Ambient
Showing 67801–67850 of 146505 results
-

CAY10564
$76.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsCAY10564
-

CAY10564
$138.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsCAY10564
-

CAY10565
$76.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsCAY10565
-

CAY10565
$138.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsCAY10565
-

CB-839
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H24F3N7O3S
-

CB-839
$149.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H24F3N7O3S
-

CB-839
$223.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H24F3N7O3S
-
CBP Tag Antibody, mAb, Mouse
$87.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsGenScript CBP Tag Antibody, mAb, Mouse recognizes CBP-tagged proteins.
-

CBP-tag Antibody, pAb, Rabbit
$87.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsGenScript CBP-tag Antibody recognizes CBP tagged fusion proteins.
-
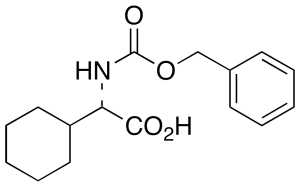
Cbz-Cyclohexyl-L-glycine
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H21NO4
-
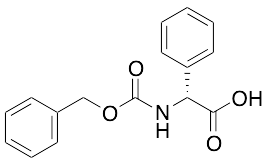
Cbz-D-(-)-Phenylglycine
$50.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H15NO4
-

Cbz-D-(-)-Phenylglycine
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H15NO4
-

Cbz-D-(-)-Phenylglycine
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H15NO4
-
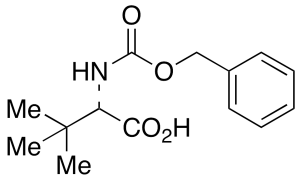
Cbz-L-tert-Leucine
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C14H19NO4
-
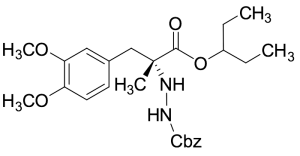
Cbz-Protected R-(+)-Carbidopa
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H34 N2 O6
-

Cbz-Protected R-(+)-Carbidopa
$402.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H34 N2 O6
-

Cbz-Protected R-(+)-Carbidopa
$770.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25 H34 N2 O6
-

CCL25, Mouse
$2,518.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsCCL25 is a new member of the CC family chemokine. It is also called Thymus-expressed chemokine (TECK) because it is restricted produced by thymus and intestine. Especially, the dendritic cells derived from thymus but not bone marrow had been identified to be the source of CCL25. By binding with CCR9, it elicits its effects of chemotactic for thymocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Additionally, CCL25 takes part in regulating the development of T-cells.
-

CCL25, Mouse
$521.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsCCL25 is a new member of the CC family chemokine. It is also called Thymus-expressed chemokine (TECK) because it is restricted produced by thymus and intestine. Especially, the dendritic cells derived from thymus but not bone marrow had been identified to be the source of CCL25. By binding with CCR9, it elicits its effects of chemotactic for thymocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Additionally, CCL25 takes part in regulating the development of T-cells.
-

CCT036477
$163.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H18ClN3
-

CCT036477
$1,235.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21H18ClN3
-
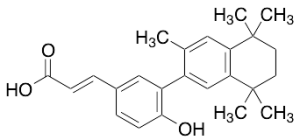
CD 3254
$111.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H28O3
-

CD 3254
$248.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H28O3
-

CD 3254
$390.71 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H28O3
-
CD160 Fc Chimera, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD160 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored Ig domain protein that is expressed on almost all intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs), γδ T (gamma delta T) cells, NK (natural killer) cells, and a minor subset of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. In terms of function, work has centered on the role of CD160 in enhancing NK or CD8 T cell activation. Such effects have been attributed to the ability of CD160 to bind classical and nonclassical MHC class I molecules, although with apparent low affinity, requiring clustering of MHC class I molecules or overexpression of CD160 or MHC class I for detection of the interaction.
-

