Ambient
Showing 109451–109500 of 166681 results
-
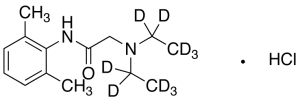
Lidocaine-d10 Hydrochloride (1.0 mg/mL in Methanol)
$208.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 D10 H12 N2 O . Cl H
-
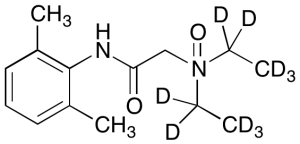
Lidocaine-d10 N-Oxide
$179.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H12D10N2O2
-

Lidocaine-d10 N-Oxide
$1,405.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H12D10N2O2
-
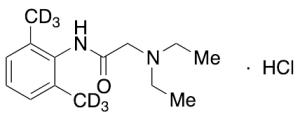
Lidocaine-d6 Hydrochloride
$221.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H17D6ClN2O
-

Lidocaine-d6 Hydrochloride
$465.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H17D6ClN2O
-

Lidocaine-d6 Hydrochloride
$1,682.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H17D6ClN2O
-

Lidocaine, USP
$92.17 Add to cart View Product DetailsLidocaine, USP
-

Lidocaine, USP
$227.65 Add to cart View Product DetailsLidocaine, USP
-

Lidocaine, USP
$825.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsLidocaine, USP
-

Lidocaine, USP
$2,687.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsLidocaine, USP
-

Lidocaine, USP
$6,873.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsLidocaine, USP
-

Lids for 25mL solution reservoirs, sterile, 5 per bag
$31.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsReservoir, divided, 50mL non-sterile, bulk pack, 100/cs
-

Lids for 50mL solution reservoirs, sterile, 5 per bag
$66.90 Add to cart View Product DetailsReservoir, 100mL sterile , Individually wrapped, 100/cs
-

Lids, 96 well Transp Btm, All 384 well plates, Pack Of 50
$117.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsLids, 96 well Transp Btm, All 384 well plates, Pack Of 50
-
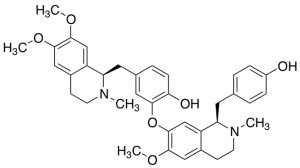
Liensinine
$56.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C37H42N2O6
-

Liensinine
$79.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C37H42N2O6
-

Liensinine
$199.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C37H42N2O6
-
LIF, Human
$1,470.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-

LIF, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-

LIF, Human
$224.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-

LIF, Mouse
$2,117.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-

LIF, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-

LIF, Mouse
$314.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsLeukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the long four-helix bundle cytokine superfamily. LIF shares tertiary structure with several other cytokines, including Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Oncostatin M, ciliary neurotropic factor, and cardiotrophin-1, and their functions in vivo are also redundant to some extent. LIF can bind to the common receptor of IL-6 subfamily, gp130, and then recruit its own receptor LIF Receptor to form a ternary complex. The basal expression of LIF in vivo is low; and its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory factors, including lipopolysaccharide, IL-1, and IL-17, and inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents, including IL-4 and IL-13. The functions of LIF include proliferation of primordial germ cells, regulation in blastocyst implantation and early pregnancy, and maintenance of pluripotent embryonic stem cells.
-
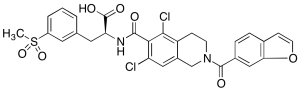
Lifitegrast
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29 H24 Cl2 N2 O7 S
-

Lifitegrast
$81.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29 H24 Cl2 N2 O7 S
-

Lifitegrast
$609.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29 H24 Cl2 N2 O7 S
-

Light Green SF Yellowish
$52.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Green SF Yellowish
-

Light Green SF Yellowish
$144.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Green SF Yellowish
-

Light Green SF Yellowish
$374.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Green SF Yellowish
-

Light Green SF Yellowish
$2,310.02 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Green SF Yellowish
-
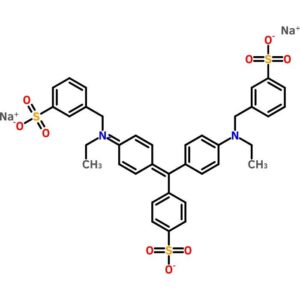
Light Green SF Yellowish
$10,271.90 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Green SF Yellowish
-
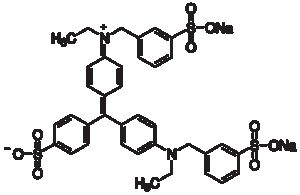
Light Green SF Yellowish
$103.86 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Green Sf Yellowish
-
Light Green SF Yellowish (Technical Grade)
$55.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C37 H34 N2 O9 S3 . 2 Na
-

Light Green SF Yellowish (Technical Grade)
$66.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C37 H34 N2 O9 S3 . 2 Na
-

Light Green SF Yellowish (Technical Grade)
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C37 H34 N2 O9 S3 . 2 Na
-

Light Meter (Foot-Candles)
$103.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Meter (Foot-Candles)
-

Light Meter (Lux & Foot-Candles)
$134.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Meter (Lux & Foot-Candles)
-

Light Meter Lux
$103.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Meter Lux
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$79.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$102.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$233.62 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$827.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$538.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$2,625.90 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$77.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$99.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$349.97 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$1,240.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$1,037.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF
-

Light Mineral Oil, NF
$2,448.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsLight Mineral Oil, NF






