50g
Showing 1451–1500 of 1859 results
-
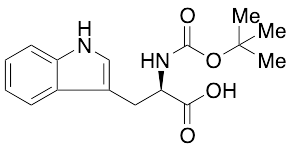
Na-Boc-D-tryptophan
$434.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H20N2O4
-
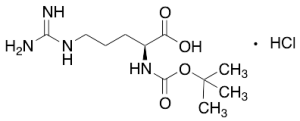
NAlpha-Boc-L-arginine Hydrochloride
$324.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11H22N4O4 . HCl
-
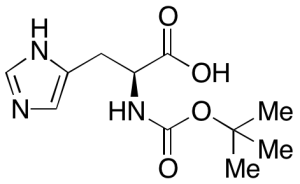
NAlpha-Boc-L-histidine
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11H17N3O4
-

Naphthalene
$150.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H8
-
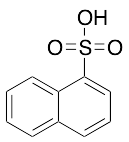
Naphthalene-1-sulfonic Acid (Technical Grade)
$467.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H8O3S
-
Nectin-2/CD112 Fc Chimera, Human
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsNectin-2, also known as CD112 (Cluster of Differentiation 226) and PVRL2 (Poliovirus receptor-related 2), is a human plasma membrane glycoprotein. This protein is a modulator of T-cell signaling and can be either a costimulator of T-cell function or a coinhibitor, depending on the receptor it binds to. Upon binding to CD226, it stimulates T-cell proliferation and cytokine production, including that of IL-2, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13, and IFNγ. It can also inhibit T-cell proliferation upon interaction with PVRIG. Nectin-2 also acts as a receptor for herpes simplex virus 1 (HHV-1) mutant Rid1, herpes simplex virus 1 (HHV-2) and pseudorabies virus (PRV).
-
Nerol
$246.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H18 O
-
Neutral Red (Technical Grade)
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15H16N4 .HCl
-

NGF R, Human
$133.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsNGF Receptor, also known as Gp80-LNGFR, p75 ICD, CD271 and TNFRSF16, is a type I transmembrane protein belonging to the TNF receptor family. It is expressed by both neuronal and non-neuronal cells. Signaling through NGF Receptor has been shown to regulate gene expression, cell migration and death. A truncated NGF Receptor containing only the extracellular domain has been detected in plasma, amniotic fluid and urine, and acts as a potent NGF antagonist.
-

Nitrobenzene
$272.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H5 N O2
-

Noggin Fc Chimera, Human
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsNoggin, also known as NOG, is a homodimeric glycoprotein that bindsto and modulates the activity of TGF-beta family ligands. It is expressed in condensing cartilage and immature chondrocytes. Noggin antagonizes bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) activities by blocking epitopes on BMPs needed for binding to their receptors. Noggin has been shown to be involved in many developmental processes, such as neural tube formation and joint formation. During development, Noggin diffuses through extracellular matrices and forms morphogenic gradients, regulating cellular responses dependent on the local concentration of the signaling molecule.
-

Noggin, Human(CHO-expressed)
$193.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsNoggin, also known as NOG, is a homodimeric glycoprotein that bindsto and modulates the activity of TGF-beta family ligands. It is expressed in condensing cartilage and immature chondrocytes. Noggin antagonizes bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) activities by blocking epitopes on BMPs needed for binding to their receptors. Noggin has been shown to be involved in many developmental processes, such as neural tube formation and joint formation. During development, Noggin diffuses through extracellular matrices and forms morphogenic gradients, regulating cellular responses dependent on the local concentration of the signaling molecule.
-

Nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonyl Fluoride
$258.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 F10 O2 S
-

Nonanal
$116.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H18 O
-

NPG Glycol
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H12 O2
-

NRG-1β2, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsNeuregulin is a signaling protein for ErbB2/ErbB4 receptor heterodimers on the cardiac muscle cells, playing an important role in heart structure and function through inducing ErbB2/ErbB4 receptor phosphorylation and cardiomyocyte differentiation. Research on molecular level discovered that recombinant neuregulin could make disturbed myocardial cell structure into order and strengthen the connection between myocardial cells by intercalated discs re-organization.
-

NT-4, Mouse
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsNeurotrophin-4 (NT-4), also known as NT-5, is a neurotrophic factor structurally related to β-NGF, BDNF, and NT-3. Human NT-4 shares 48 – 52% aa sequence identity with human β-NGF, BDNF, and NT-3. Neurotrophins have six conserved cysteine residues that are involved in the formation of three disulfide bonds. NT-4 is expressed highest levels in prostate, lower levels in thymus, placenta, and skeletal muscle. NT-4 binds and induces receptor dimerization and activation of TrkB. NT-4 can signal through TrkB receptors and promotes the survival of peripheral sensory sympathetic neurons.
-

o-Aminoazotoluene
$180.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H15 N3
-
o-Chloromethyltoluene
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H9 Cl
-

o-Cresol
$61.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H8 O
-

o-Iodochlorobenzene
$71.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H4ClI
-

o-Isopropylaniline
$149.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H13N
-
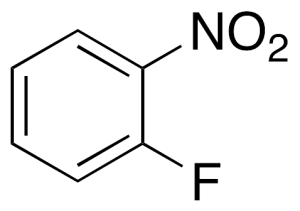
o-Nitrofluorobenzene
$199.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H4FNO2
-

o-tert-Butyl-p-cresol
$263.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H16 O
-
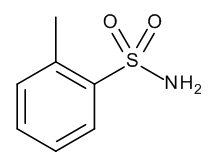
o-Toluenesulfonamide
$505.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H9 N O2 S
-

