5g
Showing 5151–5200 of 7613 results
-
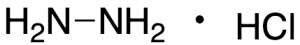
Hydrazine Hydrochloride
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : N2H4 . HCl
-

Hydrazine Sulfate Salt
$133.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : H2 O4 S . H4 N2
-

Hydrazine-1,2-dicarboxamide
$309.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H6N4O2
-
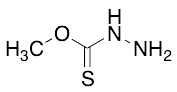
Hydrazinecarbothioic Acid O-methyl Ester
$396.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H6N2OS
-
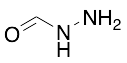
Hydrazinecarboxaldehyde
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CH4N2O
-

Hydrindantin Hydrate
$336.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydrindantin Hydrate
-
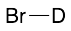
Hydrobromic Acid-d Solution (48 wt. % in D2O)
$87.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : DBr
-

Hydrocodone Bitartrate (CII), USP
$357.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydrocodone Bitartrate (CII), USP
-
Hydrocortisone 21-Acetate
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23 H32 O6
-

Hydrocortisone Acetate, Micronized, USP
$229.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydrocortisone Acetate, Micronized, USP
-

Hydrocortisone Hemisuccinate Hydrate
$554.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H34 O8 . H2 O
-

Hydrocortisone, Micronized, USP
$185.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydrocortisone, Micronized, USP
-
Hydrocoumarin
$118.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H8 O2
-

Hydrofluoric Acid
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-

Hydrogenated Soya Phosphatidylcholine
$116.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-

Hydromorphone Hydrochloride (CII), USP
$1,693.12 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydromorphone Hydrochloride (CII), USP
-
Hydroquinone
$61.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H6 O2
-

Hydroxocobalamin
$458.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydroxocobalamin
-

Hydroxocobalamin Acetate
$973.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydroxocobalamin Acetate
-

Hydroxocobalamin, USP
$1,998.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydroxocobalamin, USP
-
Hydroxy Naphthol Blue Disodium Salt (Technical Grade)
$60.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H12 N2 O11 S3 . 2Na
-

Hydroxy Naphthol Blue, Solid Dilution (This regent is deposited on crystals of sodium chloride), Reagent, ACS
$75.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydroxy Naphthol Blue, Solid Dilution (This regent is deposited on crystals of sodium chloride), Reagent, ACS
-

Hydroxy Tyrosol (>85%)
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H10 O3
-
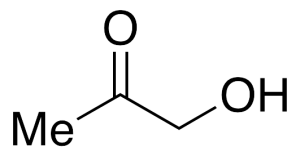
Hydroxyacetone
$69.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H6 O2
-
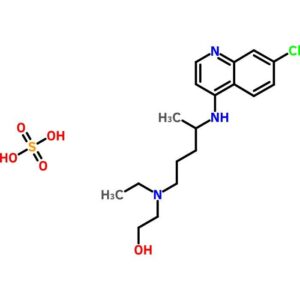
Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate
$83.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydroxychloroquine Sulfate
-
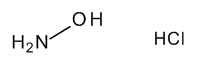
Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride
$58.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : ClH4NO
-
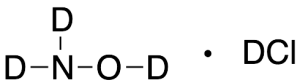
Hydroxylamine-d3 Hydrochloride-d
$1,027.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Cl D . D3 N O
-
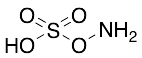
Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic Acid
$50.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : H3NO4S
-

Hydroxymethylferrocene
$374.72 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydroxymethylferrocene
-
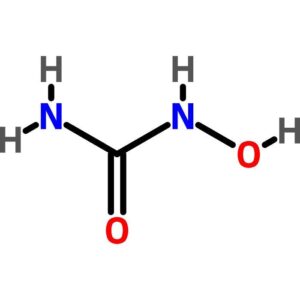
Hydroxyurea
$128.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsHydroxyurea
-
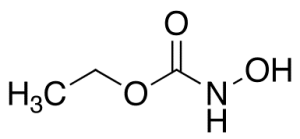
Hydroxyurethane
$313.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H7NO3
-
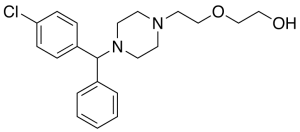
Hydroxyzine
$1,373.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H27 Cl N2 O2
-

Hygromycin B
$1,676.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H37 N3 O13
-

Hypoxanthine
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H4 N4 O
-

Hypoxanthine
$104.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsHypoxanthine
-
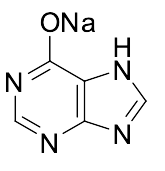
Hypoxanthine Monosodium Salt
$81.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H3N4NaO
-
Hypromellose Acetate Succinate
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-

Ibuprofen Sodium Salt Dihydrate
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H17 O2 . 2 H2 O . Na
-
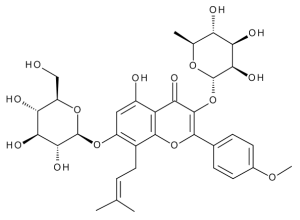
Icariin
$388.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C33 H40 O15
-

Idebenone
$131.27 Add to cart View Product DetailsIdebenone
-
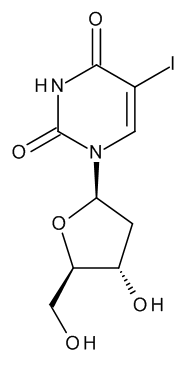
Idoxuridine
$221.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H11 I N2 O5
-

IFN-β, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-beta (IFN-β), acting via STAT1 and STAT2, is known to upregulate and downregulate a wide variety of genes, most of which are involved in the antiviral immune response. It is a member of Type I IFNs, which include IFN-α, -β, τ, and –ω. IFN-β plays an important role in inducing non-specific resistance against a broad range of viral infections. It also affects cell proliferation and modulates immune responses.
-

