Shop
Showing 157101–157150 of 279040 results
-

IFN-α 1b, Human
$133.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsAt least 23 different variants of IFN-alpha are known. The individual proteins have molecular masses between 19-26 kDa and consist of proteins with lengths of 156-166 and 172 amino acids. All IFN-alpha subtypes possess a common conserved sequence region between amino acid positions 115-151 while the amino-terminal ends are variable. Many IFN-alpha subtypes differ in their sequences at only one or two positions. Naturally occurring variants also include proteins truncated by 10 amino acids at the carboxy-terminal end.
-

IFN-α 1b, Human
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsAt least 23 different variants of IFN-alpha are known. The individual proteins have molecular masses between 19-26 kDa and consist of proteins with lengths of 156-166 and 172 amino acids. All IFN-alpha subtypes possess a common conserved sequence region between amino acid positions 115-151 while the amino-terminal ends are variable. Many IFN-alpha subtypes differ in their sequences at only one or two positions. Naturally occurring variants also include proteins truncated by 10 amino acids at the carboxy-terminal end.
-

IFN-α 2a, Human
$405.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-Alpha 2a (IFN-Alpha 2a), Human produced by leukocytes is a member of Interferon family. IFN-alpha is mainly involved in innate immune response against a broad range of viral infections. IFN-alpha 2 has three acid stable forms (a,b,c) signaling through IFNAR2. IFN-alpha 2a shares 99.4% , 98.8% aa sequence identity with IFN-alpha 2b and 2c respectively. IFN-alpha contains four highly conserved cysteine residues which form two disulfide bonds, one of which is necessary for biological activity.
-

IFN-α 2a, Human
$36.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-Alpha 2a (IFN-Alpha 2a), Human produced by leukocytes is a member of Interferon family. IFN-alpha is mainly involved in innate immune response against a broad range of viral infections. IFN-alpha 2 has three acid stable forms (a,b,c) signaling through IFNAR2. IFN-alpha 2a shares 99.4% , 98.8% aa sequence identity with IFN-alpha 2b and 2c respectively. IFN-alpha contains four highly conserved cysteine residues which form two disulfide bonds, one of which is necessary for biological activity.
-

IFN-α 2a, Human
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-Alpha 2a (IFN-Alpha 2a), Human produced by leukocytes is a member of Interferon family. IFN-alpha is mainly involved in innate immune response against a broad range of viral infections. IFN-alpha 2 has three acid stable forms (a,b,c) signaling through IFNAR2. IFN-alpha 2a shares 99.4% , 98.8% aa sequence identity with IFN-alpha 2b and 2c respectively. IFN-alpha contains four highly conserved cysteine residues which form two disulfide bonds, one of which is necessary for biological activity.
-

IFN-α 2b, Human
$931.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-Alpha 2b (IFN-Alpha 2b) produced by leukocytes is a member of Interferon family. IFN-alpha is mainly involved in innate immune response against a broad range of viral infections. IFN-alpha 2 has three acid stable forms (a,b,c) signaling through IFNAR2. IFN-alpha 2b shares 99.4% aa sequence identity with both IFN-alpha 2a and 2c. IFN-alpha contains four highly conserved cysteine residues which form two disulfide bonds, one of which is necessary for biological activity.
-

IFN-α 2b, Human
$34.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-Alpha 2b (IFN-Alpha 2b) produced by leukocytes is a member of Interferon family. IFN-alpha is mainly involved in innate immune response against a broad range of viral infections. IFN-alpha 2 has three acid stable forms (a,b,c) signaling through IFNAR2. IFN-alpha 2b shares 99.4% aa sequence identity with both IFN-alpha 2a and 2c. IFN-alpha contains four highly conserved cysteine residues which form two disulfide bonds, one of which is necessary for biological activity.
-

IFN-α 2b, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-Alpha 2b (IFN-Alpha 2b) produced by leukocytes is a member of Interferon family. IFN-alpha is mainly involved in innate immune response against a broad range of viral infections. IFN-alpha 2 has three acid stable forms (a,b,c) signaling through IFNAR2. IFN-alpha 2b shares 99.4% aa sequence identity with both IFN-alpha 2a and 2c. IFN-alpha contains four highly conserved cysteine residues which form two disulfide bonds, one of which is necessary for biological activity.
-

IFN-β, Human
$99.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-beta (IFN-β), acting via STAT1 and STAT2, is known to upregulate and downregulate a wide variety of genes, most of which are involved in the antiviral immune response. It is a member of Type I IFNs, which include IFN-α, -β, τ, and –ω. IFN-β plays an important role in inducing non-specific resistance against a broad range of viral infections. It also affects cell proliferation and modulates immune responses.
-