CD160 Fc Chimera, Human
$34.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD160 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored Ig domain protein that is expressed on almost all intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs), γδ T (gamma delta T) cells, NK (natural killer) cells, and a minor subset of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. In terms of function, work has centered on the role of CD160 in enhancing NK or CD8 T cell activation. Such effects have been attributed to the ability of CD160 to bind classical and nonclassical MHC class I molecules, although with apparent low affinity, requiring clustering of MHC class I molecules or overexpression of CD160 or MHC class I for detection of the interaction.
-

CD160 Fc Chimera, Human
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD160 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored Ig domain protein that is expressed on almost all intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs), γδ T (gamma delta T) cells, NK (natural killer) cells, and a minor subset of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. In terms of function, work has centered on the role of CD160 in enhancing NK or CD8 T cell activation. Such effects have been attributed to the ability of CD160 to bind classical and nonclassical MHC class I molecules, although with apparent low affinity, requiring clustering of MHC class I molecules or overexpression of CD160 or MHC class I for detection of the interaction.
-

CD19 Fc Chimera, Human
$1,293.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD19 is a 95 kDa coreceptor, which amplifies the signaling cascade in B cells. On the B cell surface, CD19 associates with CD21, CD81 and Leu-13 to exert its function. The cytoplasmic tail of CD19 has nine conserved tyrosine residues playing critical roles in CD19 mediated function by coupling signaling molecules to the receptor. Mature human CD19 consists of a 272aa extracellular domain (ECD) with two Ig-like domains, a 22aa transmembrane segment, and a 243aa cytoplasmic domain.
-

CD19 Fc Chimera, Human
$237.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD19 is a 95 kDa coreceptor, which amplifies the signaling cascade in B cells. On the B cell surface, CD19 associates with CD21, CD81 and Leu-13 to exert its function. The cytoplasmic tail of CD19 has nine conserved tyrosine residues playing critical roles in CD19 mediated function by coupling signaling molecules to the receptor. Mature human CD19 consists of a 272aa extracellular domain (ECD) with two Ig-like domains, a 22aa transmembrane segment, and a 243aa cytoplasmic domain.
-

CD20, His & Avi, Human
$301.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsB-lymphocyte antigen CD20 or CD20 is an activated-glycosylated phosphoprotein expressed on the surface of all B-cells beginning at the pro-B phase (CD45R , CD117 ) and progressively increasing in concentration until maturity.CD20 is the target of the monoclonal antibodies rituximab, ocrelizumab, obinutuzumab, ofatumumab, ibritumomab tiuxetan, tositumomab, and ublituximab, which are all active agents in the treatment of all B cell lymphomas, leukemias, and B cell-mediated autoimmune diseases.
-

CD200 R1, His, Human
$241.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsCell surface glycoprotein CD200 Receptor 1 (CD200R1) is the receptor for the CD200 (OX-2) membrane glycoprotein. CD200R1 contains one C2- type Ig-like domain and one V-type Ig-like domain within its extracellular domain and a PTB-signaling motif in cytoplasmic domain. CD200R1 and CD200 associate via their respective N-terminal Ig-like domains. CD200R1 is restricted primarily to mast cells, basophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It propagates inhibitory signals despite its lacking a cytoplasmic ITIM (immunoreceptor tyrosinebased inhibitory motif). The receptor-substrate interaction may function as a myeloid downregulatory signal.
-
CD24 Fc Chimera, Human
$1,293.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsSignal transducer CD24 also known as cluster of differentiation 24 or heat stable antigen CD24 (HSA) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD24 gene. CD24 is a cell adhesion molecule. CD24 is a sialoglycoprotein expressed at the surface of most B lymphocytes and differentiating neuroblasts. It is also expressed on neutrophils and neutrophil precursors from the myelocyte stage onwards. The encoded protein is anchored via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) link to the cell surface. The protein also contributes to a wide range of downstream signaling networks and is crucial for neural development. Cross-linking of CD24 on the surface of neutrophils induces apoptosis, and this appears to be defective in sepsis.
-

