Ambient
Showing 69501–69550 of 146505 results
-
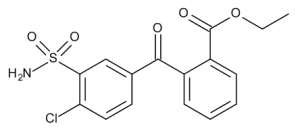
Chlorthalidone Acid Ethyl Ester
$2,024.29 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H14ClNO5S
-
Chlorthalidone Dimer Sodium Salt
$133.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H19Cl2N3O8S2.x(Na)
-
Chlorthalidone Dimer Sodium Salt
$615.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H19Cl2N3O8S2.x(Na)
-
Chlorthalidone Dimer Sodium Salt
$1,063.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H19Cl2N3O8S2.x(Na)
-
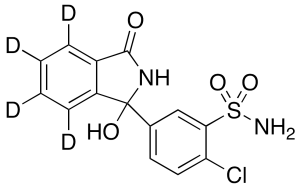
Chlorthalidone-d4
$239.78 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 2H4 H7 Cl N2 O4 S
-

Chlorthalidone-d4
$1,479.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 2H4 H7 Cl N2 O4 S
-

Chlorthalidone-d4
$3,694.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 2H4 H7 Cl N2 O4 S
-
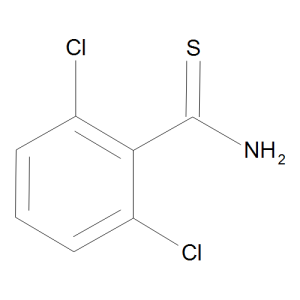
Chlorthiamid
$55.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H5 Cl2 N S
-

Chlorthiamid
$64.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H5 Cl2 N S
-
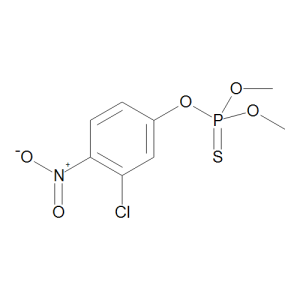
Chlorthion
$149.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H9 Cl N O5 P S
-

Chlorthion
$614.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H9 Cl N O5 P S
-

Chlorthion
$1,180.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H9 Cl N O5 P S
-
Chlorzoxazone
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H4 Cl N O2
-

Chlorzoxazone
$52.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H4 Cl N O2
-

Chlorzoxazone
$64.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H4 Cl N O2
-

Chlorzoxazone-4,6,7-d3
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 D3 H Cl N O2
-

Chlorzoxazone-4,6,7-d3
$407.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 D3 H Cl N O2
-

Chlorzoxazone-4,6,7-d3
$1,428.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 D3 H Cl N O2
-

CHO-K1/ mouse PD-1 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsProgrammed cell death protein 1, also known as PD-1 and CD279 (cluster of differentiation 279), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDCD1 gene.PD-1, functioning as an immune checkpoint, plays an important role in down regulating the immune system by preventing the activation of T-cells, which in turn reduces autoimmunity and promotes self-tolerance. The inhibitory effect of PD-1 is accomplished through a dual mechanism of promoting apoptosis (programmed cell death) in antigen specific T-cells in lymph nodes while simultaneously reducing apoptosis in regulatory T cells (suppressor T cells).
-

CHO-K1/4-1BB Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD137 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor family. Its alternative names are tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 (TNFRSF9), 4-1BB and induced by lymphocyte activation (ILA). It is currently of interest to immunologists as a co-stimulatory immune checkpoint molecule.
-

CHO-K1/5-HT1A/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A (5-HT1A) is Gi-coupled GPCRs expressed in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, septum, amygdala, and raphe nucelus, with lesser amounts in the basal ganglia and thalamus. Many functions of the central nervous system are influenced by 5-HT, including sleep, motor activity, sensory perception, arousal and appetite. 5-HT1A ligands may prove to be therapeutic in the treatment of various disorders such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia.
-

CHO-K1/5-HT2A Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product Details5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT, also commonly known as serotonin) is synthesized in enterochromaffin cells in the intestine and in serotonergic nerve terminals. In the periphery, 5-HT mediates gastrointestinal motility, platelet aggregation, and contraction of blood vessels. Many functions of the central nervous system are influenced by 5-HT, including sleep, motor activity, sensory perception, arousal, and appetite. A family of 12 GPCRs and one ion channel mediate the biological effects of 5-HT (Hoyer et al., 1994). 5-HT2A which couples to Gq/11 is expressed throughout the central nervous system in the neocortex and olfactory tubercle. 5-HT2A receptor agonists may have important clinical value in the treatment of various disorders, such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. GenScript’s cloned human 5-HT2A–expressing cell line is generated in the CHO-K1 host.
-

