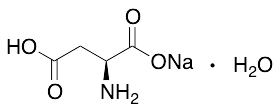
50g
Showing 1251–1300 of 1859 results
-

Isovaleric Acid Methyl Ester
$70.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H12 O2
-

Jasplakinolide
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C36H45BrN4O6
-

Kanamycin Sulfate
$304.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsKanamycin Sulfate
-

Ketamine Hydrochloride
$1,429.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H16 Cl N O . Cl H
-

KGF/FGF-7, Human
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsKeratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF) is a highly specific epithelial mitogen produced by fibroblasts and mesenchymal stem cells. KGF belongs to the heparin binding Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) family, and is known as FGF-7. However, in contrast to the FGF-1, which binds to all known FGF receptors with high affinity, KGF only binds to a splice variant of an FGF receptor, FGFR2-IIIb. FGFR2-IIIb is produced by most of the epithelial cells, indicating that KGF plays roles as a paracrine mediator. KGF induces the differen-tiation and proliferation of various epithelial cells, including keratinocytes in the epidermis, hair follicles and sebaceous glands, and is responsible for the wound repairs of various tissues, including lung, bladder, and kidney.
-

KGF/FGF-7, Mouse
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsKeratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF) is a highly specific epithelial mitogen produced by fibroblasts and mesenchymal stem cells. KGF belongs to the heparin binding Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) family, and is known as FGF-7. However, in contrast to FGF-1, which binds to all known FGF receptors with high affinity, KGF only binds to a splice variant of the FGF receptor, FGFR2-IIIb. FGFR2-IIIb is expressedby most epithelial cells, indicating KGF’s roleas a paracrine mediator. KGF induces the differentiation and proliferation of various epithelial cells such as keratinocytes in the epidermis, hair follicles and sebaceous glands., KGF is also responsible for wound repair of various tissuesincluding lung, bladder, and kidney.
-

KLK7, His, Mouse
$189.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsKallikrein-related peptidase 7 (KLK7) is a serine protease and was initially purified from the epidermis and characterised as stratum corneum chymotryptic enzyme (SCCE). It was later identified as the seventh member of the human kallikrein family. KLK7 is secreted as an inactive zymogen in the stratum granulosum layer of the epidermis and may be activated by KLK5 or matriptase. Once active, KLK7 is able to cleave desmocollin and corneodesmosin, indicating a role for KLK7 in maintaining skin homeostasis.
-

KRAS, His, Human (G12C)
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe KRAS gene provides instructions for making a protein called K-Ras, part of the RAS/MAPK pathway. The protein relays signals from outside the cell to the cell’s nucleus. These signals instruct the cell to grow and divide (proliferate) or to mature and take on specialized functions (differentiate). The K-Ras protein is a GTPase, which means it converts a molecule called GTP into another molecule called GDP. In this way the K-Ras protein acts like a switch that is turned on and off by the GTP and GDP molecules. KRAS is usually tethered to cell membranes because of the presence of an isoprene group on its C-terminus. There are two protein products of the KRAS gene in mammalian cells that result from the use of alternative exon 4 (exon 4A and 4B respectively): K-Ras4A and K-Ras4B, these proteins have different structure in their C-terminal region and use different mechanisms to localize to cellular membranes including the plasma membrane.
-

KRAS, His, Human (G12D)
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe KRAS gene provides instructions for making a protein called K-Ras, part of the RAS/MAPK pathway. The protein relays signals from outside the cell to the cell’s nucleus. These signals instruct the cell to grow and divide (proliferate) or to mature and take on specialized functions (differentiate). The K-Ras protein is a GTPase, which means it converts a molecule called GTP into another molecule called GDP. In this way the K-Ras protein acts like a switch that is turned on and off by the GTP and GDP molecules. KRAS is usually tethered to cell membranes because of the presence of an isoprene group on its C-terminus. There are two protein products of the KRAS gene in mammalian cells that result from the use of alternative exon 4 (exon 4A and 4B respectively): K-Ras4A and K-Ras4B, these proteins have different structure in their C-terminal region and use different mechanisms to localize to cellular membranes including the plasma membrane.
-

L-Alanine Benzyl Ester Hydrochloride
$119.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H14ClNO2
-

