1mg
Showing 4201–4250 of 6155 results
-
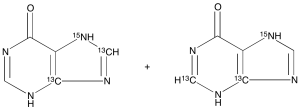
Hypoxanthine-13C2,15N (Mixture) Please see H998504
$209.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3¹³C2H4N3¹⁵NO
-

Iberin
$60.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H9 N O S2
-
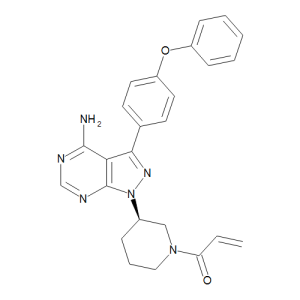
Ibrutinib
$63.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H24 N6 O2
-
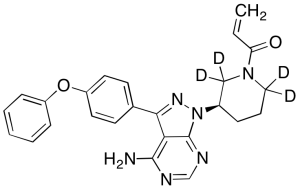
Ibrutinib-d4 (Major)
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H20D4N6O2
-
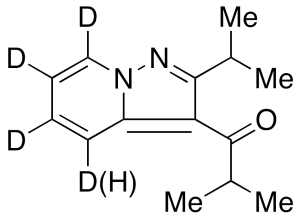
Ibudilast-d3 (Major)
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14 D4 H14 N2 O
-
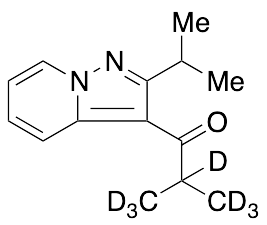
Ibudilast-d7
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H11D7N2O
-
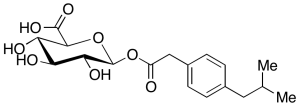
Ibufenac Acyl-Beta-D-Glucuronide
$273.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H24O8
-
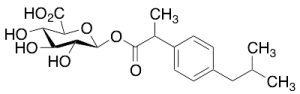
Ibuprofen Acyl-Beta-D-glucuronide (mixture of diastereomers)
$107.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 H26 O8
-
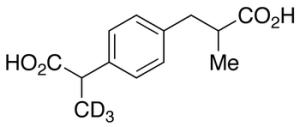
Ibuprofen Carboxylic Acid-d3 (Mixture of Diastereomers)
$222.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H13D3O4
-
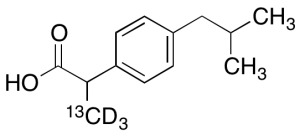
Ibuprofen-13C,d3
$112.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C1213CH15D3O2
-
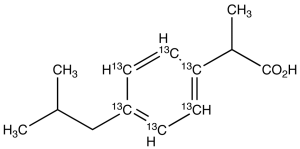
Ibuprofen-13C6
$259.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C713C6H18O2
-
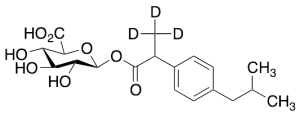
Ibuprofen-d3 Acyl-Beta-D-glucuronide (mixture of diastereomers)
$296.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C19 D3 H23 O8
-
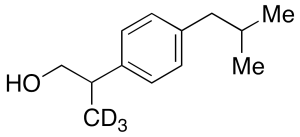
Ibuprofen-d3 Alcohol
$257.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13H17D3O
-
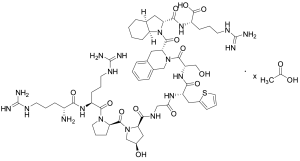
Icatibant Acetate
$156.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C59 H89 N19 O13 S . x(C2 H4 O2)
-
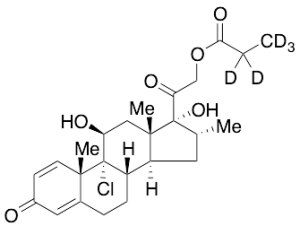
Icomethasone 21-Propionate-d5
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 D5 H28 Cl O6
-
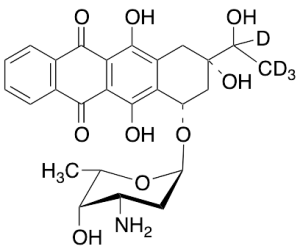
Idarubicinol-d4 (Mixture of Diastereomers) (>80%)
$4,033.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 D4 H25 N O9
-
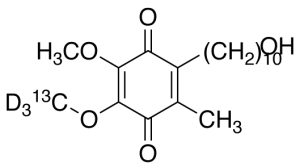
Idebenone-13C,d3
$232.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C1813CH27D3O5
-