IFN-β, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-beta (IFN-β), acting via STAT1 and STAT2, is known to upregulate and downregulate a wide variety of genes, most of which are involved in the antiviral immune response. It is a member of Type I IFNs, which include IFN-α, -β, τ, and –ω. IFN-β plays an important role in inducing non-specific resistance against a broad range of viral infections. It also affects cell proliferation and modulates immune responses.
-

IFN-γ R II, Human
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsIFN-gamma Receptor II, also known as IFNGR2 and IFNGT1, is a transmembrane protein belonging to the type II cytokine receptor family. IFNGR2 is a non-ligand-binding beta chain of the IFN-gamma receptor. It is an integral part of the IFN-gamma signaling transduction pathway and is likely to interact with GAF, JAK1 and JAK2. Defects in IFNGR2 are a cause of autosomal recessive Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease (MSMD), also known as familial disseminated atypical mycobacterial infection.
-

IFN-γ R II, Human
$133.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsIFN-gamma Receptor II, also known as IFNGR2 and IFNGT1, is a transmembrane protein belonging to the type II cytokine receptor family. IFNGR2 is a non-ligand-binding beta chain of the IFN-gamma receptor. It is an integral part of the IFN-gamma signaling transduction pathway and is likely to interact with GAF, JAK1 and JAK2. Defects in IFNGR2 are a cause of autosomal recessive Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease (MSMD), also known as familial disseminated atypical mycobacterial infection.
-

IFN-γ, Human
$487.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) is amacrophage‐activating factor and the lone member of Interferon type II.The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune‐related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Human
$34.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) is amacrophage‐activating factor and the lone member of Interferon type II.The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune‐related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Human
$99.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) is amacrophage‐activating factor and the lone member of Interferon type II.The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune‐related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Human
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) is amacrophage‐activating factor and the lone member of Interferon type II.The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune‐related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Human(CHO-expressed)
$521.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) is amacrophage-activating factor and the lone member of Interferon type II. The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Human(CHO-expressed)
$36.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) is amacrophage-activating factor and the lone member of Interferon type II. The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Human(CHO-expressed)
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) is amacrophage-activating factor and the lone member of Interferon type II. The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Mouse
$414.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsSharing 41% sequence identity with human Interferon gamma (hIFN–γ), mouse IFN gamma (mIFN–γ)is a macrophage-activating factor.The active form of IFN–γ is an antiparallel dimer that sets off IFN–γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN–γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity.While IFN–γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN–γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in avariety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsSharing 41% sequence identity with human Interferon gamma (hIFN–γ), mouse IFN gamma (mIFN–γ)is a macrophage-activating factor.The active form of IFN–γ is an antiparallel dimer that sets off IFN–γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN–γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity.While IFN–γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN–γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in avariety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Mouse
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsSharing 41% sequence identity with human Interferon gamma (hIFN–γ), mouse IFN gamma (mIFN–γ)is a macrophage-activating factor.The active form of IFN–γ is an antiparallel dimer that sets off IFN–γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN–γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity.While IFN–γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN–γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in avariety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Mouse
$280.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsSharing 41% sequence identity with human Interferon gamma (hIFN–γ), mouse IFN gamma (mIFN–γ)is a macrophage-activating factor.The active form of IFN–γ is an antiparallel dimer that sets off IFN–γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN–γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity.While IFN–γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN–γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in avariety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Rat
$836.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-gamma (IFN-γ), also known as Type II interferon or immune interferon, is a cytokine produced primarily by T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells. The protein shares no significant homology with IFN-β or the various IFN-α family proteins. Mature IFN-γ exists as noncovalently-linked homodimers. It shares high sequence indentity with mouse IFN-γ (86 %). IFN-γ was originally characterized based on its antiviral activities. The protein also exerts antiproliferative, immunoregulatory and proinflammatory activities and is thus important in host defense mechanisms. IFN-γ induces the production of cytokines, upregulates the expression of class I and II MHC antigens, Fc receptor and leukocyte adhesion molecules. It modulates macrophage effector functions, influences isotype switching and potentiates the secretion of immunoglobulins by B cells. Additionally, IFN-γ augments TH1 cell expansion and may be required for TH1 cell differentiation.
-

IFN-γ, Rat
$163.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-gamma (IFN-γ), also known as Type II interferon or immune interferon, is a cytokine produced primarily by T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells. The protein shares no significant homology with IFN-β or the various IFN-α family proteins. Mature IFN-γ exists as noncovalently-linked homodimers. It shares high sequence indentity with mouse IFN-γ (86 %). IFN-γ was originally characterized based on its antiviral activities. The protein also exerts antiproliferative, immunoregulatory and proinflammatory activities and is thus important in host defense mechanisms. IFN-γ induces the production of cytokines, upregulates the expression of class I and II MHC antigens, Fc receptor and leukocyte adhesion molecules. It modulates macrophage effector functions, influences isotype switching and potentiates the secretion of immunoglobulins by B cells. Additionally, IFN-γ augments TH1 cell expansion and may be required for TH1 cell differentiation.
-

