Ambient
Showing 91401–91450 of 146505 results
-

HEK293/EP1 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsProstaglandins are known to affect the nervous system and can modulate synaptic transmission and neurotransmitter release, the sleep/wake cycle, fever, pain, and the immune system. Prostaglandin E2 receptor, EP1 subtype (EP1/PTGER1) is a receptor for prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The members of the EP receptor family, EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4, elicit their actions by altering cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) or intracellular calcium concentrations. EP1 activates phospholipase C and phosphatidylinositol turnover and stimulates the release of intracellular calcium via a Gi/Gq-coupled mechanism. EP2 and EP4 both signal through a Gs-coupled mechanism that stimulates adenylyl cyclase and increases intracellular levels of cAMP. EP1 appears to mediate the effects of PGE2 in promoting the formation of precancerous lesions in animal models of colon cancer. In addition, EP1 has an inhibitory effect on stress-induced aggressive and risk-taking behaviors in mice.
-

HEK293/FP/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsProstaglandin F (2-alpha) is known as a potent luteolytic agent. It is involved in modulating intraocular pressure and smooth muscle contraction in uterus. Its effects on cells are mediated through specific interaction with the Prostanoid receptor FP, which is a 359-amino acid protein. Having 7 putative transmembrane domains, FP resembles the characteristic of G protein coupled receptors. Knockout studies in mice suggest that the interaction of PGF2-alpha with this receptor may initiate parturition in ovarian luteal cells and thereupon induce luteolysis.
-

HEK293/GCGR/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGlucagon regulates blood glucose via control of hepatic glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis and via regulation of insulin release from the β cell. Pharmacological administration of glucagon increases blood glucose in normal and diabetic subjects, and produces positive inotropic and chronotropic cardiovascular effects, relaxation of smooth muscle in the gastrointestinal tract and stimulation of growth hormone secretion. The actions of glucagon are mediated via a single adenylate cyclase-coupled glucagon receptor that also couples to the phospholipase C-inositol phosphate (PLC-IP) pathway leading to Ca2+ release from intracellular stores.
-

HEK293/Gα15 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsHEK293/Gα15 is a HEK293 cell line stably expressing the Gα15 alpha subunit protein which a Gq protein. It is used as a host cell for transfection expression of Gs and Gi/o -coupled receptors, the constitutively expressed Gα15 protein in the cells allows many transfected receptors which normally stimulate/inhibit the cAMP pathway, to couple to Gq signal transduction and mobilize intracellular calcium. The cell line carries the puromycin resistance gene and is resistant to puromycin
-

HEK293/H1 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe H1 histamine receptor is expressed primarily in the lungs, vasculature, and brain. The H1 mediates the contraction of smooth muscles, neurotransmission in the central nervous system, the release of catecholamine from adrenal medulla, and increases in capillary permeability due to contraction of terminal venules. H1’s role in inflammatory responses makes its antagonist suitable for treating allergies.
-

HEK293/PD-L1 Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsProgrammed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) also known as cluster of differentiation 274 (CD274) or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD274 gene. The formation of the PD-1 receptor / PD-L1 or B7.1 receptor /PD-L1 ligand complex transmits an inhibitory signal which reduces the proliferation of these CD8+ T cells at the lymph nodes. PD-1 is also able to control the accumulation of foreign antigen specific T cells in the lymph nodes through apoptosis, which is further mediated by a lower regulation of the gene Bcl-2.
-

HEK293/TP Stable Cell Line
$7,331.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe thromboxane A2 (TxA2) receptor (TP) is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily which mediates TxA2-induced platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction. Dysregulation of TxA2 synthesis and function has been implicated in the pathogenesis of a number of disease states including myocardial ischemia, asthma, pregnancy-induced hypertension, and a variety of kidney diseases. TP receptors (Thromboxane A2 receptors) are widely distributed among different organ systems and localized on both cell membranes and in intracellular structures. Two isoforms of human TPs have been cloned from placenta (TPα) and endothelium (TPβ) that differ in their mechanisms and kinetics of desensitization and internalization. The TPs are linked via the Gq/G11 class of G proteins to phospholipase C (PLC), which hydrolyzes phosphoinositides to two potent second messengers: inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, which leads to an increase in cytoplasmic free calcium, and diacylglycerol (DAG), which activates protein kinase C (PKC).
-

HEK293T/Spike Stable Cell Line
$6,468.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsRecombinant HEK293T cells stably overexpress human SARS-CoV-2 spike protein on their surface. The surface expression of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is validated by FACS analysis. This stable cell line product is designed for screening antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, as well as for measuring binding affinity and stability of antibody based biologics that bind with spike protein. GenScript also offers spike protein expressing CHO-K1 stable cell line (Cat. No. M00803) for SARS-CoV-2 study.
-
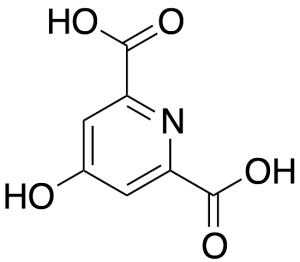
Helidaminic Acid
$54.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H5NO5
-