iFluor488-Protein L
$174.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtein L is a cell surface protein from Peptostreptoccocus magnus that binds to the variable light chains (kappa chain) of immunoglobulins without interfering with antigen binding. In contrast to IgG-binding proteins, such as protein A and protein G, which bind to the Fc region of immunoglobulins, protein L can be used for the detection and purification of mammalian kappa light chain antibodies of all classes. Since no part of the heavy chain is involved in the binding interaction, Protein L binds a wider range of antibody classes than Protein A or G. Protein L binds to representatives of all antibody classes, including IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE and IgD. Single chain variable fragments (scFv) and Fab fragments also bind to Protein L.
-

iFluor647-Protein L
$174.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtein L is a cell surface protein from Peptostreptoccocus magnus that binds to the variable light chains (kappa chain) of immunoglobulins without interfering with antigen binding. In contrast to IgG-binding proteins, such as protein A and protein G, which bind to the Fc region of immunoglobulins, protein L can be used for the detection and purification of mammalian kappa light chain antibodies of all classes. Since no part of the heavy chain is involved in the binding interaction, Protein L binds a wider range of antibody classes than Protein A or G. Protein L binds to representatives of all antibody classes, including IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE and IgD. Single chain variable fragments (scFv) and Fab fragments also bind to Protein L.
-

IFN-α 2a, Human
$405.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-Alpha 2a (IFN-Alpha 2a), Human produced by leukocytes is a member of Interferon family. IFN-alpha is mainly involved in innate immune response against a broad range of viral infections. IFN-alpha 2 has three acid stable forms (a,b,c) signaling through IFNAR2. IFN-alpha 2a shares 99.4% , 98.8% aa sequence identity with IFN-alpha 2b and 2c respectively. IFN-alpha contains four highly conserved cysteine residues which form two disulfide bonds, one of which is necessary for biological activity.
-

IFN-α 2b, Human
$931.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-Alpha 2b (IFN-Alpha 2b) produced by leukocytes is a member of Interferon family. IFN-alpha is mainly involved in innate immune response against a broad range of viral infections. IFN-alpha 2 has three acid stable forms (a,b,c) signaling through IFNAR2. IFN-alpha 2b shares 99.4% aa sequence identity with both IFN-alpha 2a and 2c. IFN-alpha contains four highly conserved cysteine residues which form two disulfide bonds, one of which is necessary for biological activity.
-

IFN-γ, Human
$487.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) is amacrophage‐activating factor and the lone member of Interferon type II.The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune‐related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Human(CHO-expressed)
$521.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman Interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) is amacrophage-activating factor and the lone member of Interferon type II. The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Mouse
$414.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsSharing 41% sequence identity with human Interferon gamma (hIFN–γ), mouse IFN gamma (mIFN–γ)is a macrophage-activating factor.The active form of IFN–γ is an antiparallel dimer that sets off IFN–γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN–γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity.While IFN–γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN–γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in avariety of cancers.
-

IFN-γ, Rat
$836.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-gamma (IFN-γ), also known as Type II interferon or immune interferon, is a cytokine produced primarily by T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells. The protein shares no significant homology with IFN-β or the various IFN-α family proteins. Mature IFN-γ exists as noncovalently-linked homodimers. It shares high sequence indentity with mouse IFN-γ (86 %). IFN-γ was originally characterized based on its antiviral activities. The protein also exerts antiproliferative, immunoregulatory and proinflammatory activities and is thus important in host defense mechanisms. IFN-γ induces the production of cytokines, upregulates the expression of class I and II MHC antigens, Fc receptor and leukocyte adhesion molecules. It modulates macrophage effector functions, influences isotype switching and potentiates the secretion of immunoglobulins by B cells. Additionally, IFN-γ augments TH1 cell expansion and may be required for TH1 cell differentiation.
-