CHO-K1/5-HT2B Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product Details5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT, also commonly known as serotonin) is synthesized in enterochromaffin cells in the intestine and in serotonergic nerve terminals. In the periphery, 5-HT mediates gastrointestinal motility, platelet aggregation, and contraction of blood vessels. Many functions of the central nervous system are influenced by 5-HT, including sleep, motor activity, sensory perception, arousal and appetite. A family of 12 GPCRs and one ion channel mediate the biological effects of 5-HT (Hoyer et al., 1994). 5-HT2B which couples to Gq/11 is expressed in embryonic and adult cardiovascular tissues, gut, and brain from the rat, mouse, and human species. 5-HT2B receptors are responsible for many cardiovascular and central nervous system functions, such as blood vessel contraction, platelet shape changes, neuronal sensitization to tactile stimuli, and mediation of the hallucinogenic effects of phenylisopropylamin hallucinogens. It has also been shown to be required for heart development. GenScript’s cloned human 5-HT2B -expressing cell line is generated in the CHO-K1 host.
-

CHO-K1/5-HT2C Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product Details5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT, also commonly known as serotonin) is synthesized in enterochromaffin cells in the intestine and in serotonergic nerve terminals. In the periphery, 5-HT mediates gastrointestinal motility, platelet aggregation, and contraction of blood vessels. Many functions of the central nervous system are influenced by 5-HT, including sleep, motor activity, sensory perception, arousal, and appetite. A family of 12 GPCRs and one ion channel mediate the biological effects of 5-HT (Hoyer et al., 1994). 5-HT2C is expressed in the brain and spinal cord, especially the choroid plexus. 5-HT2C receptor agonists may have important clinical value in the treatment of mental and eating disorders, such as depression, panic anxiety, OCD, bulimia, and obesity. GenScript’s cloned human 5-HT2C-expressing cell line is generated in the CHO-K1 host.
-

CHO-K1/ACE2 Stable Cell Line
$6,468.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsRecombinant CHO-K1 cells stably express Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) on the cell surface. The surface expression of ACE2 is validated by FACS analysis. This stable cell line product is designed for cell-based binding assays that measure binding affinity and stability of antibody based biologics binding with ACE2.
-

CHO-K1/ADORA1/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsA1 is a receptor for adenosine. It is demonstrated that the A1 receptor is ubiquitous throughout the entire body. Activation of A1 elicits an inhibition of adenylate cyclase and therefore a decrease in the cAMP concentration. A1 receptors are implicated in sleep promotion by inhibiting wake promoting cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain. Adenosine antagonists are widely used in neonatal medicine.
-

CHO-K1/ADORA2A/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe adenosine receptors ADORA2A is Gs-coupled GPCRs expressed in the thymus gland, heart, lung, kedney, brain, platelets, spleen and leukocytes. ADORA2A down-regulates chemokine receptor function and inhibits platelet aggregation. ADORA2A antagonists may be useful as therapy for Parkinson’s disease.
-

CHO-K1/ADORA2B/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe adenosine receptors ADORA2B is Gs and Gq/11-coupled GPCR expressed in the Large intestine, cecum, urinary bladder. ADORA2B receptor mediates relaxation to adenosine in human small coronary arteries which is independent of NO but dependents in part on a K+-sensitive mechanism. Pharmacological or molecular biologic activation of ADORA2B receptor may prevent glomerular remodeling associated with glomerulosclerosis, renal disease, and abnormal growth associated with hypertension and diabetes.
-

CHO-K1/ADORA3/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsExtracellular adenosine mediates a multitude of biological effects, including wakefulness, antiarrythmia, bronchoconstriction and response to ischemia and oxidative stress. A family of four G-protein coupled adrenoceptors, A1, A2A, A2B and A3, is responsible for these effects. A3, which couples to Gi/o, is expressed in a wide range of human tissues, but most predominantly in the lung and liver. Recent animal model studies have shown that A3 receptors play important roles in brain ischemia, immunosuppresion, and bronchospasm. A3 receptor agonists and/or agonists may have important clinical value in the treatment of asthma and inflammation. Mice lacking A3 receptors display reduced mast cell degranulation and bronchoconstriction in response to adenosine.
-

