10g
Showing 4401–4450 of 4637 results
-

Thionyl Chloride
$126.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : Cl2 O S
-
Thiophanate-Methyl
$357.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H14 N4 O4 S2
-
Thiophenol
$174.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H6 S
-
Thiophosgene
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CCl2S
-

Thioridazine Hydrochloride
$242.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H26 N2 S2 . Cl H
-

Thiosemicarbazide
$179.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : CH5N3S
-
Thiotriazinone
$95.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H5 N3 O2 S
-

Thiourea
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C H4 N2 S
-
Thioxanthen-9-one
$168.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H8 O S
-
Thymol
$163.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H14 O
-
Thymoquinone
$264.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H12 O2
-
Thyroxine Sodium Salt
$324.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H10 I4 N O4 . Na
-
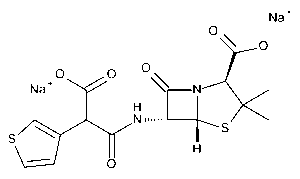
Ticillin Disodium Salt
$627.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H14 N2 O6 S2 . 2 Na
-
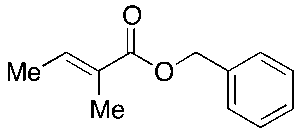
Tiglic Acid Benzyl Ester
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12H14O2
-
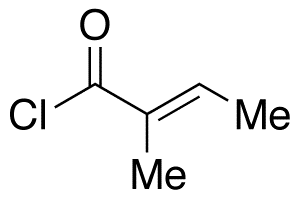
Tigloyl Chloride
$380.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H7 Cl O
-
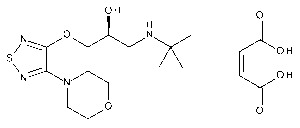
Timolol Maleate
$394.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H24 N4 O3 S . C4 H4 O4
-

Tin (II) Chloride
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : SnCl2
-

Tin(II) Oxalate
$79.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2O4Sn
-
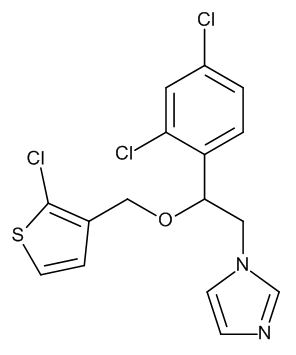
Tioconazole
$147.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16 H13 Cl3 N2 O S
-
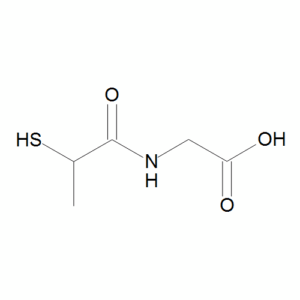
Tiopronin
$179.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H9 N O3 S
-

Tiron, Powder, Reagent
$31.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsTiron, Powder, Reagent
-

Titanium (III) Oxide, -100 Mesh
$250.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsTitanium (III) Oxide, -100 Mesh
-
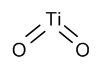
Titanium Dioxide
$163.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : O2 Ti
-

TNF R I, Human
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsTNF Receptor Type I, is also known as TNF R-p55/p60 and TNFRSF1A. It is a type I transmembrane protein member of the TNF receptor superfamily. It is expressed in most cell types. Binding of either TNF-α or TNF-β to TNF-R1 initiates a signal transduction pathway that results in the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB, whose target genes are involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses, and, in certain cells, induce apoptosis. TNF-R1 is essential for proper development of lymph node germinal centers and Peyer’s patches and for combating intracellular pathogens such as Listeria. It is stored in the Golgi and translocates to the cell surface following proinflammatory stimuli.
-

TNF-α (80-235aa), Mouse
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune disease. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune diseasesuch as Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis and graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-α, Bovine
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-α) plays a major role in regulating growth, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune diseases. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells. In addition to inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, studies indicate TNF is involved in tumor igenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis and graft-versus-host disease.
-

TNF-α, His, Human
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune diseases. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases including Crohn’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis as well as graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-α, Human
$50.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-a) is a homotrimer with a subunit molecular mass of 17.3 kDa. Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha(TNF-a) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune diseases; and in viral, bacterial, fungal, and parasitic infections. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases including Crohn’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis as well as graft-versus-host disease.
-

TNF-α, Human (P. pastoris-expressed)
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune diseases. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases including Crohn’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis as well as graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-
TNF-α, Porcine
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune disease. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune disease including Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis and graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-α, Rat
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsTumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) plays a major role in growth regulation, differentiation, inflammation, viral replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune disease. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF has been found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune disease including Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis and graft-versus-host disease. TNF alpha-1a is a potent lymphoid factor that exerts cytotoxic effects on a wide range of tumor cells and certain other target cells.
-

TNF-β, Human
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsTNF is secreted by macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, T-cells, NK-cells following their stimulation by bacterial LPS. Cells expressing CD4 secrete TNF-alpha while CD8 cells secrete little or no TNF-alpha. The synthesis of TNF-alpha is induced by many different stimuli including interferons, IL2, GM-CSF. TNF-β is a potent mediator of inflammatory and immune responses. It belongs to the TNF family of ligands, and signals through TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNF-β is produced by activated T and B lymphocytes, and has similar activities to TNF-α. It mediates a large variety of inflammatory, immunostimulatory, and antiviral responses.
-
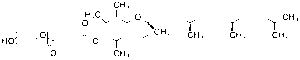
Tocofersolan
$114.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C33H54O5(C2H4O)n
-
Tolazoline Hydrochloride
$99.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H12 N2 . Cl H
-