IFN-γ, Rat (CHO-expressed)
$521.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterferon-γ (IFN-γ), also known as Type II interferon or immune interferon, is a cytokine produced primarily by T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells. The active form of IFN-γ is an antiparallel dimer that interacts with the receptor IFN-γR1 and sets off IFN-γ/JAK/STAT pathway. IFN-γ signaling does diverse biological functions primarily related to host defense and immune regulation, including antiviral and antibacterial defense, apoptosis, inflammation, and innate and acquired immunity. While IFN-γ–induced inflammatory cascade summons a variety of immune-related cell types, such as macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), IFN-γ is also implicated in resistance to NK cell and CTL responses and in immune escape in a variety of cancers.
-

IFN-λ1, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsIL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29, also named interferon-λ2 (IFN-λ2), IFN-λ3, and IFN-λ1, respectively, are newly identified class II cytokine receptor ligands that are distantly related to members of the IL-10 family (11-13% aa sequence identity) and the type I IFN family (15-19% aa sequence identity). The expression of IL-28A, B, and IL-29 is induced by virus infection or double-stranded RNA. All three cytokines exert bioactivities that overlap those of type I IFNs, including antiviral activity and up-regulation of MHC class I antigen expression. The three proteins signal through the same heterodimeric receptor complex that is composed of the IL-10 receptor β (IL-10 Rβ) and a novel IL-28 receptor α (IL-28 Rα, also known as IFN-λR1). Ligand binding to the receptor complex induces Jak kinase activation and STAT1 and STAT2 tyrosine phosphorylation.
-
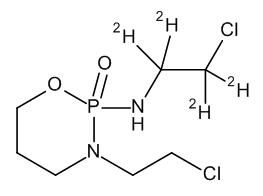
Ifosfamide-d4
$221.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 2H4 H11 Cl2 N2 O2 P
-

IGF-BP-2, His, Human
$1,863.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsIGF-BP-2, also known as Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2, IBP-2 and BP-2, is a cysteine-rich secreted protein belonging to the IGF-binding protein superfamily. It is expressed by the central nervous system, bone cells and reproductive tissues. IGF-BP-2 binds to both IGF-I and IGF-II, with a much higher binding affinity to IGF-II than IGF-I. IGF-BP-2 has been shown to inhibitand stimulate the growth promoting effects of IGFs, thus serving as a regulator for IGF distribution, function and activity.
-

IGF-BP-3, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsIGF-BP3 is a 30 kDa cysteine-rich secreted protein. It is the major IGF binding protein present in the plasma of human and animals and it is also found in α-granules of platelets. In addition to its ability to modulate the activity of IGF-I and IGF-II, IGF-BP3 exerts inhibitory effects on follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) activity. Decreased plasma levels of IGF-BP3 often results in dwarfism, whereas elevated levels of IGF-BP3 may lead to acromegaly. The expression of IGF-BP3 in fibroblasts is stimulated by mitogenic growth factors such as Bombesin, Vasopressin, PDGF, and EGF.
-

IGF-BP-4, His, Human
$1,863.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsInsulin-like growth factor-binding protein 4 (IGF-BP-4), also known as IBP-4, is a secreted glycoprotein belonging to the IGFBP family. IGF-BP-4 is produced by osteoblasts, epidermis, ovarian follicles and other tissues. It binds both insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I and II, and it circulates in the plasma in both glycosylated and non-glycosylated forms. IGF-BP-4 prolongs the half-life of the IGFs and has been shown to inhibit or stimulate the growth-promoting effects of the IGFs. Pregnancy Associated Plasma Protein A (PAPP-A) proteolytically cleaves IGF-BP-4 and reduces its affinity to bind IGFs, and thus serves as an important regulator of IGF-BP-4 function.
-

IGF-I, Bovine
$120.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsInsulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called Somatomedin, is a hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin but has a much higher growth-promoting activity. IGF-1 consists of 70 amino acids in a single chain with three intramolecular disulfide bridges. IGF-1 may be a physiological regulator of [1-14C]-2-deoxy-D-glucose (2DG) transport and glycogen synthesis in osteoblasts. It is able to stimulate glucose transport in bone-derived osteoblastic (PyMS) cells and is effective at much lower concentrations than insulin, not only regarding glycogen and DNA synthesis but also with regard to enhancing glucose uptake. It may also play a role in synapse maturation.
-
IGF-I, Human
$120.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsInsulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) also known as Somatamedin C is a hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin. Human IGF-I has two isoforms (IGF-IA and IGF-IB) which are differentially expressed by various tissues. Mature human IGF-I shares 94% and 96% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat IGF-I, respectively. Both IGF-I and IGF-II (another ligand of IGF) can signal through the IGF-I receptor (IGFIR), but only IGF-II can bind the IGF-II receptor (IGFIIR/ Mannose-6-phosphate receptor). IGF-I plays an important role in childhood growth and continues to have anabolic effects in adults.
-