CHO-K1/ADRA1A Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe α1-adrenergic receptor (AR) family consists of three closely related gene products (α1A, α1B, and α1D) that mediate the actions of norepinephrine (NE) and epinephrine in sympathetically innervated tissues and brain. α1-ARs belong to the G protein-coupled receptor family and consist of single polypeptide chains predicted to have seven transmembrane spanning domains. With similar pharmacological and signaling properties, α1-AR subtypes act through Gq/11 proteins to activate phospholipase C, increase both inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate production and intracellular Ca2+. Once activated by binding, α1-ARs initiate the cellular pathways leading to the regulation of physiological effects, including blood pressure maintenance, glucose metabolism, renal sodium reabsorption, and cardiac inotropy.
-

CHO-K1/ADRA1B Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe α1-adrenergic receptor (AR) family consists of three closely related gene products (α1A, α1B, and α1D). They mediate the actions of norepinephrine (NE) and epinephrine in sympathetically innervated tissues and brain. Α1-ARs belong to the G protein-coupled receptor family and consist of single polypeptide chains that are predicted to form seven transmembrane spanning domains. With similar pharmacological and signaling properties, α1-AR subtypes act through Gq/11 proteins to activate phospholipase C, increase inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate production, and increase intracellular Ca2+. ADRA1B functions in diverse settings include vasoconstriction and myocardial contractility, neuronal dopaminergic responses, dendritic cell migration and inflammatory responses, as well as neuroendocrine regulation of fertility.
-

CHO-K1/ADRA1D Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe α1-adrenergic receptor (AR) family consists of three closely related gene products (α1A, α1B, and α1D). They mediate the actions of norepinephrine (NE) and epinephrine in sympathetically innervated tissues and brain. α1-ARs belong to the G protein-coupled receptor family and consist of single polypeptide chains that are predicted to form seven transmembrane spanning domains. With similar pharmacological and signaling properties, α1-AR subtypes act through Gq/11 proteins to activate phospholipase C, increase inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate production, and increase intracellular Ca2+.
-

CHO-K1/ADRA2A/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe adrenoceptors ADRA2A is expressed in the brain, spleen, kidney, aorta, lung, skeletal muscle, heart and liver. ADRA2A -adrenoceptor knockout mice exhibit disruption of presynaptic inhibition of noradrenaline release at high stimulation frequencies. ADRA2A receptor is the principal autoreceptor in the presynaptic feedback loop regulating noradrenaline release. However, another α2 autoreceptor is also present.
-

CHO-K1/ADRA2B/Gqi5 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsAdrenoceptors are 7-transmembrane receptors which mediate the central and peripheral actions of the neurotransmitter, noradrenaline (norepinephrine), and the hormone and neurotransmitter, adrenaline (epinephrine). Based on both pharmacological and molecular evidence, they are divided into three major types – α1, α2, and β. The α2 adrenoceptors include 3 subtypes – α2A, α2B, and α2C – each of which couples to Gi/o protein primarily.
The α2B adrenoceptors (ADRA2B) is expressed in the kidney, liver, brain, lung, heart, and skeletal muscle. The development of α2B and α2C knock-out mice has shown that these two subtypes are not involved in the central hypotensive response to α2 agonists. -

CHO-K1/ADRA2C/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe adrenoceptors ADRA2C is expressed in the brain, kidney, aorta, lung, skeletal muscle, heart and spleen. ADRA2C knockout mice exhibited disrupts presynaptic inhibition of noradrenaline release at low stimulation frequencies.
-

CHO-K1/ADRB1/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe ß-adrenergic receptors are linked to G proteins. The ß-receptor has three known subtypes. Beta-1 receptors primarily regulate myocardial tissue and affect the rate of contraction via impulse conduction. Beta-2 receptors regulate smooth muscle tone and influence vascular and bronchiolar relaxation. Beta-3 receptors are less well studied but are thought to primarily affect lypolysis and may have effects on cardiac inotropy (Greene Shepherd,2006). In the human heart, beta (1)- and beta (2)AR are the most powerful physiologic mechanism to acutely increase cardiac performance. Changes in betaAR play an important role in chronic heart failure (CHF). Thus, due to increased sympathetic activity in CHF, betaAR are chronically (over) stimulated, and that results in beta (1) AR desensitization and alterations of down-stream mechanisms (Brodde OE,2006).
-

