Ambient
Showing 88651–88700 of 146505 results
-
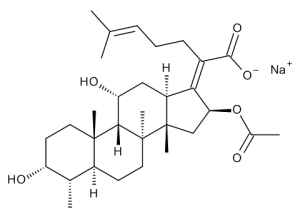
Fusidic Acid Sodium Salt
$244.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31 H47 O6 . Na
-
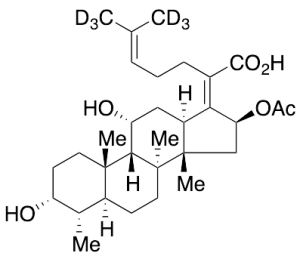
Fusidic Acid-d6
$745.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31H42D6O6
-

Fusidic Acid-d6
$5,898.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31H42D6O6
-
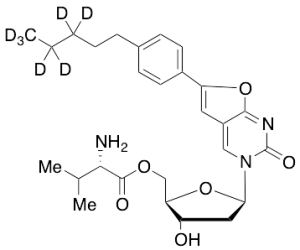
FV 100-d7 (Major)
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 D7 H28 N3 O6
-

FV 100-d7 (Major)
$1,712.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 D7 H28 N3 O6
-
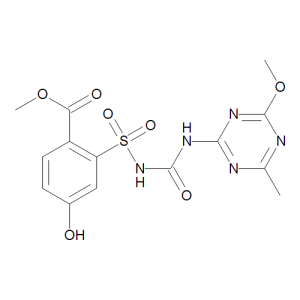
G 7460
$231.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H15 N5 O7 S
-

G 7460
$1,008.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H15 N5 O7 S
-

G 7460
$1,837.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H15 N5 O7 S
-
G-1
$111.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H18BrNO3
-
G-1
$236.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H18BrNO3
-
G-1
$384.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H18BrNO3
-
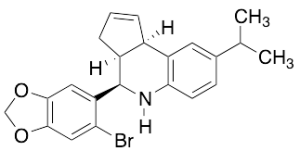
G-36
$109.54 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H22BrNO2
-

G-36
$241.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H22BrNO2
-

G-36
$434.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H22BrNO2
-

G-C GLOBULIN
$721.92 Add to cart View Product DetailsG-C GLOBULIN
-

G-CSF, Human
$1,651.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) contains internal disulfide bonds. Among the family of colony-stimulating factors, Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is the most potent inducer of terminal differentiation to granulocytes and macrophages of leukemic myeloid cell lines. The synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) can be induced by bacterial endotoxins, TNF, Interleukin-1 and GM-CSF. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF). In epithelial, endothelial, and fibroblastic cells secretion of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is induced by Interleukin-17.
-

G-CSF, Human
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) contains internal disulfide bonds. Among the family of colony-stimulating factors, Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is the most potent inducer of terminal differentiation to granulocytes and macrophages of leukemic myeloid cell lines. The synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) can be induced by bacterial endotoxins, TNF, Interleukin-1 and GM-CSF. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF). In epithelial, endothelial, and fibroblastic cells secretion of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is induced by Interleukin-17.
-

G-CSF, Human
$245.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) contains internal disulfide bonds. Among the family of colony-stimulating factors, Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is the most potent inducer of terminal differentiation to granulocytes and macrophages of leukemic myeloid cell lines. The synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) can be induced by bacterial endotoxins, TNF, Interleukin-1 and GM-CSF. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF). In epithelial, endothelial, and fibroblastic cells secretion of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is induced by Interleukin-17.
-

G-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) contains internal disulfide bonds. Among the family of colony-stimulating factors, Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is the most potent inducer of terminal differentiation to granulocytes and macrophages of leukemic myeloid cell lines. The synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) can be induced by bacterial endotoxins, TNF, Interleukin-1 and GM-CSF. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF). In epithelial, endothelial, and fibroblastic cells, the secretion of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is induced by Interleukin-17.
-

G-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) contains internal disulfide bonds. Among the family of colony-stimulating factors, Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is the most potent inducer of terminal differentiation to granulocytes and macrophages of leukemic myeloid cell lines. The synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) can be induced by bacterial endotoxins, TNF, Interleukin-1 and GM-CSF. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF). In epithelial, endothelial, and fibroblastic cells, the secretion of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is induced by Interleukin-17.
-

G-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) contains internal disulfide bonds. Among the family of colony-stimulating factors, Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is the most potent inducer of terminal differentiation to granulocytes and macrophages of leukemic myeloid cell lines. The synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) can be induced by bacterial endotoxins, TNF, Interleukin-1 and GM-CSF. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the synthesis of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF). In epithelial, endothelial, and fibroblastic cells, the secretion of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is induced by Interleukin-17.
-

