50g
Showing 1501–1550 of 1859 results
-

p-Toluidine Hydrochloride
$77.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H9 N . H Cl
-
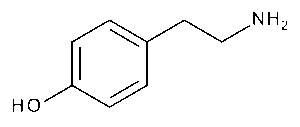
p-Tyramine
$81.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H11 N O
-
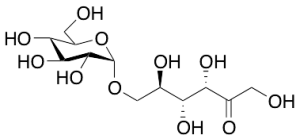
Palatinose
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H22 O11
-
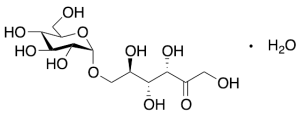
Palatinose Monohydrate
$1,258.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H22O11 . H2O
-
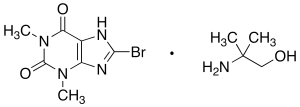
Pamabrom
$156.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H7 Br N4 O2 . C4 H11 N O
-
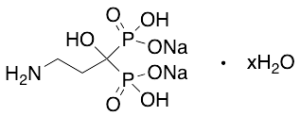
Pamidronic Acid Sodium Salt Hydrate
$346.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H9 N O7 P2 . 2 Na
-
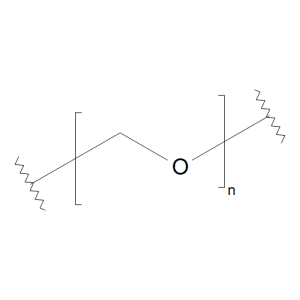
Paraformaldehyde
$106.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : (C H2 O)n
-
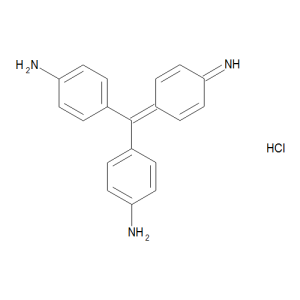
Pararosaniline Hydrochloride
$326.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H17 N3 . Cl H
-

PD-1 Fc Chimera, Human
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsProgrammed cell death protein 1, also known as PD-1 and CD279 (cluster of differentiation 279) or PDCD1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDCD1 gene. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor that belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and is expressed on T cells and pro-B cells.PD-1 binds two ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2. PD-1 and its ligands play an important role in down regulating the immune system by preventing the activation of T-cells, which in turn reduces autoimmunity and promotes self-tolerance. The inhibitory effect of PD-1 is accomplished through a dual mechanism of promoting apoptosis (programmed cell death) in antigen specific T-cells in lymph nodes while simultaneously reducing apoptosis in regulatory T cells (suppressor T cells)
-

PD-1 Fc Chimera, Mouse
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsProgrammed cell death protein 1, also known as PD-1 and CD279 (cluster of differentiation 279) or PDCD1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDCD1 gene. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor that belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and is expressed on T cells and pro-B cells.PD-1 binds two ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2. PD-1 and its ligands play an important role in down regulating the immune system by preventing the activation of T-cells, which in turn reduces autoimmunity and promotes self-tolerance. The inhibitory effect of PD-1 is accomplished through a dual mechanism of promoting apoptosis (programmed cell death) in antigen specific T-cells in lymph nodes while simultaneously reducing apoptosis in regulatory T cells (suppressor T cells).
-

PD-L1 Fc Chimera, Human
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsProgrammed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) also known as cluster of differentiation 274 (CD274) or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD274 gene. PD-L1 is a 40 kDa type 1 transmembrane protein that has been speculated to play a major role in suppressing the immune system during particular events such as pregnancy, tissue allografts, autoimmune disease and other disease states such as hepatitis. Normally the immune system reacts to foreign antigens where there is some accumulation in the lymph nodes or spleen which triggers a proliferation of antigen-specific CD8+ T cell. The formation of PD-1 receptor / PD-L1 or B7.1 receptor /PD-L1 ligand complex transmits an inhibitory signal which reduces the proliferation of these CD8+ T cells at the lymph nodes and supplementary to that PD-1 is also able to control the accumulation of foreign antigen specific T cells in the lymph nodes through apoptosis which is further mediated by a lower regulation of the gene Bcl-2. PD-L1 binds to its receptor, PD-1, found on activated T cells, B cells, and myeloid cells, to modulate activation or inhibition. Recombinant Human PD-L1(B7-H1) Fc Chimera produced in CHO cells is a polypeptide chain containing 457 amino acids. A fully biologically active molecule, rh PD‑L1(B7-H1) has a molecular mass of 70-72 kDa analyzed by reducing SDS-PAGE and is obtained by chromatographic techniques at GenScript.
-

