Ambient
Showing 107601–107650 of 153674 results
-
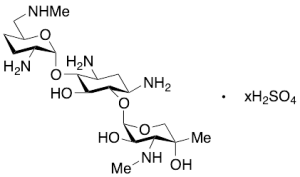
Micronomicin Sulfate (~80%)
$683.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C20 H41 N5 O7 . H2 O4 S
-
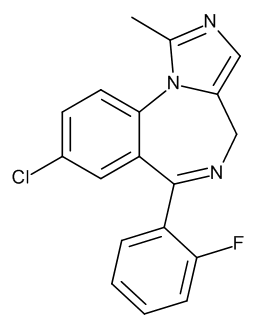
Midazolam
$239.78 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H13 Cl F N3
-

Midazolam
$533.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H13 Cl F N3
-

Midazolam
$1,867.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H13 Cl F N3
-
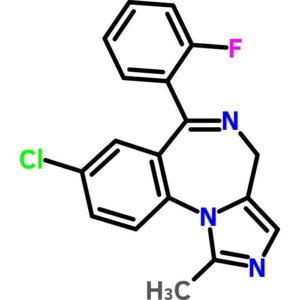
Midazolam (CIV), USP
$1,014.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMidazolam (CIV), USP
-

Midazolam (CIV), USP
$1,638.97 Add to cart View Product DetailsMidazolam (CIV), USP
-

Midazolam (CIV), USP
$4,388.92 Add to cart View Product DetailsMidazolam (CIV), USP
-

Midazolam (CIV), USP
$7,178.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMidazolam (CIV), USP
-

Midazolam (CIV), USP
$26,290.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMidazolam (CIV), USP
-
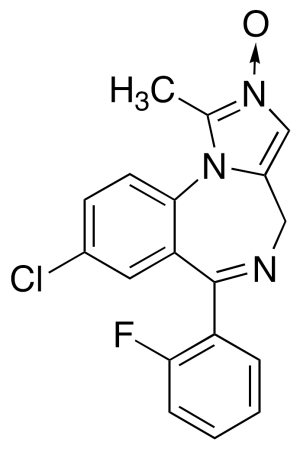
Midazolam 2-Oxide
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H13 Cl F N3 O
-

Midazolam 2-Oxide
$150.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H13 Cl F N3 O
-

Midazolam 2-Oxide
$257.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H13 Cl F N3 O
-
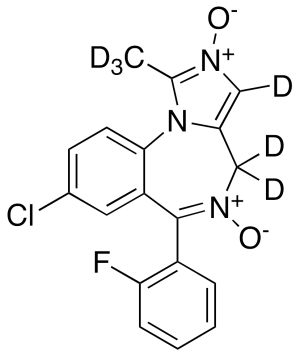
Midazolam 2,5-Dioxide-d6
$1,296.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H7D6ClFN3O2
-

Midazolam 2,5-Dioxide-d6
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H7D6ClFN3O2
-
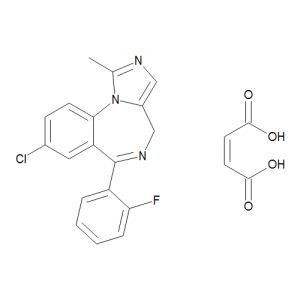
Midazolam Maleate
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H13 Cl F N3 . C4 H4 O4
-

Midazolam Maleate
$877.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H13 Cl F N3 . C4 H4 O4
-

Midazolam Maleate
$1,506.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H13 Cl F N3 . C4 H4 O4
-
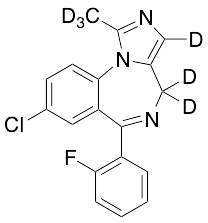
Midazolam-d6
$289.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18D6H7ClFN3
-

Midazolam-d6
$2,079.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18D6H7ClFN3
-

Midazolam-d6 (1mg/ml in Acetonitrile)
$793.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18D6H7ClFN3
-
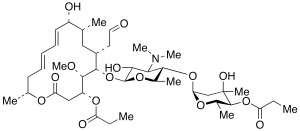
Midecamycin
$116.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C41 H67 N O15
-

Midecamycin
$188.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C41 H67 N O15
-
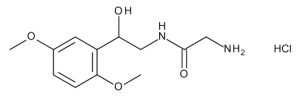
Midodrine Hydrochloride
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H18 N2 O4 . Cl H
-