CD24 Fc Chimera, Human
$189.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsSignal transducer CD24 also known as cluster of differentiation 24 or heat stable antigen CD24 (HSA) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD24 gene. CD24 is a cell adhesion molecule. CD24 is a sialoglycoprotein expressed at the surface of most B lymphocytes and differentiating neuroblasts. It is also expressed on neutrophils and neutrophil precursors from the myelocyte stage onwards. The encoded protein is anchored via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) link to the cell surface. The protein also contributes to a wide range of downstream signaling networks and is crucial for neural development. Cross-linking of CD24 on the surface of neutrophils induces apoptosis, and this appears to be defective in sepsis.
-

CD24 Fc Chimera, Human
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsSignal transducer CD24 also known as cluster of differentiation 24 or heat stable antigen CD24 (HSA) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD24 gene. CD24 is a cell adhesion molecule. CD24 is a sialoglycoprotein expressed at the surface of most B lymphocytes and differentiating neuroblasts. It is also expressed on neutrophils and neutrophil precursors from the myelocyte stage onwards. The encoded protein is anchored via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) link to the cell surface. The protein also contributes to a wide range of downstream signaling networks and is crucial for neural development. Cross-linking of CD24 on the surface of neutrophils induces apoptosis, and this appears to be defective in sepsis.
-

CD24 Fc Chimera, Mouse
$1,293.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsSignal transducer CD24 also known as cluster of differentiation 24 or heat stable antigen CD24 (HSA) is a protein that in mouse is encoded by the CD24 gene. CD24 is a cell adhesion molecule. CD24 is a sialoglycoprotein expressed at the surface of most B lymphocytes and differentiating neuroblasts. It is also expressed on neutrophils and neutrophil precursors from the myelocyte stage onwards. The encoded protein is anchored via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) link to the cell surface. The protein also contributes to a wide range of downstream signaling networks and is crucial for neural development. Cross-linking of CD24 on the surface of neutrophils induces apoptosis, and this appears to be defective in sepsis.
-

CD24 Fc Chimera, Mouse
$189.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsSignal transducer CD24 also known as cluster of differentiation 24 or heat stable antigen CD24 (HSA) is a protein that in mouse is encoded by the CD24 gene. CD24 is a cell adhesion molecule. CD24 is a sialoglycoprotein expressed at the surface of most B lymphocytes and differentiating neuroblasts. It is also expressed on neutrophils and neutrophil precursors from the myelocyte stage onwards. The encoded protein is anchored via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) link to the cell surface. The protein also contributes to a wide range of downstream signaling networks and is crucial for neural development. Cross-linking of CD24 on the surface of neutrophils induces apoptosis, and this appears to be defective in sepsis.
-

CD24 Fc Chimera, Mouse
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsSignal transducer CD24 also known as cluster of differentiation 24 or heat stable antigen CD24 (HSA) is a protein that in mouse is encoded by the CD24 gene. CD24 is a cell adhesion molecule. CD24 is a sialoglycoprotein expressed at the surface of most B lymphocytes and differentiating neuroblasts. It is also expressed on neutrophils and neutrophil precursors from the myelocyte stage onwards. The encoded protein is anchored via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) link to the cell surface. The protein also contributes to a wide range of downstream signaling networks and is crucial for neural development. Cross-linking of CD24 on the surface of neutrophils induces apoptosis, and this appears to be defective in sepsis.
-

CD25/IL-2Rα Fc Chimera, Human
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe IL-2 receptor system consists of three non-covalently linked subunits termed IL-2Rα, IL-2Rβ, and IL-2Rγ. The IL-2Rα is a type I transmembrane protein consisting of a 219 amino acid (a.a.) extracellular domain, a 19 a.a. transmembrane domain and a 13 a.a. intracellular domain, which is not involved in the transduction of IL-2 signal. Activated T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs) and NK cells express high levels of CD25 and expression of the high-affinity IL-2Rα is mostly limited to these cell populations. Signaling via IL-2Rα mediates multiple biological processes in various cell populations, e.g. proliferation and differentiation of B cells and NK cells. A soluble form of IL-2Rα (IL-2Rα) appears in serum, concomitant with its increased expression on cells. The function of the soluble IL-2Rα is unclear. Increased levels of IL-2Rα in biological fluids reportedly correlate with increased T and B cell activation and immune system activation. Increased serum concentration of IL-2Rα has been observed in patients with a variety of inflammatory conditions and in the course of some leukemias and lymphomas.
-