Helidaminic Acid
$142.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H5NO5
-

Helidaminic Acid
$288.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H5NO5
-

Heliomethylamine Hydrochloride
$168.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H17 N O2 . Cl H
-

Heliomethylamine Hydrochloride
$1,297.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H17 N O2 . Cl H
-
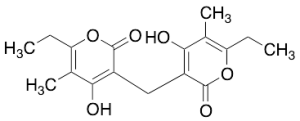
Helipyrone A
$180.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H20 O6
-

Helipyrone A
$489.90 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H20 O6
-

Helipyrone A
$1,778.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H20 O6
-
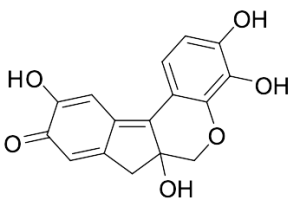
Hematein (Technical Grade)
$62.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H12O6
-

Hematein (Technical Grade)
$95.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H12O6
-

Hematein (Technical Grade)
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H12O6
-
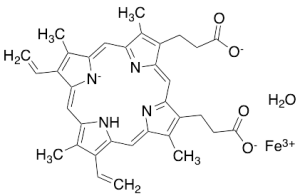
Hematin
$169.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H33N4O5Fe
-

Hematin
$282.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H33N4O5Fe
-

Hematin
$500.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H33N4O5Fe
-
Hematin
$822.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematin
-

Hematin
$2,161.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematin
-

Hematin
$16,731.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematin
-
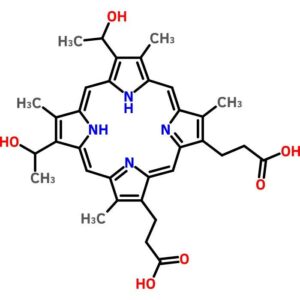
Hematoporphyrin
$139.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoporphyrin
-

Hematoporphyrin
$153.17 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoporphyrin
-

Hematoporphyrin
$579.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoporphyrin
-

Hematoporphyrin
$2,804.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoporphyrin
-
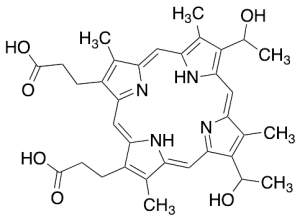
Hematoporphyrin (Technical Grade, ~30%)
$60.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H38N4O6
-

Hematoporphyrin (Technical Grade, ~30%)
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H38N4O6
-

Hematoporphyrin (Technical Grade, ~30%)
$202.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H38N4O6
-
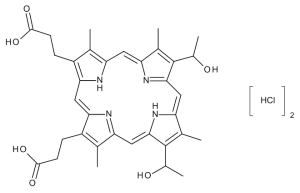
Hematoporphyrin Dihydrochloride
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H38 N4 O6 . 2 Cl H
-

Hematoporphyrin Dihydrochloride
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H38 N4 O6 . 2 Cl H
-

Hematoporphyrin Dihydrochloride
$369.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H38 N4 O6 . 2 Cl H
-

Hematoxylin
$161.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoxylin
-

Hematoxylin
$222.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoxylin
-

Hematoxylin
$409.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoxylin
-

Hematoxylin
$1,264.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoxylin
-

Hematoxylin
$9,253.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoxylin
-

HEMATOXYLIN
$292.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsHEMATOXYLIN
-

Hematoxylin (Technical Grade)
$62.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H14 O6
-

Hematoxylin (Technical Grade)
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H14 O6
-

Hematoxylin (Technical Grade)
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H14 O6
-
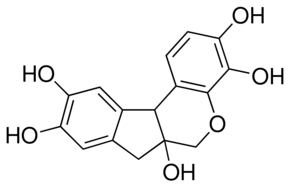
Hematoxylin hydrate
$34.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoxylin Hydrate
-

Hematoxylin hydrate
$97.12 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoxylin Hydrate
-

Hematoxylin hydrate
$293.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoxylin Hydrate
-

Hematoxylin, Hydrate
$94.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoxylin, Hydrate
-

Hematoxylin, Hydrate
$278.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoxylin, Hydrate
-
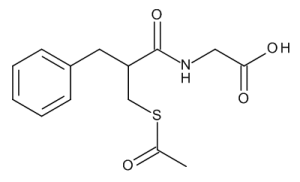
Hemiacetorphan
$201.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H17 N O4 S