Midodrine Hydrochloride
$81.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H18 N2 O4 . Cl H
-

Midodrine Hydrochloride
$122.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H18 N2 O4 . Cl H
-
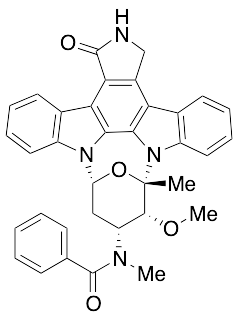
Midostaurin
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 H30 N4 O4
-

Midostaurin
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 H30 N4 O4
-

Midostaurin
$895.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 H30 N4 O4
-
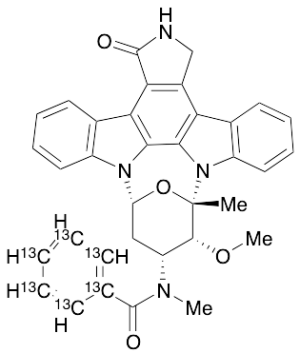
Midostaurin-13C6
$223.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29¹³C6H30N4O4
-

Midostaurin-13C6
$857.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29¹³C6H30N4O4
-

Midostaurin-13C6
$1,716.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29¹³C6H30N4O4
-
Midostaurin-D5
$645.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 D5 H25 N4 O4
-
Midostaurin-D5
$1,112.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C35 D5 H25 N4 O4
-
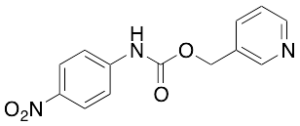
Mieshuan
$187.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H11N3O4
-

Mieshuan
$1,511.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H11N3O4
-

MIF, Human
$1,177.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine, existing as a homotrimer in vivo. MIF was originally identified as a T cell derived factor responsible for the inhibition of macrophage migration. However, recently MIF has received much more attention because of its possible roles in angiogenesis and cancer development. MIF is over-expressed in various cancers, including pancreatic, breast, colon, brain, prostate, skin, and lung. The intratumoral expression of MIF is strongly correlated with angiogenic growth factor expression, such as the expression of Interleukin 8 (IL-8) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), and with risk of recurrence after resection.
-
MIF, Human
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine, existing as a homotrimer in vivo. MIF was originally identified as a T cell derived factor responsible for the inhibition of macrophage migration. However, recently MIF has received much more attention because of its possible roles in angiogenesis and cancer development. MIF is over-expressed in various cancers, including pancreatic, breast, colon, brain, prostate, skin, and lung. The intratumoral expression of MIF is strongly correlated with angiogenic growth factor expression, such as the expression of Interleukin 8 (IL-8) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), and with risk of recurrence after resection.
-

MIF, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine, existing as a homotrimer in vivo. MIF was originally identified as a T cell derived factor responsible for the inhibition of macrophage migration. However, recently MIF has received much more attention because of its possible roles in angiogenesis and cancer development. MIF is over-expressed in various cancers, including pancreatic, breast, colon, brain, prostate, skin, and lung. The intratumoral expression of MIF is strongly correlated with angiogenic growth factor expression, such as the expression of Interleukin 8 (IL-8) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), and with risk of recurrence after resection.
-

MIF, Mouse
$2,518.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF or MMIF), also named as glycosylation-inhibiting factor (GIF), L-dopachrome isomerase, or phenylpyruvate tautomerase, is a protein encoded by the MIF gene. It is released from white blood cells by bacterial antigen stimulation to trigger an acute immune response, or by glucocorticoids to counter-act the inhibitory effects of glucocorticoids on immune system. MIF is a homotrimer of which each subunit contains 115 amino acids. As mentioned above, MIF is involved in the innate immune response to bacterial pathogens and counter-acts the anti-inflammatory activity of glucocorticoids. Furthermore, it also plays a role as mediator in regulating the function of macrophages in host defense and has phenylpyruvate tautomerase and dopachrome tautomerase activity in vitro. Mouse MIF is active on human cells, while human MIF is active on mouse cells. Mouse MIF is 99 %, 84 %, 90 %, and 90 % a.a. identical to rat, porcine, bovine and human MIF, respectively.
-