CHO-K1/AGTRL1/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe apelin receptor AGTRL1 is Gi/Go-coupled GPCRs expressed in the heart, coronary artery, aorta, internal mammary artery, pulmonary artery and saphenous vein, it also expressed in lung, kidney and adrenal gland. In AGTRL1 receptor knockout mice baseline blood pressure is not changed compared to wild-type animals. Vasoconstrictor responses to angiotensin II however are significantly more pronounced in the knockout animals.
-

CHO-K1/B2/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsBradykinin (BK) is a pro-inflammatory polypeptide that can cause pain, inflammation, increased vascular permeability, vasodilation, contraction of various smooth muscles, and cell proliferation by stimulating B1and B2 receptors. B2 receptors are most commonly distributed in the vascular and non-vascular smooth muscle and in the heart. The B2 receptor mediates the action of bradykinin (BK) and lysyl-bradykinin (Lys-BK). The stimulation of BK B2 receptors is not only implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammation, pain, and tissue injury but also in cardioprotective mechanisms. So B2 receptor agonists may have important clinical value in the treatment and prevention of various cardiovascular disorders such as hypertension, ischaemic heart disease, left ventricular hypertrophy, ventricular remodeling, congestive heart failure, and diabetic disorders.
-

CHO-K1/B7-H2 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsLigand for the T-cell-specific cell surface receptor ICOS acts as a costimulatory signal for T-cell proliferation and cytokine secretion. It also induces B-cell proliferation and differentiation into plasma cells. It could also play an important role in mediating local tissue responses to inflammatory conditions, as well as modulating the secondary immune response by co-stimulating memory T-cell function.
-

CHO-K1/B7-H3 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsB7-H3, a new member of the B7 family of immune-regulatory molecules, was identified in 2001 by database searches of a human dendritic cell-derived cDNA library. It is a type I transmembrane protein, which expresses in certain normal cells and tissues, such as dendritic cells, as well as the liver, lung, breast, placenta, and prostate. Aberrant expression of B7-H3 has been reported in a wide range of solid cancers, including brain, lung, pancreatic, colorectal, liver, and breast cancers, as well as in hematologic malignancies, such as acute leukemia and multiple myeloma, and it is associated with more advanced disease and poor prognosis.
-

CHO-K1/B7-H4 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsB7-H4 is a transmembrane protein that binds an unknown receptor on activated T cells resulting in inhibition of T-cell effector function via cell cycle arrest, decreased proliferation, and reduced IL-2 production. B7-H4 is up-regulated on the surface of cancer cells and immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in a variety of human cancers.
-

CHO-K1/BB1 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe bombesin receptor family is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily and consists of three subtypes of receptors: BB1 (neuromedin B receptor), BB2 (gastrin-releasing peptide receptor), and BB3. These receptors are widely distributed in mammals especially in the CNS and gastrointestinal tract and have numerous effects both physiologically and in pathologic processes including having an autocrine growth action on normal tissues and tumors; potent CNS effects (satiety, circadian rhythm, various behaviors); and potent effects in the immune, gastrointestinal, respiratory and urogenital systems.
The human BB1 receptor has a greater than 100-fold higher affinity for neuromedin B than gastrin-releasing peptide. Interaction of ligand and BB1 activates the Gαq/11 pathway and increase the intracellular calcium concentration. GenScript’s BB1-expressing stable cell line was made in CHO-K1 host cell and optimized for calcium assays. -

CHO-K1/BB2 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe bombesin receptor family is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily and consists of three subtypes of receptors: BB1 (neuromedin B receptor), BB2 (gastrin-releasing peptide receptor), and BB3. These receptors are widely distributed in mammals especially in the CNS and gastrointestinal tract and have numerous effects both physiologically and in pathologic processes including having an autocrine growth action on normal tissues and tumors; potent CNS effects (satiety, circadian rhythm, various behaviors); and potent effects in the immune, gastrointestinal, respiratory and urogenital systems.
The human BB2 receptor has a greater than 50-fold higher affinity for gastrin-releasing peptide than neuromedin B. Interaction of ligand and BB2 activates the Gαq/11 pathway and increase the intracellular calcium concentration. GenScript’s BB2-expressing stable cell line was made in CHO-K1 host cell and optimized for calcium assays. -