IL-11, Human(CHO-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-11 is a pleiotropic cytokine that was originally detected in the conditioned medium of an IL-1α-stimulated primate bone marrow stromal cell line (PU-34) as a mitogen for the IL-6-responsive mouse plasmacytoma cell line T11. IL-11 has multiple effects on both hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells. Many of the biological effects described for IL-11 overlap with those for IL-6. In vitro, IL-11 can synergize with IL-3, IL-4 and SCF to shorten the G0 period of early hematopoietic progenitors. IL-11 also enhances the IL-3-dependent megakaryocyte colony formation. IL-11 has been found to stimulate the T cell-dependent development of specific immunoglobulin-secreting B cells.
-

IL-12, Human(HEK 293-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin 12 (IL-12), also known as natural killer cell stimulatory factor (NKSF) or cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor (CLMF), is a pleiotropic cytokine originally identified in the medium of activated human B lymphoblastoid cell lines. The p40 subunit of IL-12 has been shown to have extensive amino acid sequence homology to the extracellular domain of the human IL-6 receptor while the p35 subunit shows distant but significant sequence similarity to IL-6, G-CSF, and chicken MGF. These observations have led to the suggestion that IL-12 might have evolved from a cytokine/soluble receptor complex. Human and mouse IL-12 share 70% and 60% amino acid sequence homology in their p40 and p35 subunits, respectively. IL-12 apparently shows species specificity with human IL-12 reportedly showing minimal activity in the mouse system.
-

IL-4, His, Rat
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-4 (IL-4) is a pleiotropic cytokine regulates diverse T and B cell responses including cell proliferation, survival, and gene expression. It has important effects on the growth and differentiation of different immunologically competent cells. Interleukin-4 is produced by mast cells, T cells, and bone marrow stromal cells. IL-4 regulates the differentiation of native CD4+ T cells (Th0 cells) into helper Th2 cells, and regulates the immunoglobulin class switching to the IgG1 and IgE isotypes. IL-4 has numerous important biological functions including stimulating B-cells activation, T-cell proliferation and CD4+ T-cells differentiation to Th2 cells. It is a key regulator in hormone control and adaptive immunity. IL-4 also plays a major role in inflammation response and wound repair via activation of macrophage into M2 cells. IL-4 is stabilized by three disulphide bonds forming a compact globular protein structure. Four alpha-helix bundle with left-handed twist is dominated half of the protein structure with 2 overhand connections and fall into a 2-stranded anti-parallel beta sheet.
-

IL-6, His, Mouse
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-6 (IL-6), also known as BSF-2, CDF and IFNB2, is a pleiotropic cytokine that participates in both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses. It is produced mainly by T cells, macrophages, monocytes, endothelial cells and muscle cells. IL-6 binds to IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) to trigger the association of IL-6R with gp130, inducing signal transduction through JAKs and STATs. The biological functions of IL-6 are diverse. It stimulates B cell differentiation and antibody production, myeloma and plasmacytoma growth, and nerve cell differentiation. It also acts as a myokine, produced by muscle cells in response to muscle contraction and released into the blood stream to help break down fats and improve insulin resistance.
-

IL-6, Rat (HEK 293-expressed)
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-6 (IL-6), also known as BSF-2, CDF and IFNB2, is a pleiotropic cytokine that participates in both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses. It is produced mainly by T cells, macrophages, monocytes, endothelial cells and muscle cells. IL-6 binds to IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) to trigger the association of IL-6R with gp130, inducing signal transduction through JAKs and STATs. The biological functions of IL-6 are diverse. It stimulates B cell differentiation and antibody production, myeloma and plasmacytoma growth, and nerve cell differentiation. It also acts as a myokine, produced by muscle cells in response to muscle contraction and released into the blood stream to help break down fats and improve insulin resistance.
-
IL-8 (77aa)/CXCL8, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-8 (IL-8), also known as CXCL8, GCP-1 and NAP-1, is one of the first discovered chemokines and belongs to the CXCL family, in which the first two conserved cysteines are separated by one residue. In vivo, IL-8 exists in two forms: a 77 a.a. protein produced by endothelial cells, and the more active 72 a.a. protein produced by monocytes. The receptors for IL-8 are the seven-helical G-protein coupled receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2, exclusively expressed on neutrophils. The functions of IL-8 are to induce rapid changes in cell morphology, activate integrins, and release the granule contents of neutrophils. Thus, IL-8 can enhance the antimicrobial actions of defense cells. It is secreted by monocytes, macrophages and endothelial cells. IL-8 signals through CXCR1 and CXCR2 to chemoattract neutrophils, basophils, and T cells. IL-8 is also a potent promoter of angiogenesis. Other functions of this protein, such as involvement in bronchiolitis pathogenesis, have also been reported.
-
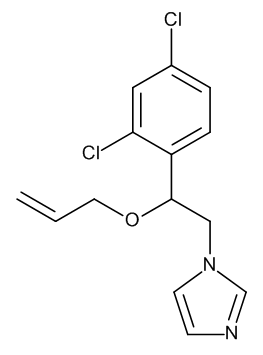
Imazalil
$85.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H14 Cl2 N2 O
-
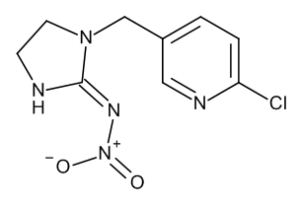
Imidacloprid
$594.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H10 Cl N5 O2






