Description
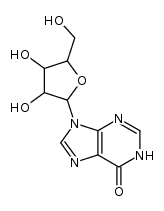
Inosine is the deaminated form of adenosine. It is a nucleoside consisting of hypoxathine and ribose. Its phosphate ester is inosinic acid. Inosine easily permeates the cell membrane and, taking part in glycolysis and the TCA cycle via the pentose phosphate pathway, elevates the intracellular level of ATP and stimulates biosynthesis of nucleic acids. Adaptation of these metabolic processes activates the cell, and the nucleoside is applicable to various disorders. Inosine accumulates in tissue during periods of ischemia and has been shown to degranulate mast cells in the hamster cheek pouch via activation of an A3 receptor.