PD-L1 Fc Chimera, Mouse
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsProgrammed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) also known as cluster of differentiation 274 (CD274) or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD274 gene. PD-L1 is a 40 kDa type 1 transmembrane protein that has been speculated to play a major role in suppressing the immune system during particular events such as pregnancy, tissue allografts, autoimmune disease and other disease states such as hepatitis. Normally the immune system reacts to foreign antigens where there is some accumulation in the lymph nodes or spleen which triggers a proliferation of antigen-specific CD8+ T cell. The formation of PD-1 receptor / PD-L1 or B7.1 receptor /PD-L1 ligand complex transmits an inhibitory signal which reduces the proliferation of these CD8+ T cells at the lymph nodes and supplementary to that PD-1 is also able to control the accumulation of foreign antigen specific T cells in the lymph nodes through apoptosis which is further mediated by a lower regulation of the gene Bcl-2. PD-L1 binds to its receptor, PD-1, found on activated T cells, B cells, and myeloid cells, to modulate activation or inhibition.
-
PDGF-AA, Mouse
$207.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-Derived Growth Factor-AA (PDGF-AA) is one of five dimers (PDGF-AA, AB, BB, CC, and DD) formed by 4 different PDGF subunits. In chemical terms, platelet-derived growth factor is a dimeric glycoprotein composed of two A (-AA) or two B (-BB) chains or a combination of the two (-AB). The dimeric isoforms PDGFAA, AB and BB are differentially expressed in various cell types, and their effects are mediated through two distinct receptors termed α and β. Differences exist in isoform binding to each receptor. Ingeneral, PDGF isoforms are potent mitogens for connective tissue cells including dermal fibroblasts, glial cells, arterial smooth muscle cells and some epithelial andendothelial cells. In addition to its activity as a mitogen, PDGF is chemotactic for fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, neutrophils and mononuclear cells. PDGF-AA plays a significant role in blood vessel formation (angiogenesis).
-

PDGF-BB, Human (P. pastoris-expressed)
$258.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB (PDGF-BB) is one of five dimers (PDGF-AA, AB, BB, CC, and DD) formed by 4 different PDGF subunits. In vivo, PDGF-BB is mainly produced in heart and placenta, and predominantly expressed by osteoblasts, fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and glial cells. An inactive precursor of PDGF-BB is produced in the endoplasmic reticulum and then activated by a proprotein convertase after secretion. PDGF-BB functions in a paracrine manner and promotes organogenesis, human skeletal development, and wound healing. PDGF-BB also promotes angiogenesis, particularly in the presence of Fibroblast Growth Factor basic. Therefore, PDGF-BB and its related pathways are potential pharmacological targets.
-

PDGF-BB, Mouse
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB (PDGF-BB) is one of five dimers (PDGF-AA, AB, BB, CC, and DD) formed by 4 different PDGF subunits. In vivo, PDGF-BB is mainly produced in heart and placenta, and predominantly expressed by osteoblasts, fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and glial cells. An inactive precursor of PDGF-BB is produced in the endoplasmic reticulum and then activated by a proprotein convertase after secretion. PDGF-BB functions in a paracrine manner and promotes organogenesis, human skeletal development, and wound healing. PDGF-BB also promotes angiogenesis, particularly in the presence of Fibroblast Growth Factor basic. Therefore, PDGF-BB and its related pathways are potential pharmacological targets.
-

PDGF-BB, Rat
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB (PDGF-BB) is one of five dimers (PDGF-AA, AB, BB, CC, and DD) formed by 4 different PDGF subunits. In vivo, PDGF-BB is mainly produced in heart and placenta, and predominantly expressed by osteoblasts, fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and glial cells. An inactive precursor of PDGF-BB is produced in the endoplasmic reticulum and then activated by a proprotein convertase after secretion. PDGF-BB functions in a paracrine manner and promotes organogenesis, human skeletal development, and wound healing. PDGF-BB also promotes angiogenesis, particularly in the presence of Fibroblast Growth Factor basic. Therefore, PDGF-BB and its related pathways are potential pharmacological targets.
-

PDGF-CC, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) is a potent mitogen for a wide range of cell types including fibroblasts, smooth muscle, connective tissue, bone and cartilage cells, and some blood cells. The PDGF is involved in a number of biological processes, including hyperplasia, chemotaxis, embryonic neuron development, and respiratory tubule epithelial cell development. The PDGF family consists of proteins derived from four genes (PDGF -A, -B, -C, and -D) that form four disulfide-linked homodimers (PDGF-AA, -BB, -CC, and -DD) and one heterodimer (PDGF-AB).
-

PDGF-DD, Human
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsPDGF-DD, also known as platelet-derived growth factor D, IEGF and SCDGFB, is asecreted growth factor belonging to the PDGF/VEGFfamily. It is highly expressed in the heart, pancreas, adrenal glands and ovary. PDGF-DD forms functional homodimers that bind and induce PDGF Rβ homodimers and PDGF Rα/β heterodimers that promote intracellular signaling. This plays an important role in the regulation of cell differentiation, migration and survival. It has also been reported that PDGF-DD can induce monocyte and macrophage recruitment, increase interstitial pressure and facilitate wound healing.
-
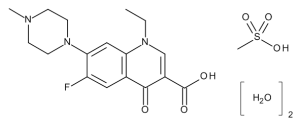
Pefloxacin Mesylate Dihydrate
$199.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H20 F N3 O3 . C H4 O3 S . 2 H2 O
-

