10g
Showing 4551–4600 of 4637 results
-
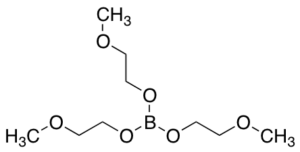
Tris(2-methoxyethyl)orthoborate (>90%)
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H21BO6
-

Tris(2-methylphenyl)phosphine
$149.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H21P
-
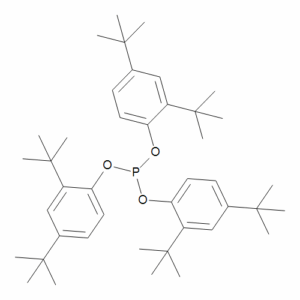
Tris(2,4-tert-butylphenyl) Phosphite
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C42 H63 O3 P
-
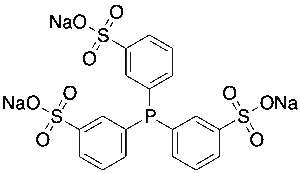
Tris(3-sulfophenyl)phosphine Trisodium (~85%)
$281.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H12Na3O9PS3
-
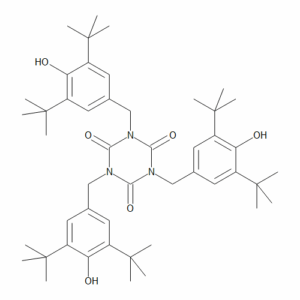
Tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl) Isocyanurate
$116.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C48 H69 N3 O6
-
Tris(4-nitrophenyl)phosphate
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H12 N3 O10 P
-
Tris(4-tert-butyl-3-hydroxy-2,6-dimethylbenzyl) Isocyanurate
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C42 H57 N3 O6
-
Tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium
$342.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 3 C17 H14 O . 2 Pd
-
Tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0)-chloroform Adduct
$602.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C52 H43 Cl3 O3 Pd2
-
Tris(p-tert-butylphenyl) Phosphate
$1,621.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H39 O4 P
-
Trisodium Isocitric Acid
$685.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H5 O7 . 3 Na
-
Triticonazole
$175.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H20 Cl N3 O
-

Triton X-100
$238.91 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H22O.(OCH2CH2)n
-
Trityl Chloride
$60.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19H15Cl
-

TrkA, Human
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsTyrosine kinase receptor A (Trk-A) is a member of the neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor family which includes three members: Trk-A, Trk-B and Trk-C. Trk-A is involved in the development and maturation of the central and peripheral nervous systems through regulation of proliferation, differentiation and survival of sympathetic neurons.
-
Trolox
$576.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 H18 O4
-

Tropic Acid
$238.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H10 O3
-
Tropicamide
$225.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsTropicamide
-
Tropine
$139.73 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H15 N O
-

Tropolone
$61.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H6 O2
-
Trypan Blue (Technical Grade)
$219.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H24 N6 O14 S4 . 4 Na
-
Tryptamine
$55.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H12 N2
-

TSLP, Human
$163.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsTSLP is a hemopoietic protein that is expressed in the heart, liver and prostate. TSLP overlaps biological activities with IL-7 and binds with the heterodimeric receptor complex consisting of the IL-7R alpha chain (IL-7Rα) and the TSLP-specific chain (TSLPR). Like IL-7, TSLP induces phosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT5, but uses kinases other than the JAKs for activation. TSLP prohibited apoptosis and stimulated growth of the human acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-derived cell line MUTZ3. It induces the release of T cell-attracting chemokines TARC and MDC from monocytes and activates CD11c(+) dendritic cells (DCs). TSLP activated DCs primed naive T cells to produce the proallergic cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, TNFα) while down-regulating IL-10 and IFN-γ suggesting a role in initiating allergic inflammation.
-
Tungsten(VI) Oxide
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : WO3
-

TWEAK, Human
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsTWEAK, short for TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis, is also known as TNFSF12 and DR3LG. It is a type II transmembrane protein belonging to the TNF superfamily. It is expressed widely in many tissues, such as the heart, skeletal muscle, spleen and peripheral blood. Binding of TWEAK to its receptor TWEAKR induces NF-κB activation, chemokine secretion and apoptosis in certain cell types. TWEAK has also been reported to promote endothelial cell proliferation and migration, thus serving as a regulator of angiogenesis.
-
Tyrosol
$169.91 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H10 O2
-

United Scientific® HEXAGONAL MASS, 10G
$0.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsHEXAGONAL MASS, 10G
-

United Scientific® INDIVIDUAL BRASS MASS, 10G
$2.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsINDIVIDUAL BRASS MASS, 10G
-