L-Arabinose
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H10 O5
-

L-Arginine Hydrochloride
$95.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H14 N4 O2 . Cl H
-

L-Asparagine Monohydrate
$258.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H8 N2 O3 . H2 O
-

L-Aspartic Acid Sodium Salt Monohydrate
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H6NO4Na . H2O
-

L-Cysteic Acid Monohydrate
$501.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H7 N O5 S . H2 O
-

L-Cysteine Ethyl Ester Hydrochloride
$212.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H11NO2S.HCl
-

L-Glutamic Acid 5-Methyl Ester
$242.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H11 N O4
-

L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hydrochloride
$195.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H13 N O4 . Cl H
-

L-Histidine
$83.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H9 N3 O2
-

L-Histidine Methyl Ester Dihydrochloride
$119.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H11N3O2 . 2(HCl)
-

L-Homoserine Lactone, Hydrochloride
$507.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H7 N O2 . Cl H
-

L-Isoleucine
$131.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H13 N O2
-

L-Leucine
$48.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsL-Leucine
-

L-Phenylalanine
$113.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H11 N O2
-

L-Phenylglycine Amide
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H10 N2 O
-

L-Rhamnose Diethyl Dithioacetal
$402.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H22 O4 S2
-
L-Rhamnose Monohydrate
$306.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H12 O5 . H2 O
-

L-Sorbose
$131.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H12 O6
-

L-tert-Leucine
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H13NO2
-

L-Threonine
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H9 N O3
-

L-Valine Methyl Ester Hydrochloride
$217.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H13 N O2 . Cl H
-

L-Xylo-2-Hexulosonic Acid Hydrate
$126.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H10 O7 . H2 O
-

Lanolin (Technical Grade)
$61.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H68O2
-

Lanthanum Oxide, Powder
$277.17 Add to cart View Product DetailsLanthanum Oxide, Powder
-
Lawesson’s Reagent
$336.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H14 O2 P2 S4
-

Lead Acetate Basic
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H8O6Pb2
-

Levulinic Acid
$81.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H8 O3
-

LIF, Human
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-

LIF, Mouse
$314.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-

LIGHT, Human
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsLIGHT, also known as tumor-necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily member 14 (TNFSF14), is predominantly expressed on activated immune cells and some tumor cells. LIGHT (homologous to lymphotoxin, exhibits inducible expression and competes with Herpes Simplex Virus glycoprotein D for Herpes Virus Entry Mediator, a receptor expressed by T cells), is a protein primarily expressed on activated T cells, activated Natural Killer (NK) cells, and immature dendritic cells (DC). LIGHT can function as both a soluble and cell surface-bound type II membrane protein and must be in its homotrimeric form to interact with its two primary functional receptors: Herpes Virus Entry Mediator (HVEM) and Lymphotoxin-β Receptor (LTβR). LIGHT signaling through these receptors have distinct functions that are cell-type dependent, but interactions with both types of receptors have immune-related implications in tumor biology.
-

Lindane
$401.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H6 Cl6
-

Lithium Dodecyl Sulfate
$266.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsLithium Dodecyl Sulfate
-

Lithium Hydroxide
$81.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : HLiO
-

Lithium sulfate, anhydrous
$87.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Li2SO4
-

Lithium Tetrafluoroborate
$189.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : BF4Li
-

LIX/CXCL5 (74aa), Mouse
$150.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMouse LIX (C-X-C motif chemokine 5) is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family that is cleaved into the following 2 chains [GCP-2(1-78) and GCP-2(9-78)]. Mouse LIX plays a role in reducing sensitivity to sunburn pain in some subjects, and is a potential target which could be used to understand more about pain in other inflammatory conditions. It is most closely related to two highly homologous human neutrophil chemoattractants GCP-2 and ENA-78. The first 78 amino acid residues within the predicted mature mouse LIX shares approximately 61% and 55% amino acid identity with human GCP-2 and ENA-78. This chemokine stimulates the chemotaxis of neutrophils possessing angiogenic properties. It elicits these effects by interacting with the cell surface chemokine receptor CXCR2.
-

Luminol
$233.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H7 N3 O2
-

M-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Mouse
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Mouse
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.