IFN-γ, Rat (CHO-expressed)
$521.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-γ (IFN-γ), also known as Type II interferon or immune interferon, is a cytokine produced primarily by T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells. The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Rat (CHO-expressed)
$36.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-γ (IFN-γ), also known as Type II interferon or immune interferon, is a cytokine produced primarily by T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells. The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Rat (CHO-expressed)
$76.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-γ (IFN-γ), also known as Type II interferon or immune interferon, is a cytokine produced primarily by T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells. The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-λ1, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsIL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29, also named interferon-λ2 (IFN-λ2), IFN-λ3, and IFN-λ1, respectively, are newly identified class II cytokine receptor ligands that are distantly related to members of the IL-10 family (11-13% aa sequence identity) and the type I IFN family (15-19% aa sequence identity). The expression of IL-28A, B, and IL-29 is induced by virus infection or double-stranded RNA. All three cytokines exert bioactivities that overlap those of type I IFNs, including antiviral activity and up-regulation of MHC class I antigen expression. The three proteins signal through the same heterodimeric receptor complex that is composed of the IL-10 receptor β (IL-10 Rβ) and a novel IL-28 receptor α (IL-28 Rα, also known as IFN-λR1). Ligand binding to the receptor complex induces Jak kinase activation and STAT1 and STAT2 tyrosine phosphorylation.
-

IFN-λ1, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsIL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29, also named interferon-λ2 (IFN-λ2), IFN-λ3, and IFN-λ1, respectively, are newly identified class II cytokine receptor ligands that are distantly related to members of the IL-10 family (11-13% aa sequence identity) and the type I IFN family (15-19% aa sequence identity). The expression of IL-28A, B, and IL-29 is induced by virus infection or double-stranded RNA. All three cytokines exert bioactivities that overlap those of type I IFNs, including antiviral activity and up-regulation of MHC class I antigen expression. The three proteins signal through the same heterodimeric receptor complex that is composed of the IL-10 receptor β (IL-10 Rβ) and a novel IL-28 receptor α (IL-28 Rα, also known as IFN-λR1). Ligand binding to the receptor complex induces Jak kinase activation and STAT1 and STAT2 tyrosine phosphorylation.
-

IFN-ω, Human
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-Omega (IFN-ω) coded by IFNW1 gene in human, is a number of the type I interferon family, which includes IFN-a, IFN-β, and IFN-ω. The IFNAR-1/IFNAR-2 receptor complex can help with the signal transduction, followed the antiviral or the antiproliferative actions. IFN-ω is derived from IFN-a/β and share 75% sequence with IFN-a. It has two intramolecular disulfide bonds which are crucial for activities. Mire-Sluis et al have described bioassays for IFN-α, IFN-β, and IFN-ω that exploit the ability of these factors to inhibit proliferation of TF-1 cells induced by GM-CSF. The bioassays can be used also with Epo and TF-1 cells, or Epo and Epo-transfected UT-7 cells.
-
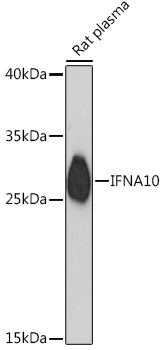
IFNA10 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IFNA10 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
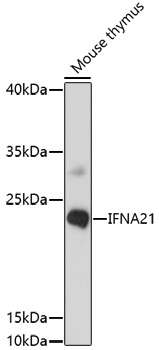
IFNA21 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IFNA21 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
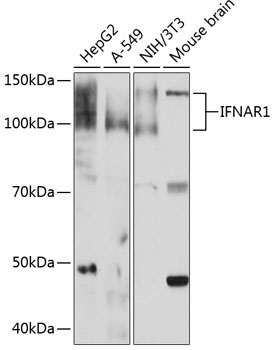
IFNAR1 Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IFNAR1 Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IFNAR1 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IFNAR1 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IFNAR1 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IFNAR1 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IFNAR2 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IFNAR2 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IFNGR1 Rabbit mAb
$264.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IFNGR1 Rabbit mAb
$103.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMonoclonal Antibodies
-

IFNGR1 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IFNGR1 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
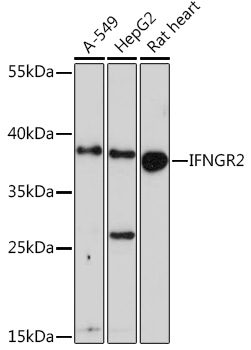
IFNGR2 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-
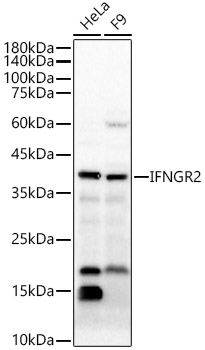
IFNGR2 Rabbit pAb
$86.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies
-

IFNGR2 Rabbit pAb
$239.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsPolyclonal Antibodies