G-CSF, Mouse
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF), also known as CSF-3 and MGI-1G, is a cytokine and hormone belonging to the IL-6 superfamily. It is expressed by monocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and bone marrow stroma. G-CSF stimulates the bone marrow to produce granulocytes and stem cells, and specifically stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of the neutrophilic granulocyte lineage. G-CSF has been used to stimulate white blood cell production after chemotherapy. It has also been used to boost the number of hematopoietic stem cells after bone marrow transplantation.
-

G-CSF, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF), also known as CSF-3 and MGI-1G, is a cytokine and hormone belonging to the IL-6 superfamily. It is expressed by monocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and bone marrow stroma. G-CSF stimulates the bone marrow to produce granulocytes and stem cells, and specifically stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of the neutrophilic granulocyte lineage. G-CSF has been used to stimulate white blood cell production after chemotherapy. It has also been used to boost the number of hematopoietic stem cells after bone marrow transplantation.
-

G-CSF, Mouse
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF), also known as CSF-3 and MGI-1G, is a cytokine and hormone belonging to the IL-6 superfamily. It is expressed by monocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and bone marrow stroma. G-CSF stimulates the bone marrow to produce granulocytes and stem cells, and specifically stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of the neutrophilic granulocyte lineage. G-CSF has been used to stimulate white blood cell production after chemotherapy. It has also been used to boost the number of hematopoietic stem cells after bone marrow transplantation.
-
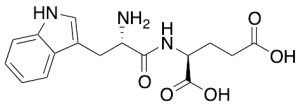
G3335
$79.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H19N3O5
-

G3335
$182.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H19N3O5
-

G418 Disulfate
$136.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsG418 Disulfate
-

G418 Disulfate
$522.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsG418 Disulfate
-

G418 Disulfate, PhytoPure
$90.82 Add to cart View Product DetailsG418 Disulfate, PhytoPure
-

G418 Disulfate, PhytoPure
$1,050.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsG418 Disulfate, PhytoPure
-

G418 Sulfate
$480.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsG418 Sulfate
-

G418 Sulfate
$1,901.82 Add to cart View Product DetailsG418 Sulfate
-
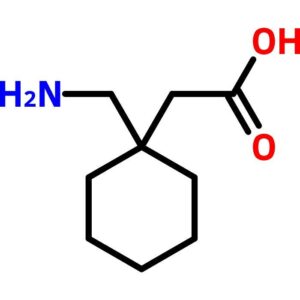
Gabapentin
$95.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsGabapentin
-

Gabapentin
$291.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsGabapentin
-
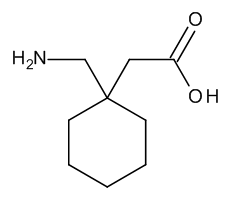
Gabapentin
$77.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H17 N O2
-

Gabapentin
$119.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H17 N O2
-

Gabapentin
$169.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H17 N O2
-
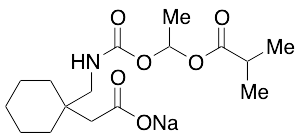
Gabapentin Enacarbil Sodium Salt
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H26 N O6 . Na
-

Gabapentin Enacarbil Sodium Salt
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H26 N O6 . Na
-

Gabapentin Ethyl Ester Hydrochloride
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H21 N O2 . Cl H
-

Gabapentin Ethyl Ester Hydrochloride
$1,391.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H21 N O2 . Cl H
-

Gabapentin Lactam-d6
$232.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H9D6NO
-

Gabapentin Lactam-d6
$1,775.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H9D6NO
-
Gabapentin Related Compound A
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H15 N O
-
Gabapentin Related Compound A
$260.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H15 N O
-
Gabapentin Related Compound A
$551.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H15 N O
-
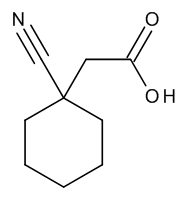
Gabapentin Related Compound B
$119.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H13 N O2
-

Gabapentin Related Compound B
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H13 N O2
-

Gabapentin Related Compound B
$508.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H13 N O2
-
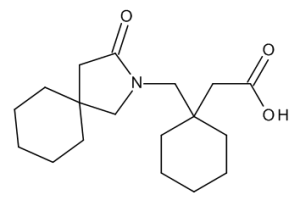
Gabapentin Related Compound D
$131.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H29 N O3






