Ambient
Showing 88351–88400 of 146505 results
-
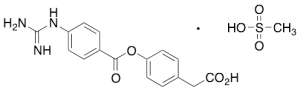
FOY 251
$203.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H15 N3 O4 . C H4 O3 S
-

FOY 251
$904.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H15 N3 O4 . C H4 O3 S
-

FOY 251
$1,559.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H15 N3 O4 . C H4 O3 S
-
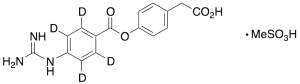
FOY 251-D4
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H15D4N3O7S
-

FOY 251-D4
$1,647.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H15D4N3O7S
-
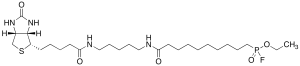
FP-Biotin (Mixture of Diastereomers)
$476.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27H50FN4O5PS
-

FP-Biotin (Mixture of Diastereomers)
$1,105.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27H50FN4O5PS
-

FP-Biotin (Mixture of Diastereomers)
$3,976.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27H50FN4O5PS
-

FPL 64176, NeuroPure
$91.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsFPL 64176, NeuroPure
-

FPL 64176, NeuroPure
$486.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsFPL 64176, NeuroPure
-
FPR A14
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H20N2O5
-
FPR A14
$708.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H20N2O5
-
FPR A14
$1,219.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H20N2O5
-
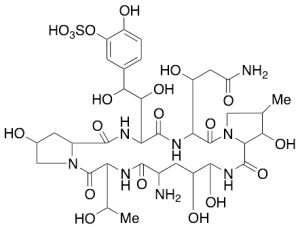
FR 179642
$240.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35H52N8O20S
-

FR 179642
$600.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35H52N8O20S
-
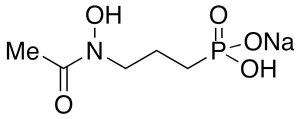
FR 900098 Monosodium Salt
$119.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H11 N O5 P . Na
-

FR 900098 Monosodium Salt
$169.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H11 N O5 P . Na
-

FR 900098 Monosodium Salt
$417.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H11 N O5 P . Na
-
Fractalkine/CX3CL1, Human
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsChemokine (C-X3-C motif) ligand 1 (CX3CL1) is a known member of the CX3C chemokine family. It is also commonly known under the names fractalkine (in humans) and neurotactin (in mice). The polypeptide structure of CXC3L1 differs from the typical structure of other chemokines. For example, the spacing of the characteristic N-terminal cysteines is different; there are three amino acids separating the initial pair of cysteines in CX3CL1, while there are none in CC chemokines and only one in CXC chemokines. CX3CL1 is produced as a long protein (with 373-amino acid in humans) with an extended mucin-like stalk and a chemokine domain on top. The mucin-like stalk allows it to bind to the surface of certain cells. Soluble CX3CL1 potently chemoattracts T cells and monocytes, while the cell-bound chemokine promotes strong adhesion of leukocytes to activated endothelial cells, where it is primarily expressed. CX3CL1 can signal through the chemokine receptor CX3CR1.
-

Fractalkine/CX3CL1, Human
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsChemokine (C-X3-C motif) ligand 1 (CX3CL1) is a known member of the CX3C chemokine family. It is also commonly known under the names fractalkine (in humans) and neurotactin (in mice). The polypeptide structure of CXC3L1 differs from the typical structure of other chemokines. For example, the spacing of the characteristic N-terminal cysteines is different; there are three amino acids separating the initial pair of cysteines in CX3CL1, while there are none in CC chemokines and only one in CXC chemokines. CX3CL1 is produced as a long protein (with 373-amino acid in humans) with an extended mucin-like stalk and a chemokine domain on top. The mucin-like stalk allows it to bind to the surface of certain cells. Soluble CX3CL1 potently chemoattracts T cells and monocytes, while the cell-bound chemokine promotes strong adhesion of leukocytes to activated endothelial cells, where it is primarily expressed. CX3CL1 can signal through the chemokine receptor CX3CR1.
-

Fractalkine/CX3CL1, Human
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsChemokine (C-X3-C motif) ligand 1 (CX3CL1) is a known member of the CX3C chemokine family. It is also commonly known under the names fractalkine (in humans) and neurotactin (in mice). The polypeptide structure of CXC3L1 differs from the typical structure of other chemokines. For example, the spacing of the characteristic N-terminal cysteines is different; there are three amino acids separating the initial pair of cysteines in CX3CL1, while there are none in CC chemokines and only one in CXC chemokines. CX3CL1 is produced as a long protein (with 373-amino acid in humans) with an extended mucin-like stalk and a chemokine domain on top. The mucin-like stalk allows it to bind to the surface of certain cells. Soluble CX3CL1 potently chemoattracts T cells and monocytes, while the cell-bound chemokine promotes strong adhesion of leukocytes to activated endothelial cells, where it is primarily expressed. CX3CL1 can signal through the chemokine receptor CX3CR1.
-

Fractalkine/CX3CL1, Human
$2,190.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsFractalkine, also named neurotactin, is a novel chemokine recently identified through bioinformatics. Fractalkine has a unique C-X3-C cysteine motif near the amino-terminus and is the first member of a fourth branch of the chemokine superfamily. Unlike other known chemokines, fractalkine is a type 1 membrane protein containing a chemokine domain tethered on a long mucin-like stalk. Human fractalkine cDNA encodes a 397 amino acid (aa) residue membrane protein with a 24 aa residue predicted signal peptide, a 76 aa residue chemokine domain, a 241 aa residue stalk region containing 17 degenerate mucin-like repeats, a 19 aa residue transmembrane segment and a 37 aa residue cytoplasmic domain. The extracellular domain of human fractalkine can be released, possibly by proteolysis at the dibasic cleavage site proximal to the membrane, to generate soluble fractalkine. The soluble chemokine domain of human fractalkine was reported to be chemotactic for T cells and monocytes while the soluble chemokine domain of mouse fractalkine was reported to chemoattract neutrophils and T-lymphocytes but not monocytes.
-

