Shop
Showing 81951–82000 of 278485 results
-

B4GALT4 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

B4GALT4 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
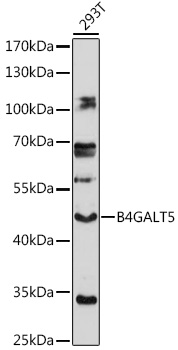
B4GALT5 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

B4GALT5 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

B6R Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

B6R Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

B7-1(CD80) Fc Chimera, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsB7-1/CD80 and B7-2/CD86, together with their receptors CD28 and CTLA-4, constitute one of the dominant co-stimulatory pathways that regulate T- and B-cell responses. Although both CTLA-4 and CD28 can bind to the same ligands, CTLA-4 binds to B7-1 and B7-2 with a 20-100 fold higher affinity than CD28 and is involved in the down-regulation of the immune response. Mature human B7-1 consists of a 208 amino acid extracellular domain (ECD) with two immunoglobulin-like domains, a 21 amino acid transmembrane domain, and a 25 amino acid cytoplasmic domain. Both human and mouse B7-1 and B7-2 can bind to either human or mouse CD28 and sCTLA-4. B7-1 is expressed on activated B cells, activated T cells, and macrophages. B7-2 is constitutively expressed on interdigitating dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, peripheral blood dendritic cells, memory B cells, and germinal center B cells.
-

B7-1(CD80) Fc Chimera, Human
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsB7-1/CD80 and B7-2/CD86, together with their receptors CD28 and CTLA-4, constitute one of the dominant co-stimulatory pathways that regulate T- and B-cell responses. Although both CTLA-4 and CD28 can bind to the same ligands, CTLA-4 binds to B7-1 and B7-2 with a 20-100 fold higher affinity than CD28 and is involved in the down-regulation of the immune response. Mature human B7-1 consists of a 208 amino acid extracellular domain (ECD) with two immunoglobulin-like domains, a 21 amino acid transmembrane domain, and a 25 amino acid cytoplasmic domain. Both human and mouse B7-1 and B7-2 can bind to either human or mouse CD28 and sCTLA-4. B7-1 is expressed on activated B cells, activated T cells, and macrophages. B7-2 is constitutively expressed on interdigitating dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, peripheral blood dendritic cells, memory B cells, and germinal center B cells.
-

B7-1(CD80) Fc Chimera, Human
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsB7-1/CD80 and B7-2/CD86, together with their receptors CD28 and CTLA-4, constitute one of the dominant co-stimulatory pathways that regulate T- and B-cell responses. Although both CTLA-4 and CD28 can bind to the same ligands, CTLA-4 binds to B7-1 and B7-2 with a 20-100 fold higher affinity than CD28 and is involved in the down-regulation of the immune response. Mature human B7-1 consists of a 208 amino acid extracellular domain (ECD) with two immunoglobulin-like domains, a 21 amino acid transmembrane domain, and a 25 amino acid cytoplasmic domain. Both human and mouse B7-1 and B7-2 can bind to either human or mouse CD28 and sCTLA-4. B7-1 is expressed on activated B cells, activated T cells, and macrophages. B7-2 is constitutively expressed on interdigitating dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, peripheral blood dendritic cells, memory B cells, and germinal center B cells.
-
B7-2/CD86 Fc Chimera, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsB7-1 and B7-2 are homologous costimulatory ligands expressed on the surface of antigen presenting cells (APCs), both are type 1 transmembrane proteins with a membrane distal IgV and a membrane proximal IgC domain. They share ~25% sequence homology and interact with the same receptors, CD28 and CTLA-4.Binding of these molecules to the T cell costimulatory receptors, CD28 and CTLA-4, is essential for the activation and regulation of T cell immunity. T cell activation requires engagement of the T cell receptor (TCR) with the peptide–MHC complex presented on the cell surface of antigen presenting cells (APCs). In addition to this antigen-specific interaction, a second interaction involving costimulatory receptors (CD28, ICOS) on T cells and their respective ligands (B7-1/B7-2, ICOS-L) on APCs is required for optimal T cell activation. B7-1 and B7-2 may also function to deliver signal into dendritic cells. While B7-1 favors binding to CTLA-4, B7-2 shows a preference for CD28.
-

B7-2/CD86 Fc Chimera, Human
$215.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsB7-1 and B7-2 are homologous costimulatory ligands expressed on the surface of antigen presenting cells (APCs), both are type 1 transmembrane proteins with a membrane distal IgV and a membrane proximal IgC domain. They share ~25% sequence homology and interact with the same receptors, CD28 and CTLA-4.Binding of these molecules to the T cell costimulatory receptors, CD28 and CTLA-4, is essential for the activation and regulation of T cell immunity. T cell activation requires engagement of the T cell receptor (TCR) with the peptide–MHC complex presented on the cell surface of antigen presenting cells (APCs). In addition to this antigen-specific interaction, a second interaction involving costimulatory receptors (CD28, ICOS) on T cells and their respective ligands (B7-1/B7-2, ICOS-L) on APCs is required for optimal T cell activation. B7-1 and B7-2 may also function to deliver signal into dendritic cells. While B7-1 favors binding to CTLA-4, B7-2 shows a preference for CD28.
-

