10g
Showing 2951–3000 of 4637 results
-

Glutathione reduced form
$75.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsGlutathione reduced form
-
Glycerin Rosin Ester
$83.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-
Glycerine Trioleate
$151.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C57 H104 O6
-

Glycerol Phosphate Disodium Salt Hydrate, Isomeric Mixture
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H7Na2O6P • xH2O
-
![Glycerol, [Matrix for FABMS and liquid SIMS]](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/56-81-5-300x300.jpg)
Glycerol, [Matrix for FABMS and liquid SIMS]
$138.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsGlycerol, [Matrix for FABMS and liquid SIMS]
-
Glycidol (~90%)
$71.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3 H6 O2
-
Glycine
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2 H5 N O2
-

Glycine Anhydride(2,5-Piperazinedione)
$87.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H6 N2 O2
-

Glycine Methyl Ester Hydrochloride
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H8ClNO2
-

Glycochenodeoxycholic Acid Sodium Salt
$3,414.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsGlycochenodeoxycholic Acid Sodium Salt
-
Glycocholic Acid
$427.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H43 N O6
-
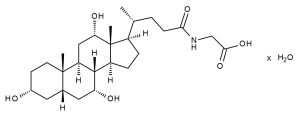
Glycocholic Acid Hydrate
$550.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H43 N O6 . x[H2 O]
-

Glycolic Acid
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2 H4 O3
-
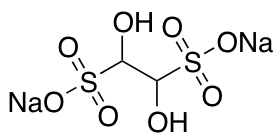
Glyoxal Sodium Bisulfite (contains oligomers)
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H4Na2O8S2
-
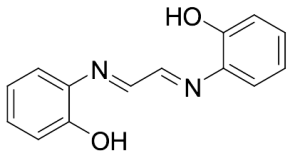
Glyoxalbis(2-hydroxyanil)
$423.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H12 N2 O2
-

Glyoxylic Acid (50% aqueous solution)
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2 H2 O3
-

Glyoxylic Acid Monohydrate
$56.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H4O4
-

GM-CSF, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can induce human endothelial cells to migrate and proliferate. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-
GM-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Human Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can induce human endothelial cells to migrate and proliferate. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

GM-CSF, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

GM-CSF, Mouse
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

GM-CSF, Rat
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

GM-CSF, RhesusMacaque
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsGranulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) was initially characterized as a growth factor that can support the in vitro colony formation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is produced by a number of different cell types, including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to cytokine of immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) is a growth factor for erythroid, megakaryocyte, and eosinophil progenitors. On mature hematopoietic, monocytes/macrophages and eosinophils. Additionally, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) can stimulate the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines, including osteogenic sarcoma, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma cell lines.
-

Gold Chloride, Trihydrate, Reagent, ACS
$1,816.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsGold Chloride, Trihydrate, Reagent, ACS
-

Gold Chloride, Trihydrate, Reagent, ACS
$7,502.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsGold Chloride, Trihydrate, Reagent, ACS
-

Gold Potassium Cyanide, Powder
$3,190.17 Add to cart View Product DetailsGold Potassium Cyanide, Powder
-
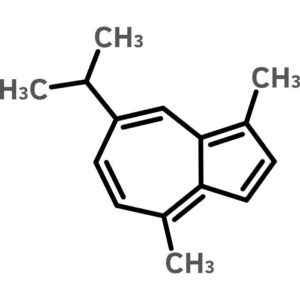
Guaiazulene
$88.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsGuaiazulene
-
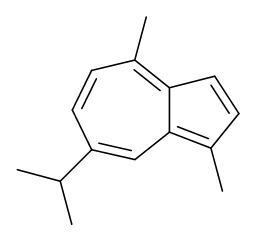
Guaiazulene
$357.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H18
-

Guanidine Hydrochloride
$50.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C H5 N3 . Cl H
-
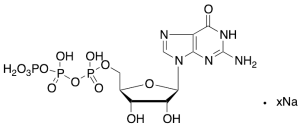
Guanosine 5′-(Tetrahydrogen triphosphate) Sodium Salt (>80%)
$1,617.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H16N5O14P3 xNa
-
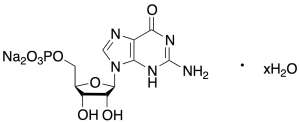
Guanosine 5′-Monophosphate Disodium Salt
$84.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H12N5Na2O8P • x(H2O)
-
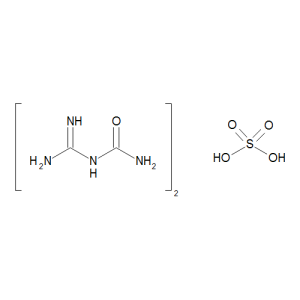
Guanyl Urea Sulfate
$100.91 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C2 H6 N4 O . H2 O4 S
-
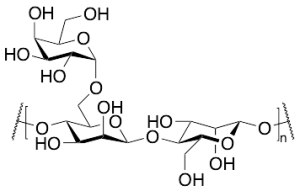
Guar Gum
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : (C18H30O16)n
-

Gum Rosin
$146.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-

H1N1 (A/California/04/2009), Hemagglutinin
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsInfluenza hemagglutinin (HA) is a glycoprotein found on the surface of the influenzavirus. It is responsible for binding the virus to cells with sialic acid on their membranes, such as cells in the upper respiratory tract or erythrocytes. It is also responsible for the fusion of the viral envelope with the endosome membrane after the pH has been reduced. The name “hemagglutinin” comes from the protein’s ability to cause red blood cells (erythrocytes) to clump together in vitro. HA has two functions. First, it allows the recognition of target vertebrate cells, accomplished through binding to these cells’ sialic acid-containing receptors. Second, once bound it facilitates the entry of the viral genome into the target cells by causing the fusion of the host endosomal membrane with the viral membrane. H1N1 is a subtype of influenza virus A and the most common cause of influenza in humans.
-