CD25/IL-2Rα Fc Chimera, Human
$301.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe IL-2 receptor system consists of three non-covalently linked subunits termed IL-2Rα, IL-2Rβ, and IL-2Rγ. The IL-2Rα is a type I transmembrane protein consisting of a 219 amino acid (a.a.) extracellular domain, a 19 a.a. transmembrane domain and a 13 a.a. intracellular domain, which is not involved in the transduction of IL-2 signal. Activated T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs) and NK cells express high levels of CD25 and expression of the high-affinity IL-2Rα is mostly limited to these cell populations. Signaling via IL-2Rα mediates multiple biological processes in various cell populations, e.g. proliferation and differentiation of B cells and NK cells. A soluble form of IL-2Rα (IL-2Rα) appears in serum, concomitant with its increased expression on cells. The function of the soluble IL-2Rα is unclear. Increased levels of IL-2Rα in biological fluids reportedly correlate with increased T and B cell activation and immune system activation. Increased serum concentration of IL-2Rα has been observed in patients with a variety of inflammatory conditions and in the course of some leukemias and lymphomas.
-
CD27 Ligand/CD70 Fc Chimera, Human
$1,293.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD70 (Cluster of Differentiation 70) is a protein that in humans is encoded by CD70 gene. CD70 is a ligand for CD27. The CD70-CD27 pathway plays an important role in the generation and maintenance of T cell immunity, in particular during antiviral responses. Upon CD27 binding, induces the proliferation of costimulated T-cells and enhances the generation of cytolytic T-cells.The CD70 protein is expressed on highly activated lymphocytes (like in T- and B-cell lymphomas). It is therefore suggested that anti-CD70 antibodies might be a possible treatment for CD70 positive lymphomas as normal lymphocytes have low CD70 expression.
-

CD27 Ligand/CD70 Fc Chimera, Human
$189.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD70 (Cluster of Differentiation 70) is a protein that in humans is encoded by CD70 gene. CD70 is a ligand for CD27. The CD70-CD27 pathway plays an important role in the generation and maintenance of T cell immunity, in particular during antiviral responses. Upon CD27 binding, induces the proliferation of costimulated T-cells and enhances the generation of cytolytic T-cells.The CD70 protein is expressed on highly activated lymphocytes (like in T- and B-cell lymphomas). It is therefore suggested that anti-CD70 antibodies might be a possible treatment for CD70 positive lymphomas as normal lymphocytes have low CD70 expression.
-

CD28 Fc Chimera, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman CD28 is composed of four exons encoding a protein of 220 amino acids that is expressed on the cell surface as a glycosylated, disulfide-linked homodimer of 44 kDa. Members of the CD28 family share a number of common features. These receptors consist of paired V-set immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) domains attached to single transmembrane domains and cytoplasmic domains that contain critical signaling motifs. The CD28 and CTLA4 ligands, CD80 and CD86, consist of single V-set and C1-set IgSF domains. The interaction of these costimulatory receptors with ligands is mediated through the MYPPPY motif within the receptor V-set domains. CD28 is expressed constitutively on almost all human CD4 T cells and approximately 50% of CD8 T cells. CD28 costimulation has diverse effects on T cell function, including biochemical events at the immunological synapse, downstream phosphorylation and other post-translational modifications, transcriptional changes, and cytoskeletal remodeling. At the most basic level, CD28 signals increase a cell’s glycolytic rate, allowing cells to generate the energy necessary for growth and proliferation.
-