Tolfenamic Acid
$91.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H12 Cl N O2
-
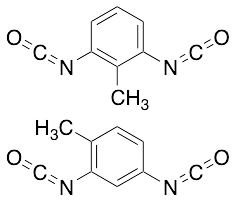
Toluene Diisocyanate
$231.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C9 H6 N2 O2
-
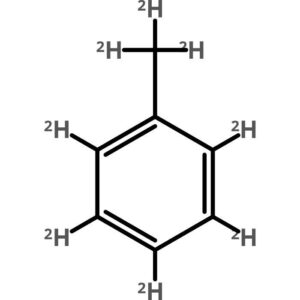
Toluene-d8, 99.6 Atom Percent D
$323.12 Add to cart View Product DetailsToluene-d8, 99.6 Atom Percent D
-

Toluidine Blue O
$110.02 Add to cart View Product DetailsToluidine Blue O
-
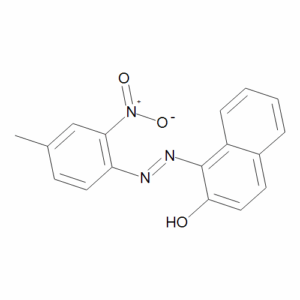
Toluidine Red
$163.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H13 N3 O3
-
Tosylurethane
$1,358.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H13 N O4 S
-

TPO, His, Human
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsThrombopoietin (TPO) is a glycoprotein hormone which belongs to the EPO/TPO family. It produced by the liver and kidney which regulates the production of platelets. TPO stimulates the production and differentiation of megakaryocytes, the bone marrow cells that bud off large numbers of platelets. Lineage-specific cytokine affects the proliferation and maturation of megakaryocytes from their committed progenitor cells. It acts at a late stage of megakaryocyte development. It may be the major physiological regulator of circulating platelets.
-

TPO, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThrombopoietin (TPO), also known as C-mpl ligand, MGDF and Thpo, is a glycoprotein hormone belonging to the EPO/TPO family. It is expressed mainly in the liver, kidney and skeletal muscle. TPO binds and signals through MLP/C_MPL receptor. It stimulates the proliferation and maturation of megakaryocytes from their committed progenitor cells, and it regulates the production and circulation of platelets. TPO has also been reported to promote the apoptosis of hypoxia-sensitized neurons and to inhibit neuronal differentiation.
-
TRAIL, Mouse
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsTNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), also known as Tumor Necrosis Factor Super-Family 10 (TNFSF10) or apoptosis 2 ligand (Apo2L), is a pleiotropic cytokine thatbelongs to the TNF superfamily. Full length TRAIL expressed in vivo is a type II transmembrane protein, although the soluble form also exists and functions. TRAIL has four major receptors: two death receptors DR4 and DR5, and two decoy receptors DcR1 and DcR2. TRAIL binds to the death receptors which recruits the FAS-associated death domain and activates caspases 8 and 10 which eventually leads to apoptosis. Because of its antitumor potential, TRAIL is activelystudied as a therapeutic agent. On the other hand, abnormal expression of TRAIL in small arteries can induce the proliferation of smooth muscle cells, thereby increasing vascular remodeling and pulmonary arterial hypertension.
-

TRAIL/Apo2L, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsTRAIL/Apo2L, also known as Tumor Necrosis Factor Super-Family 10 (TNFSF10), is a pleiotropic cytokine thatbelongs to the TNF superfamily. The full length TRAIL expressed in vivo is a Type II transmembrane protein, although the soluble form also exists and functions. TRAIL has four major receptors: two death receptors DR4 and DR5, two decoy receptors DcR1 and DcR2. TRAIL binds to the death receptors, recruits the FAS-associated death domain, activates caspases 8 and 10, and eventually leads to apoptosis. Because of its antitumor potential, TRAIL is actively studied as a therapeutic agent. On the other hand, abnormal expression of TRAIL in small arteries can induce the proliferation of smooth muscle cells, resulting in increasing vascular remodeling and pulmonary arterial hypertension.
-
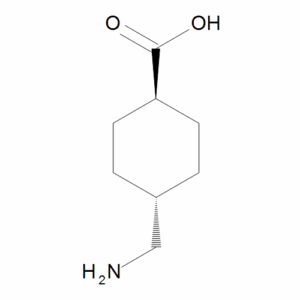
Tranexamic Acid
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H15 N O2
-
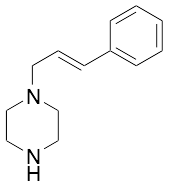
trans-1-Cinnamylpiperazine
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H29 N O3
-

trans-1-Cinnamylpiperazine Dihydrochloride
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H18N2 . 2(HCl)
-

trans-1,2-Cyclohexanediol
$111.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H12 O2
-
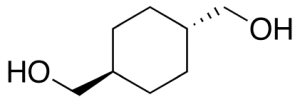
trans-1,4-Cyclohexanedimethanol
$116.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8H16O2
-

trans-2-Butene-1,4-diol
$357.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4 H8 O2






