid
$119.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : H3NO4S
-

Hydroxyurea, USP
$1,066.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydroxyurea, USP
-

Ibuprofen Sodium Salt Dihydrate
$148.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H17 O2 . 2 H2 O . Na