IGF-I, Mouse
$612.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsInsulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I) is a single chain 7 kDa growth-promoting polypeptide originally identified as somatomedin-c. It belongs to the IGF family of peptides, which also includes IGF-II and insulin. The gene expression of IGF-I is mainly regulated by Growth Hormone, and IGF-I executes its functions via signaling through transmembrane tyrosine receptors (IGF Receptors). Most circulating IFG-I is associated with the IGF Binding Protein 3 (IGFBP-3), and the IGFBPs may inhibit the actions of IGFs by competing against the IGF Receptors. IGF-I is active in post-natal and adult animals, and is crucial for somatic growth, as IGF-I null mice show marked retardation in utero. IGF-I is involved in carcinogenesis, and related to prostate cancer as well.
-

IGF-I, Rat
$612.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsInsulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I) is a single chain 7 kDa growth-promoting polypeptide originally identified as somatomedin-c. It belongs to the IGF family of peptides, which also includes IGF-II and insulin. The gene expression of IGF-I is mainly regulated by Growth Hormone, and IGF-I executes its functions via signaling through transmembrane tyrosine receptors (IGF Receptors). Most circulating IFG-I is associated with the IGF Binding Protein 3 (IGFBP-3), and the IGFBPs may inhibit the actions of IGFs by competing against the IGF Receptors. IGF-I is active in post-natal and adult animals, and is crucial for somatic growth, as IGF-I null mice show marked retardation in utero. IGF-I is involved in the carcinogenesis, and related to the prostate cancer as well.
-

IGF-I, Salmon
$1,138.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsInsulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called Somatomedin, is a hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin but has a much higher growth-promoting activity. IGF-1 consists of 70 amino acids in a single chain with three intramolecular disulfide bridges. IGF-1 may be a physiological regulator of [1-14C]-2-deoxy-D-glucose (5DG) transport and glycogen synthesis in osteoblasts. It is able to stimulate glucose transport in bone-derived osteoblastic (PyMS) cells and is effective at much lower concentrations than insulin, not only regarding glycogen and DNA synthesis but also with regard to enhancing glucose uptake. It may also play a role in synapse maturation.
-

IGF-II, Human
$560.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsInsulin-like Growth Factor II (IGF-II) is a single chain 7 kDa polypeptide, and shares a high degree of homology with insulin. During circulation in vivo, IGF-II is complexed to high affinity binding proteins, IGF Binding Proteins (IGFBP), which act as circulating reservoirs, transport IGF-II, and prolong the half life of IGF-II. The receptors of IGF-II (IGFRs) are transmembrane tyrosine receptors, and are heterotetrameric consisting of two α-subunits and two β-subunits. IGFRs execute their role via intracellullar signaling molecules, such as IRS, shc, and PI3K. The functions of IGF-II include promoting cell survival, growth, proliferation, differentiation and motility. In particular, IGF-II promotes proliferation, inhibits death, and stimulates transformation in breast cancer cells.
-
IHH, Human
$1,177.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe Indian Hedgehog protein (IHH) is one of three proteins in the mammalian hedgehog family, the others being desert hedgehog (DHH) and Sonic hedgehog (SHH). Hedgehog proteins are important signaling molecules during embryonic development and are highly conserved across species. Mouse and human IHH share 100% amino acid identity in the signaling domain, while mouse IHH and SHH share 90% amino acid identity in the N-terminal signaling domain. IHH mRNA expression is detected in fetal lung, gut, stomach, liver, kidney, pancreas and strongly in cartilage in growth regions of the developing bone. IHH has a specific role in bone growth and differentiation. In addition, IHH is involved in yolk sac vasculogenesis, having a central role in differentiation of epiblast cells into endothelial and red blood cells. IHH gene mutations cause the brachydactyly type A1 which is characterized by shortening or malformation of the phalanges and also the acrocapitofemoral dysplasia.
-