B7-H3 Fc Chimera, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3), a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is also known CD276, which contains two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains and two Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains. B7-H3 may participate in the regulation of T-cell-mediated immune response. B7-H3 also plays a protective role in tumor cells by inhibiting natural-killer mediated cell lysis as well as a role of marker for detection of neuroblastoma cells. Furthermore, B7-H3 is involved in the development of acute and chronic transplant rejection and in the regulation of lymphocytic activity at mucosal surfaces. Human B7-H3 does not bind any known members of the CD28 family of immunoreceptor. However, B7-H3 has been shown to bind an unidentified counter-receptor on activated T cells to co-stimulate the proliferation of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells. B7-H3 has also been found to enhance the induction of primary cytotoxic T lymphocytes and stimulate IFN-gamma production.
-

B7-H3 Fc Chimera, Human
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3), a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is also known CD276, which contains two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains and two Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains. B7-H3 may participate in the regulation of T-cell-mediated immune response. B7-H3 also plays a protective role in tumor cells by inhibiting natural-killer mediated cell lysis as well as a role of marker for detection of neuroblastoma cells. Furthermore, B7-H3 is involved in the development of acute and chronic transplant rejection and in the regulation of lymphocytic activity at mucosal surfaces. Human B7-H3 does not bind any known members of the CD28 family of immunoreceptor. However, B7-H3 has been shown to bind an unidentified counter-receptor on activated T cells to co-stimulate the proliferation of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells. B7-H3 has also been found to enhance the induction of primary cytotoxic T lymphocytes and stimulate IFN-gamma production.
-

B7-H3, His, Human
$1,293.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3), a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is also known CD276, which contains two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains and two Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains. B7-H3 may participate in the regulation of T-cell-mediated immune response. B7-H3 also plays a protective role in tumor cells by inhibiting natural-killer mediated cell lysis as well as a role of marker for detection of neuroblastoma cells. Furthermore, B7-H3 is involved in the development of acute and chronic transplant rejection and in the regulation of lymphocytic activity at mucosal surfaces. Human B7-H3 does not bind any known members of the CD28 family of immunoreceptor. However, B7-H3 has been shown to bind an unidentified counter-receptor on activated T cells to costimulate the proliferation of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells. B7-H3 has also been found to enhance the induction of primary cytotoxic T lymphocytes and stimulate IFN-gamma production.
-

B7-H3, His, Human
$340.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3), a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is also known CD276, which contains two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains and two Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains. B7-H3 may participate in the regulation of T-cell-mediated immune response. B7-H3 also plays a protective role in tumor cells by inhibiting natural-killer mediated cell lysis as well as a role of marker for detection of neuroblastoma cells. Furthermore, B7-H3 is involved in the development of acute and chronic transplant rejection and in the regulation of lymphocytic activity at mucosal surfaces. Human B7-H3 does not bind any known members of the CD28 family of immunoreceptor. However, B7-H3 has been shown to bind an unidentified counter-receptor on activated T cells to costimulate the proliferation of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells. B7-H3 has also been found to enhance the induction of primary cytotoxic T lymphocytes and stimulate IFN-gamma production.
-
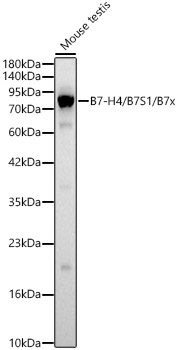
B7-H4 / B7S1 / B7x Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

B7-H4 / B7S1 / B7x Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
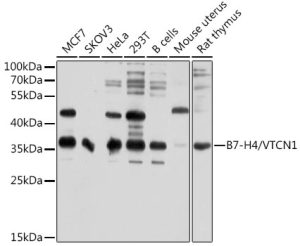
B7-H4/VTCN1 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

B7-H4/VTCN1 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

B9D1 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

B9D1 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
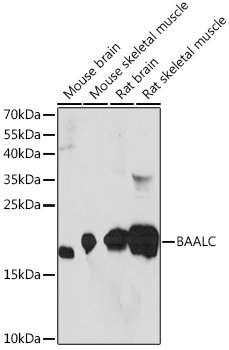
BAALC Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

BAALC Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

BAAT Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

BAAT Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

Baby rabbit complement, 3-4 weeks
$177.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsComplement obtained from a pool of baby rabbits, 3-4 weeks old. The rabbits are of United States origin. The complement is supplied as a liquid and does not contain any preservatives.
-

Baccatin III
$181.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31 H38 O11
-

Baccatin III
$218.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31 H38 O11
-

Baccatin III
$250.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31 H38 O11
-
Baccatin VI
$253.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C37 H46 O14
-

Baccatin VI
$1,976.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C37 H46 O14
-

Bacdown Antimicrobial Soap, 5 L Refill
$331.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsBacdown Antimicrobial Soap, 5 L Refill
-

BACE1 Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

BACE1 Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

BACE1 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

BACE1 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

BACE2 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

BACE2 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

BACH1 Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

BACH1 Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

BACH1 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

BACH1 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

Bacillus cereus Agar Base (PEMBA), 500 g
$109.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsBacillus cereus Agar Base (PEMBA), 500 g
-

Bacillus cereus MYP Agar, 5 kg
$1,365.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsBacillus cereus MYP Agar, 5 kg
-

Bacillus cereus MYP Agar, 500 g
$144.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsBacillus cereus MYP Agar, 500 g
-

Bacitracin (>80%)
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C66 H103 N17 O16 S . 3 [C65 H101 N17 O16 S]
-

Bacitracin (>80%)
$91.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C66 H103 N17 O16 S . 3 [C65 H101 N17 O16 S]
-

Bacitracin (>80%)
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C66 H103 N17 O16 S . 3 [C65 H101 N17 O16 S]
-
Bacitracin A
$411.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C66H103N17O16S
-

Bacitracin A (Technical Grade)
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C66H103N17O16S