MIF, Mouse
$521.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF or MMIF), also named as glycosylation-inhibiting factor (GIF), L-dopachrome isomerase, or phenylpyruvate tautomerase, is a protein encoded by the MIF gene. It is released from white blood cells by bacterial antigen stimulation to trigger an acute immune response, or by glucocorticoids to counter-act the inhibitory effects of glucocorticoids on immune system. MIF is a homotrimer of which each subunit contains 115 amino acids. As mentioned above, MIF is involved in the innate immune response to bacterial pathogens and counter-acts the anti-inflammatory activity of glucocorticoids. Furthermore, it also plays a role as mediator in regulating the function of macrophages in host defense and has phenylpyruvate tautomerase and dopachrome tautomerase activity in vitro. Mouse MIF is active on human cells, while human MIF is active on mouse cells. Mouse MIF is 99 %, 84 %, 90 %, and 90 % a.a. identical to rat, porcine, bovine and human MIF, respectively.
-
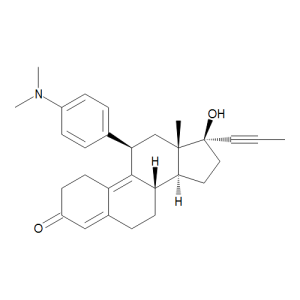
Mifepristone
$61.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29 H35 N O2
-

Mifepristone
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29 H35 N O2
-

Mifepristone
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29 H35 N O2
-
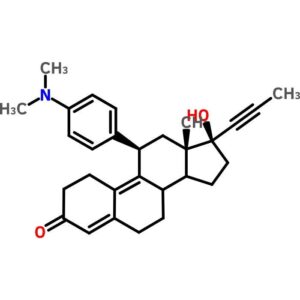
Mifepristone
$264.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMifepristone
-

Mifepristone
$874.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMifepristone
-
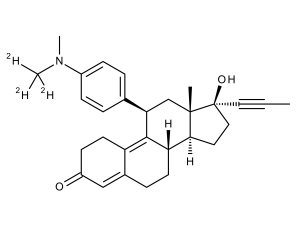
Mifepristone-D3
$257.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29 D3 H32 N O2
-

Mifepristone-d3
$2,000.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29 D3 H32 N O2
-

MIG/CXCL9, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsChemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9 (CXCL9), also known as monokine induced by interferon gamma (MIG), is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family. The CXCL9 gene is induced in macrophages and in primary glial cells of the central nervous system specifically in response to IFNγ. CXCL9 has been shown to be a chemoattractant for activated T-lymphocytes and TIL but not for neutrophils or monocytes. The human CXCL9 cDNA encodes a 125 amino acid residue precursor protein with a 22 amino acid residue signal peptide that is cleaved to yield a 103 amino acid residue mature protein. CXCL9 has an extended carboxy-terminus containing greater than 50% basic amino acid residues and is larger than most other chemokines. A chemokine receptor (CXCR3) specific for CXCL9 and IP-10 has recently been cloned and shown to be highly expressed in IL-2-activated T-lymphocytes.
-

MIG/CXCL9, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsChemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9 (CXCL9), also known as monokine induced by interferon gamma (MIG), is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family. The CXCL9 gene is induced in macrophages and in primary glial cells of the central nervous system specifically in response to IFNγ. CXCL9 has been shown to be a chemoattractant for activated T-lymphocytes and TIL but not for neutrophils or monocytes. The human CXCL9 cDNA encodes a 125 amino acid residue precursor protein with a 22 amino acid residue signal peptide that is cleaved to yield a 103 amino acid residue mature protein. CXCL9 has an extended carboxy-terminus containing greater than 50% basic amino acid residues and is larger than most other chemokines. A chemokine receptor (CXCR3) specific for CXCL9 and IP-10 has recently been cloned and shown to be highly expressed in IL-2-activated T-lymphocytes.
-
MIG/CXCL9, Mouse
$1,323.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsChemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9 (CXCL9), also known as monokine induced by interferon gamma (MIG), is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family.The CXCL9 gene is induced in macrophages and in primary glialcells of the central nervous systemin response to IFNγ. CXCL9 has been shown to be achemo attractant for activated Th1lymphocytes and tumor-infiltrating leukocytes (TILs) but not for neutrophils or monocytes. CXCL is also involved in other cellular activities including inhibition of tumor growth, angiogenesis, and inhibition of colony formation of hematopoietic progenitors. CXCL9 is closely related to two other CXC chemokines, CXCL10 and CXCL11.CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 all elicit their chemotactic functions by interacting with the chemokine receptor CXCR3.