United Scientific® INDIVIDUAL HOOKED BRASS MASS, 10G
$0.78 Add to cart View Product DetailsINDIVIDUAL HOOKED BRASS MASS, 10G
-
Urea
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C H4 N2 O
-

Urea-d4
$1,332.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C D4 N2 O
-
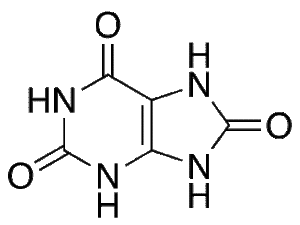
Uric Acid
$1,241.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H4 N4 O3
-
Uridine 5’-Monophosphate Disodium Salt
$146.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H11 N2 O9 P . 2 Na
-
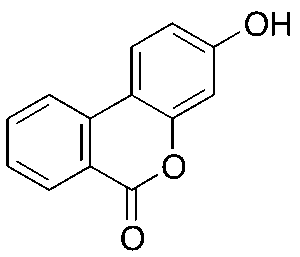
Urolithin B
$1,143.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H8O3
-
Ursodeoxycholic Acid Methyl Ester
$379.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H42 O4
-
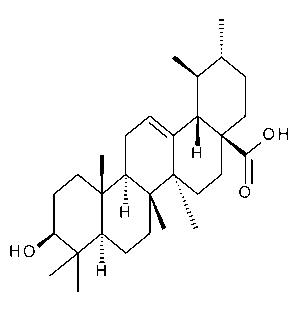
Ursolic Acid
$401.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C30 H48 O3
-

Usnic Acid Sodium
$440.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18 H15 O7 . Na
-

Valeraldehyde(Pentanal)
$250.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H10 O
-

Valerophenone
$81.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H14 O
-

Valeryl Chloride
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H9ClO
-
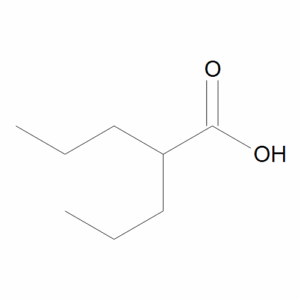
Valproic Acid
$125.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H16 O2
-
Valproic Acid Methyl Ester
$1,561.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H18 O2
-
Vanadium Chloride
$90.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : VCl3
-
Vanadium(IV) Oxide Acetylacetonate
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10H14O5V
-
Vanadium(V) Oxide
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : O5 V2
-

Vancomycin Hydrochloride
$346.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsVancomycin Hydrochloride
-
Vanillin
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C8 H8 O3
-
VEGF-A164, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) was initially purified from media conditioned by normal bovine pituitary folliculo-stellate cells and by a variety of transformed cell lines as a mitogen specific for vascular endothelial cells. It was subsequently found to be identical to an independently discovered vascular permeability factor (VPF), which was previously identified in media conditioned by tumor cell lines based on its ability to increase the permeability of capillary blood vessels. Three mouse cDNA clones, which arise through alternative splicing and which encode mature mouse monomeric VEGF having 120, 164, or 188, amino acids, respectively, have been identified. Two receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), Flt-1 and Flk-1 (the mouse homologue of human KDR), both members of the type III subclass of RTKs containing seven immunoglobulin-like repeats in their extracellular domains, have been shown to bind VEGF with high affinity. The roles of the homodimers of KDR, Flt, and the heterodimer of KDR/Flt in VEGF signal transduction remain to be elucidated. In vivo, VEGF has been found to be a potent angiogenesis inducer.
-

VEGF-C, Human
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family, is active in angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and endothelial cell growth and survival, and can also affect the permeability of blood vessels. VEGF-C is expressed in various tissues, however it is not produced in peripheral blood lymphocytes. It forms cell surface-associated non-covalent disulfide linked homodimers, and can bind and activate both VEGFR-2 (flk1) and VEGFR-3 (flt4) receptors. The structure and function of VEGF-C is similar to those of vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D).
-

VEGF-D, Human
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsVascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-D, also known as c-Fos-induced growth factor (FIGF), is a member of the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. It is expressed highly in lung, heart and small intestine, and at lower levels in skeletal muscle, colon and pancreas. It binds to VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 receptors and activates downstream signals. VEGF-D is a growth factor active in angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and endothelial cell growth. It is involved in many developmental and physiological processes including the formation of venous and lymphatic vascular systems during embryogenesis and the maintenance of differentiated lymphatic endothelium in adults. In tumor pathology, it has been reported to play a role in restructuring of lymphatic channels and regional lymph node metastasis.