HB-EGF, Human
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsProheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF), also known as DTR, DTS and HEGFL, is a member of the EGF family of mitogens. It is expressed in macrophages, monocytes, endothelial cells and muscle cells. HB-EGF signals through the EGF receptor to stimulate the proliferation of smooth muscle cells, epithelial cells and keratinocytes. Compared to EGF, HB-EGF binds to the EGF receptor with a higher affinity and has been shown to bemore mitogenic, likely due to its ability to bind to heparin and heparin sulfate proteoglycans. HB-EGF has also been reported to act as a diphtheria toxin receptor, mediating endocytosis of the bound toxin. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor has been shown to interact with NRD1, Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 and BAG1.
-

HB-EGF, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsProheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF), also known as DTR, DTS and HEGFL, is a member of the EGF family of mitogens. It is expressed in macrophages, monocytes, endothelial cells and muscle cells. HB-EGF signals through the EGF receptor to stimulate the proliferation of smooth muscle cells, epithelial cells and keratinocytes. Compared to EGF, HB-EGF binds to the EGF receptor with a higher affinity and has been shown to bemore mitogenic, likely due to its ability to bind to heparin and heparin sulfate proteoglycans. HB-EGF has also been reported to act as a diphtheria toxin receptor, mediating endocytosis of the bound toxin. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor has been shown to interact with NRD1, Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 and BAG1.
-

HB-EGF, Mouse
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsHeparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) is a member of the EGF family of proteins. HB-EGF-like growth factor is synthesized as a membrane-anchored mitogenic and chemotactic glycoprotein. An epidermal growth factor produced by monocytes and macrophages, due to an affinity for heparin is termed HB-EGF. It has been shown to play a role in wound healing, cardiac hypertrophy and heart development and function. The transmembrane form of HB-EGF is the unique receptor for diptheria toxin and functions in juxtacrine signaling in cells. Both forms of HB-EGF participate in normal physiological processes and in pathological processes including tumor progression and metastasis, organ hyperplasia, and atherosclerotic disease. HB-EGF can bind two locations on cell surfaces, heparan sulfate proteoglycans and EGF-receptor effecting cell to cell interactions.
-

Heat Stable FGF-basic, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsHeat Stable FGF-basic, Human is a pleiotropic cytokine and one of the prototypic members of the heparin-binding FGF family. Like other FGF family members, FGF-basic has the β trefoil structure. In vivo, FGF-basic is produced by a variety of cells, including cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, and vascular cells. FGF-basic regulates a variety of processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, adhesion, motility, apoptosis, limb formation and wound healing. FGF-basic can be tumorigenic due to its role in angiogenesis and blood vessel remodeling. The angiogenic effects of FGF-basic can produce beneficial cardioprotection during acute heart injury.
-
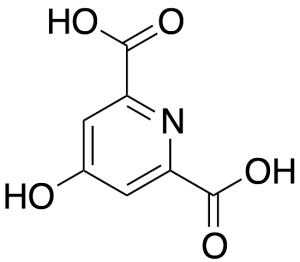
Helidaminic Acid
$142.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7H5NO5
-

Hematoxylin
$222.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsHematoxylin
-
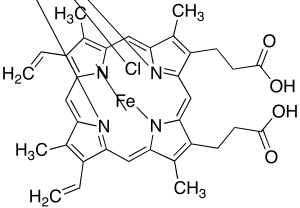
Hemin Chloride (Technical grade)
$131.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H32ClFeN4O4
-

Heneicosane
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H44
-
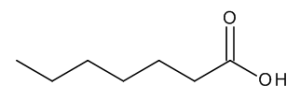
Heptanoic Acid
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H14 O2
-
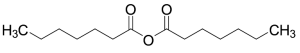
Heptanoic Anhydride
$50.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H26O3
-
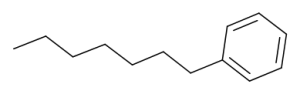
Heptylbenzene
$204.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H20
-

Heregulin β-1, Human
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsNeuregulins or neuroregulins are a family of four structurally related proteins (NRG1, NRG2, NRG3 and NRG4) that are members of the EGF family of proteins. Studies indicate neuregulins function in nervous system development with essential roles in vertebrate embryogenesis including: cardiac development, Schwann cell and oligodendrocyte differentiation, certain aspects of neuronal development, and the formation of neuromuscular synapses. Neuregulin 1 is essential for the normal development of the nervous system and the heart. It is produced in numerous isoforms by alternative splicing, allowing it to perform a variety of functions. All NRG1 isoforms contain an EGF-like domain that is required for direct binding to ErbB3 or ErbB4 receptor tyrosine kinases. The transmembrane NRG1 isoforms contain an extracellular domain that can be proteolytically cleaved to release soluble growth factors.
-
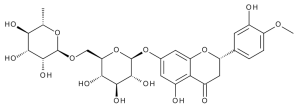
Hesperidine
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28 H34 O15
-
Hetastarch, Technical Grade
$112.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-
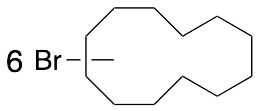
Hexabromocyclododecane (Mixture of Diastereomers)
$114.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H18Br6