CHO-K1/BB3 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe bombesin receptor family is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily and consists of three subtypes of receptors: BB1 (neuromedin B receptor), BB2 (gastrin-releasing peptide receptor), and BB3. These receptors are widely distributed in mammals especially in the CNS and gastrointestinal tract and have numerous effects both physiologically and in pathologic processes including having an autocrine growth action on normal tissues and tumors; potent CNS effects (satiety, circadian rhythm, various behaviors); and potent effects in the immune, gastrointestinal, respiratory and urogenital systems.
BB3 is an orphan receptor, with a high degree of homology to the BB1 and BB2 receptors, but has an unknown natural ligand because it has low affinity for all naturally occurring bombesin-related peptides. Interaction of ligand and BB3 activates the Gαq/11 pathway and increase the intracellular calcium concentration. GenScript’s BB3-expressing stable cell line was made in CHO-K1 host cell and optimized for calcium assays. -

CHO-K1/BDCA2 and FcER1G Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsBDCA-2 is a novel type II C-type lectin, which shows 50.7% sequence identity at the amino acid level to its putative murine ortholog, the murine dendritic cell–associated C-type lectin 2. In addition to its antigen capturing function, BDCA-2 can mediate potent inhibition of induction of IFN-α/β expression in PDCs. Production of IFN-α/β in response to several different types of viruses, bacteria, CpG-DNA, dsRNA, and SLE serum is by far the most prominent feature of PDCs.
-

CHO-K1/BDCA2 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsBDCA-2 is a novel type II C-type lectin, which shows 50.7% sequence identity at the amino acid level to its putative murine ortholog, the murine dendritic cell–associated C-type lectin 2. In addition to its antigen capturing function, BDCA-2 can mediate potent inhibition of induction of IFN-α/β expression in PDCs. Production of IFN-α/β in response to several different types of viruses, bacteria, CpG-DNA, dsRNA, and SLE serum is by far the most prominent feature of PDCs.
-

CHO-K1/BTLA Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) is an Ig super family protein with an intermediate type Ig fold in the ectodomain and an ITIM inhibitory signaling domain in the cytosol. BTLA interacts with the herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM; TNFRSF14), a TNFR super family member. Engagement of BTLA by HVEM, induces tyrosine phosphorylation of the ITIM motifs in the cytoplasmic tail of BTLA, allowing the recruitment of the phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2, which attenuate signaling.
-

CHO-K1/C5a/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe complement component 5a receptor 1 (C5a) is Gq/11 and Gi/o-coupled GPCRs. C5a is a significant pathogenic driver in a number of immuno-inflammatory diseases, making C5a inhibition an attractive therapeutic strategy. C5a receptor plays an important role in mediating acute kidney allograft rejection.
-

CHO-K1/CASR Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsCASR is a calcium-sensing receptor and plays an important role in regulating PTH secretion. It is expressed in many different tissues, such as parathyroid, pancreatic islet and insulinoma cells, breast, gastrinoma cells, pituitary, keratinocytes and human colon epithelial cells. CASR Inhibits PTH secretion and parathyroid cellular proliferation in parathyroid glands or cells, and also inhibits proliferation of colonic crypt cells. Besides, it can stimulate PTHrP secretion in prostate cell line, and stimulate calcitonin secretion from thyroidal C-cells.
-

CHO-K1/CB1/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe cannabinoid receptor CNR1 is Gs-coupled GPCRs expressed in primarily CNS and some peripheral neurones; particularly prevalent in basal ganglia, hippocampus, cerebellum, cerebral cortex and also presented in some non-neuronal cells and tissues, for example leukocytes and testis. A shorter human splice variant (411aa) has been identified in the brain and other tissues by reverse-transcriptase PCR but mRNA levels were less than 10-fold the levels of the longer isoform. The pharmacological characteristics of the isoforms are similar.