Fractalkine/CX3CL1, Human
$163.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsFractalkine, also named neurotactin, is a novel chemokine recently identified through bioinformatics. Fractalkine has a unique C-X3-C cysteine motif near the amino-terminus and is the first member of a fourth branch of the chemokine superfamily. Unlike other known chemokines, fractalkine is a type 1 membrane protein containing a chemokine domain tethered on a long mucin-like stalk. Human fractalkine cDNA encodes a 397 amino acid (aa) residue membrane protein with a 24 aa residue predicted signal peptide, a 76 aa residue chemokine domain, a 241 aa residue stalk region containing 17 degenerate mucin-like repeats, a 19 aa residue transmembrane segment and a 37 aa residue cytoplasmic domain. The extracellular domain of human fractalkine can be released, possibly by proteolysis at the dibasic cleavage site proximal to the membrane, to generate soluble fractalkine. The soluble chemokine domain of human fractalkine was reported to be chemotactic for T cells and monocytes while the soluble chemokine domain of mouse fractalkine was reported to chemoattract neutrophils and T-lymphocytes but not monocytes.
-

Frame TransDNA
$233.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsFrame TransDNA
-

FRAX 597
$188.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H28ClN7OS
-
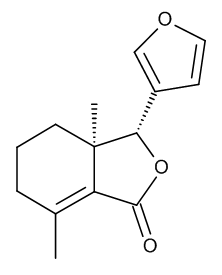
Fraxinellone
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H16 O3
-

Fraxinellone
$1,306.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H16 O3
-

Free Fatty Acid Test Kit
$386.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsContains all reagents and calibrators necessary to run samples for percent free fatty acid. Control included. For testing of approximately 100 samples. Quantitation range is from 0.1 – 2.01% free fatty acid
-
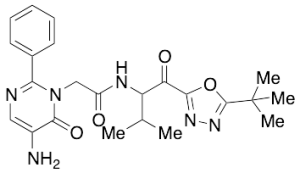
Freselestat
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H28N6O4
-

Freselestat
$258.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H28N6O4
-

Freselestat
$495.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H28N6O4
-
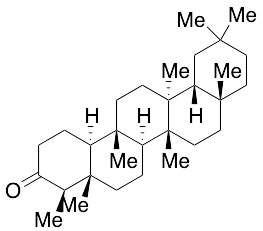
Friedelin
$181.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H50 O
-

Friedelin
$299.29 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H50 O
-

Friedelin
$1,129.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H50 O
-

FRONT PANEL FOR TEMPLATE-TAMER
$420.90 Add to cart View Product DetailsFRONT PANEL FOR TEMPLATE-TAMER
-
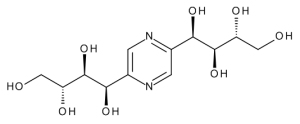
fructosazine
$200.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H20 N2 O8
-

Fructosazine
$398.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H20 N2 O8
-

Fructosazine
$1,432.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H20 N2 O8
-
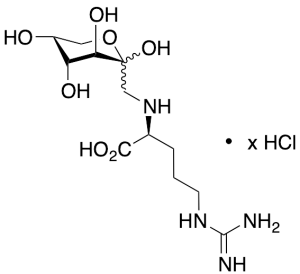
Fructose L-Arginine Adduct Hydrochloride, >80%
$173.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H24N4O7 • x(HCl)
-

Fructose L-Arginine Adduct Hydrochloride, >80%
$1,365.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H24N4O7 • x(HCl)
-
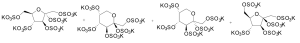
Fructose Persulfate Potassium Salt, Technical Grade
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 4 C6 H7 K5 O21 S5
-
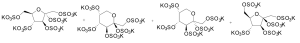
Fructose Persulfate Potassium Salt, Technical Grade
$643.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 4 C6 H7 K5 O21 S5
-
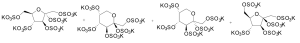
Fructose Persulfate Potassium Salt, Technical Grade
$1,231.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 4 C6 H7 K5 O21 S5
-
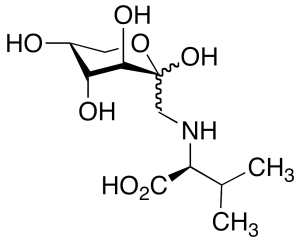
Fructose Valine (mixture of diastereomers)
$249.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H21 N O7
-

Fructose Valine (mixture of diastereomers)
$1,906.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H21 N O7
-
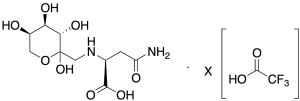
Fructose-asparagine TFA Salt(Mixture of diastereomers)
$213.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H18N2O8 • x(C2HF3O2)
-

Fructose-asparagine TFA Salt(Mixture of diastereomers)
$1,604.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H18N2O8 • x(C2HF3O2)
-
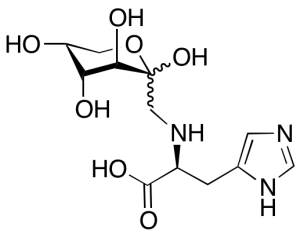
Fructose-histidine
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H19N3O7
-

Fructose-histidine
$1,721.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H19N3O7
-
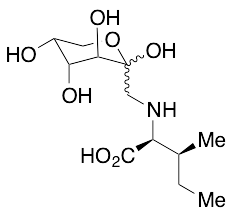
Fructose-isoleucine (mixture of diastereomers)
$215.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H23NO7