O-Toluoyl Chloride
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H7ClO
-

o-Tolyl Cyanide
$264.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H7 N
-

O,O-Dimethyl Methylphosphonate
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H9 O3 P
-
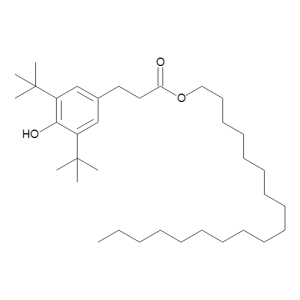
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-Di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate
$107.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 H62 O3
-
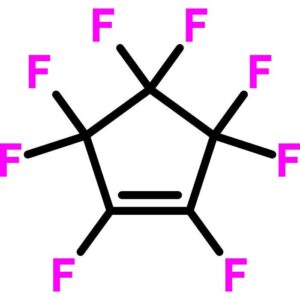
Octafluorocyclopentene
$956.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsOctafluorocyclopentene
-
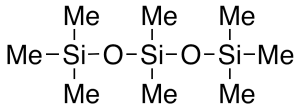
Octamethyltrisiloxane
$1,528.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H24 O2 Si3
-
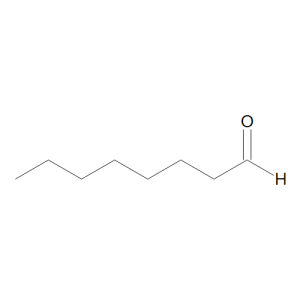
Octanal
$181.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H16 O
-
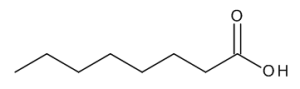
Octanoic Acid
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H16 O2
-
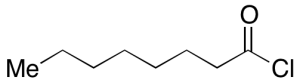
Octanoyl Chloride
$114.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H15ClO
-
Octylamine
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H19 N
-

Orotic Acid, Anhydrous
$171.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsOrotic Acid, Anhydrous
-

OSM (209aa), Human
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsOncostatin M (OSM) is a multifunctional cytokine, and belongs to Interleukin-6 (IL-6) subfamily, which also includes IL-11, leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), ciliary neurotropic factor, cardiotrophin-1, and novel neurotropin-1. In vivo, OSM is secreted from activated T cells, monocytes, neutrophils, and endothelial cells. OSM is related to LIF, and shares a receptor with LIF in human. Human OSM can bind to gp130 and recruit OSM Receptor β or LIF Receptor β to form a ternary complex. OSM stimulates the growth of different types of cells, including megakaryocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells, and T cells. OSM inhibits the proliferation of several cancer cell lines, such as solid tissue tumor cells, lung cancer cells, melanoma cells, and breast cancer cells.
-

OSM (227aa), Human
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsOncostatin M (OSM) is a multifunctional cytokine, and belongs to Interleukin-6 (IL-6) subfamily, including IL-11, leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), ciliary neurotropic factor, cardiotrophin-1, and novel neurotropin-1. In vivo, OSM is secreted from activated T cells, monocytes, neutrophils, and endothelial cells. OSM is related to LIF, and share a receptor with LIF in human. Human OSM can bind to gp130 and recruit OSM Receptor β or LIF Receptor β to form a ternary complex. OSM stimulates the growth of different types of cells, including megakaryocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells, and T cells. On the other hand, OSM inhibits the proliferation of several cancer cell lines, such as solid tissue tumor cells, lung cancer cells, melanoma cells, and breast cancer cells.
-

OSM, Mouse
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsOncostatin M (OSM) is a multifunctional cytokine, and belongs to Interleukin-6 (IL-6) subfamily, which also includes IL-11, leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), ciliary neurotropic factor, cardiotrophin-1, and novel neurotropin-1. In vivo, OSM is secreted from activated T cells, monocytes, neutrophils, and endothelial cells. OSM is related to LIF, and shares a receptor with LIF in human. Human OSM can bind to gp130 and recruit OSM Receptor β or LIF Receptor β to form a ternary complex. OSM stimulates the growth of different types of cells, including megakaryocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells, and T cells. OSM inhibits the proliferation of several cancer cell lines, such as solid tissue tumor cells, lung cancer cells, melanoma cells, and breast cancer cells.
-

OSM, Mouse(HEK 293-expressed)
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsOncostatin M (OSM) is a multifunctional cytokine, and belongs to Interleukin-6 (IL-6) subfamily, which also includes IL-11, leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), ciliary neurotropic factor, cardiotrophin-1, and novel neurotropin-1. In vivo, OSM is secreted from activated T cells, monocytes, neutrophils, and endothelial cells. OSM is related to LIF, and shares a receptor with LIF in human. Human OSM can bind to gp130 and recruit OSM Receptor β or LIF Receptor β to form a ternary complex. OSM stimulates the growth of different types of cells, including megakaryocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells, and T cells. OSM inhibits the proliferation of several cancer cell lines, such as solid tissue tumor cells, lung cancer cells, melanoma cells, and breast cancer cells.
-

Oxalyl Chloride
$55.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2Cl2O2
-
Oxindole (2-Indolone)
$288.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H7 N O
-
p-Anisidine
$206.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H9 N O
-

p-Benzoquinone
$169.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H4 O2
-
p-Coumaric acid
$106.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H8 O3
-
p-Cresol
$175.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H8 O
-

p-Ethylphenol
$136.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H10 O
-

p-Nitrophenyl 2-(Furfurylsulfinyl)acetate
$1,129.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H11NO6S
-
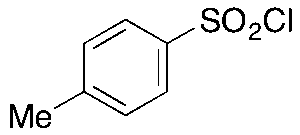
p-Toluenesulfonyl Chloride
$50.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H7ClO2S
-

p-Toluic Acid
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H8 O2