Pentadecanoic Acid
$374.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H30 O2
-
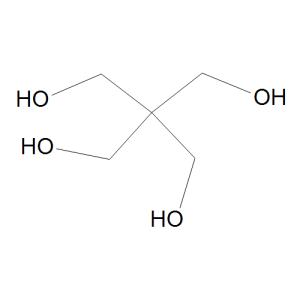
Pentaerythritol
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H12 O4
-

Pentaerythritol Tetraacrylate (~80%)
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H20O8
-

Pentaerythritol Tetrakis(3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate)
$106.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C73 H108 O12
-
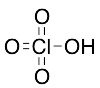
Perchloric Acid (60%)
$66.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Cl H O4
-

Perchloromethyl Mercaptan
$212.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C Cl4 S
-

Perfluorodecalin
$288.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10F18
-

Perfluorohexylethyl Iodide
$614.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H4 F13 I
-
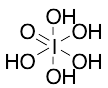
Periodic Acid
$152.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : H5IO6
-

PF-4/CXCL4, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsPlatelet factor 4, also known as CXCL4, is expressed in megakaryocytes and stored in the α-granules of platelets. Recombinant human PF-4 is a 7.8 kDa protein containing 70 amino acid residues, including the four highly conserved residues present in CXC chemokines. Platelet factor 4 can be antiproliferative and antiangiogenic, at least in part via interfering with FGF2 and VEGF heparin binding and thus inhibiting their signaling. However, it can also be proinflammatory and proatherogenic through multiple effects on monocytes, macrophages and endothelial cells.
-

Phenformin Hydrochloride
$102.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H15 N5 . Cl H
-
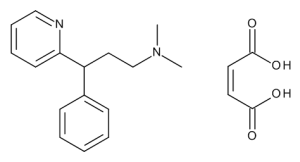
Pheniramine Maleate
$635.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H20 N2 . C4 H4 O4
-
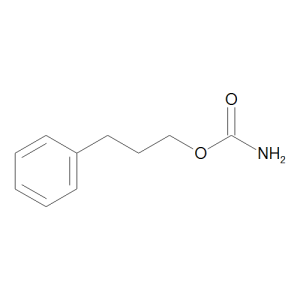
Phenprobamate
$109.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H13 N O2
-
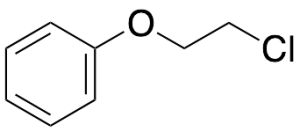
Phenyl 2-Chloroethyl Ether
$242.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H9 Cl O
-

Phenyl Acetate
$319.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H8 O2
-

Phenyl Benzoate
$114.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H10 O2
-
Phenyl Chloroformate
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H5ClO2
-
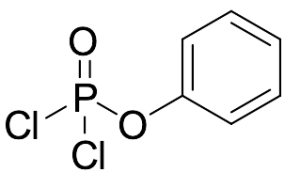
Phenyl Dichlorophosphate
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H5Cl2O2P
-
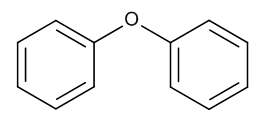
Phenyl Ether
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H10 O
-

Phenylhydrazine Hydrochloride (1:1)
$120.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H8 N2 . Cl H
-

Phenylmercuric Acetate
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H8 Hg O2
-

Phenylpiracetam Hydrazide Powder – 50G
$170.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsCAS Number 77472-71-0 Molecular Weight 233.27 Molecular Formula C12H15N3O2 -
Phloroglucinol
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H6 O3 . 2 H2 O
-

Phosphoric Acid
$250.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : H3 O4 P
-
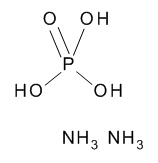
Phosphoric Acid Diammonium Salt
$174.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 H3 N . H3 O4 P
-
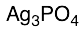
Phosphoric Acid Silver Salt
$217.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Ag3O4P
-

Phosphoric Acid Tripropyl Ester
$328.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H21 O4 P
-
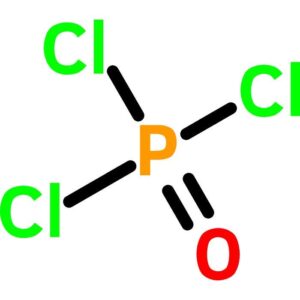
Phosphorus Oxychloride, High Purity
$2,630.02 Add to cart View Product DetailsPhosphorus Oxychloride, High Purity
-
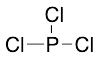
Phosphorus Trichloride
$65.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Cl3P
-
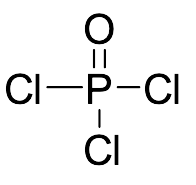
Phosphorus(V) Oxychloride
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Cl3OP
-
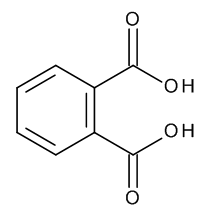
Phthalic Acid
$188.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H6 O4