IL-1 RA, Human(HEK 293-expressed)
$737.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsIL-1 Receptor Antagonist, also known as IL-1RA, ICIL-1RA, IRAP and IL-1RN, is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. It is expressed by monocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, epithelial cells and fibroblasts. IL-1RA inhibits the activity of both IL-1alpha and IL-1beta, and modulates a variety of IL-1 related immune and inflammatory responses. It inhibits the activity of IL-1 by binding to the receptor IL-1R1 and preventing its association with the coreceptor IL-1RAP for signaling. Clinical studies are being conducted to investigate the use of IL-1RA in the treatment of sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis and chronic myelogenous leukemia.
-

IL-10, Human(CHO-expressed)
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-10 (IL-10), initially known as Cytokine Synthesis Inhibitory Factor (CSIF), belongs to the IL-10 family and shares more than 80% sequence homology with Epstein-Barr Virus protein BCRFI. It is produced by many immune cells, such as T-cells, macrophages, mast cells, and dendritic cells. It is usually secreted as a homodimer and, upon binding to its receptor, inhibits the synthesis of a number of cytokines, including IFN-gamma, IL-2, IL-3, TNF and GM-CSF produced by activated macrophages and Th2 cells. It also displays ability to suppress Antigen-Presenting Cell (APC) function. The net effect of Interleukin-10 appears to be inhibitory; however, stimulatory effects, such as stimulation of B cell maturation and antibody production, are also reported.
-

IL-10, Mouse(CHO-expressed)
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-10 (IL-10), initially known as Cytokine Synthesis Inhibitory Factor (CSIF), belongs to the IL-10 family and shares more than 80% sequence homology with the Epstein-Barr Virus protein BCRFI. It is produced by many immune cells, such as T-cells, macrophages, mast cells and dendritic cells. It is usually secreted as a homodimer and, upon binding to its receptor, inhibits the synthesis of a number of cytokines, including IFN-gamma, IL-2, IL-3, TNF and GM-CSF, by activated macrophages and Th2 cells. It also displays the ability to suppress Antigen-Presenting Cell (APC) function. The net effect of Interleukin-10 appears to be inhibitory; however, stimulatory effects, such as stimulation of B cell maturation and antibody production, are also reported.
-

IL-10, Rat (CHO-expressed)
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-10 (IL-10), initially known as Cytokine Synthesis Inhibitory Factor (CSIF), belongs to the IL-10 family and shares more than 80% sequence homology with the Epstein-Barr Virus protein BCRFI. It is produced by many immune cells, such as T-cells, macrophages, mast cells and dendritic cells. It is usually secreted as a homodimer and, upon binding to its receptor, inhibits the synthesis of a number of cytokines, including IFN-gamma, IL-2, IL-3, TNF and GM-CSF produced by activated macrophages and Th2 cells. It also displays the ability to suppress Antigen-Presenting Cell (APC) function. The net effect of Interleukin-10 appears to be inhibitory; however, stimulatory effects, such as stimulation of B cell maturation and antibody production, are also reported.
-

IL-11 Fc Chimera, Human
$2,328.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-11 is a pleiotropic cytokine that was originally detected in the conditioned medium ofan IL-1α-stimulated primate bone marrow stromal cell line (PU-34) as a mitogen for the IL-6-responsive mouse plasmacytoma cell line T11. IL-11 has multiple effects on both hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells. Many of the biological effects described for IL-11 overlap with those for IL-6. In vitro, IL-11 can synergize with IL-3, IL-4 and SCF to shorten the G0 period of early hematopoietic progenitors. IL-11 alsoenhances the IL-3-dependent megakaryocyte colony formation. IL-11 has been found to stimulate the T cell-dependent development of specific immunoglobulin-secreting B cells.
-

IL-11, Human(CHO-expressed)
$2,785.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-11 is a pleiotropic cytokine that was originally detected in the conditioned medium of an IL-1α-stimulated primate bone marrow stromal cell line (PU-34) as a mitogen for the IL-6-responsive mouse plasmacytoma cell line T11. IL-11 has multiple effects on both hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells. Many of the biological effects described for IL-11 overlap with those for IL-6. In vitro, IL-11 can synergize with IL-3, IL-4 and SCF to shorten the G0 period of early hematopoietic progenitors. IL-11 also enhances the IL-3-dependent megakaryocyte colony formation. IL-11 has been found to stimulate the T cell-dependent development of specific immunoglobulin-secreting B cells.
-

IL-11, Mouse(HEK 293-expressed)
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-11 (IL-11) is a pleiotropic cytokine that was originally detected in the conditioned medium of an IL-1α-stimulated primate bone marrow stromal cell line (PU-34) as a mitogen for the IL-6-responsive mouse plasmacytoma cell line T11. IL-11 contains no cysteine residues or potential glycosylation sites. IL-11 has multiple effects on both hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells. Many of the biological effects described for IL-11 overlap those for IL-6. In vitro, IL-11 can synergize with IL-3, IL-4 and SCF to shorten the G0 period of early hematopoietic progenitors. IL-11 also enhances the IL-3-dependent megakaryocyte colony formation. IL-11 has been found to stimulate the T cell dependent development of specific immunoglobulin-secreting B cell.
-

IL-12, His, Rat
$3,070.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-12 (IL-12), also known as NKSF, TCMF, CLMF and TSF, is a heterodimeric cytokine composed of p35 and p40 subunits. It is produced by monocytes, macrophages, B cells and dendritic cells in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharides and intracellular pathogens. IL-12 signals through the IL-12 receptor complex, which is comprised of IL-12 Rβ1 and IL-12 Rβ2. IL-12 induces the proliferation and activation of hematopoietic stem cells, natural killer cells and T- cells. It is indispensible during the development of Th1 cells, leading to the production of IFN-gamma and IL-2.
-

IL-12, Human(HEK 293-expressed)
$2,785.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin 12 (IL-12), also known as natural killer cell stimulatory factor (NKSF) or cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor (CLMF), is a pleiotropic cytokine originally identified in the medium of activated human B lymphoblastoid cell lines. The p40 subunit of IL-12 has been shown to have extensive amino acid sequence homology to the extracellular domain of the human IL-6 receptor while the p35 subunit shows distant but significant sequence similarity to IL-6, G-CSF, and chicken MGF. These observations have led to the suggestion that IL-12 might have evolved from a cytokine/soluble receptor complex. Human and mouse IL-12 share 70% and 60% amino acid sequence homology in their p40 and p35 subunits, respectively. IL-12 apparently shows species specificity with human IL-12 reportedly showing minimal activity in the mouse system.
-

IL-12, Mouse
$3,070.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin-12 (IL-12), also known as NKSF, TCMF, CLMF and TSF, is a heterodimeric cytokine composed of p35 and p40 subunits. It is produced by monocytes, macrophages, B cells and dendritic cells in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharides and intracellular pathogens. IL-12 signals throughtheIL-12 receptor complex, which is comprised of IL-12 Rβ1 and IL-12 Rβ2. IL-12 induces the proliferation and activation of hematopoietic stem cells, natural killer cells and T- cells. It is indispensible during the development of Th1 cells, leading to the production of IFN-gamma and IL-2.
-

IL-13 Variant, Human
$3,820.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe human IL-13 cDNA encodes a 132 amino acid protein containing a proposed 20 amino acid signal peptide. Human IL-13 shares approximately 30% amino acid sequence homology to human IL-4 and the two cytokines exhibit overlapping biological activities. Human IL-13 is produced by activated Th0, Th1-like Th2-like and CD8 T cells. Similarly to IL-4, IL-13 has multiple effects on the differentiation and functions of monocytes/macrophages. IL-13 can suppress the cytotoxic functions of monocytes/macrophages. It can also suppress the production of proinflammatory cytokines and upregulate the production of IL-1ra by monocytes/macrophages.
-

IL-13, Human(CHO-expressed)
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsInterleukin 13 (IL-13) is an immunoregulatory cytokine produced primarily by activated Th2 cells, and also by mast cells and NK cells. Targeted deletion of IL-13 in mice resulted in impaired Th2 cell development and indicated an important role for IL-13 in the expulsion of gastrointestinal parasites. IL-13 exerts anti-inflammatory effects on monocytes and macrophages and it inhibits the expression of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, IL-6 and IL-8. IL-13 has also been shown to enhance B cell proliferation and to induce isotype switching resulting in increased production of IgE. Blocking of IL-13 activity inhibits the pathophysiology of asthma. Human and mouse IL-13 is cross-species reactive.