CD28 Fc Chimera, Human
$129.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsHuman CD28 is composed of four exons encoding a protein of 220 amino acids that is expressed on the cell surface as a glycosylated, disulfide-linked homodimer of 44 kDa. Members of the CD28 family share a number of common features. These receptors consist of paired V-set immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) domains attached to single transmembrane domains and cytoplasmic domains that contain critical signaling motifs. The CD28 and CTLA4 ligands, CD80 and CD86, consist of single V-set and C1-set IgSF domains. The interaction of these costimulatory receptors with ligands is mediated through the MYPPPY motif within the receptor V-set domains. CD28 is expressed constitutively on almost all human CD4 T cells and approximately 50% of CD8 T cells. CD28 costimulation has diverse effects on T cell function, including biochemical events at the immunological synapse, downstream phosphorylation and other post-translational modifications, transcriptional changes, and cytoskeletal remodeling. At the most basic level, CD28 signals increase a cell’s glycolytic rate, allowing cells to generate the energy necessary for growth and proliferation.
-

CD30, hFc, Human
$172.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD30, also known as TNFRSF8, is a cell membrane protein of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family, which regulates proliferation/apoptosis and antibody responses. CD30 is expressed by activated, but not by resting, T and B cells. Aberrant expression of CD30 by mastocytosis mast cells and interaction with its ligand CD30L (CD153) appears to play an important role in the pathogenesis and clinical presentation of systemic mastocytosis. CD30 has been considered as a specific diagnostic biomarker of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) and classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL). CD30 is also a biomarker used for targeted therapy by an antibody–drug conjugate.
-

CD30, His, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD30, also known as TNFRSF8, is a cell membrane protein of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family, which regulates proliferation/apoptosis and antibody responses. CD30 is expressed by activated, but not by resting, T and B cells. Aberrant expression of CD30 by mastocytosis mast cells and interaction with its ligand CD30L (CD153) appears to play an important role in the pathogenesis and clinical presentation of systemic mastocytosis. CD30 has been considered as a specific diagnostic biomarker of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) and classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL). CD30 is also a biomarker used for targeted therapy by an antibody–drug conjugate.
-

CD30, His, Human
$172.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD30, also known as TNFRSF8, is a cell membrane protein of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family, which regulates proliferation/apoptosis and antibody responses. CD30 is expressed by activated, but not by resting, T and B cells. Aberrant expression of CD30 by mastocytosis mast cells and interaction with its ligand CD30L (CD153) appears to play an important role in the pathogenesis and clinical presentation of systemic mastocytosis. CD30 has been considered as a specific diagnostic biomarker of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) and classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL). CD30 is also a biomarker used for targeted therapy by an antibody–drug conjugate.
-

CD38, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD38 (also referred to as T10 antigen) is a nonlineage-restricted type II transmembrane glycoprotein that has emerged as an intracellular calcium ion mobilizing messenger. It can serve as an ectoenzyme that catalyzes the synthesis and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose. The enzymatic functions of CD38 probably contribute to an array of its immunoregulatory functions. It has been found on the surface of many immune cells (white blood cells), including CD4+, CD8+, B lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Soluble CD38 and the ability of membrane-bound CD38 to become internalized in response to appropriate stimuli suggest that extracellular and intracellular roles for this protein are equally plausible.
-

CD38, Human
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD38 (also referred to as T10 antigen) is a nonlineage-restricted type II transmembrane glycoprotein that has emerged as an intracellular calcium ion mobilizing messenger. It can serve as an ectoenzyme that catalyzes the synthesis and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose. The enzymatic functions of CD38 probably contribute to an array of its immunoregulatory functions. It has been found on the surface of many immune cells (white blood cells), including CD4+, CD8+, B lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Soluble CD38 and the ability of membrane-bound CD38 to become internalized in response to appropriate stimuli suggest that extracellular and intracellular roles for this protein are equally plausible.
-

CD40, His, Human
$189.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD40 is a costimulatory protein found on antigen presenting cells and is required for their activation. The binding of CD154 (CD40L) on TH cells to CD40 activates antigen presenting cells and induces a variety of downstream effects.CD40 molecule is a potential target for cancer immunotherapy. There are number of completed and ongoing clinical trials where agonistic anti-CD40 monoclonal antibodies are employed to activate an anti-tumor T cell response via activation of dendritic cells.
-

CD40L/CD154/TRAP, Human
$1,035.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD40 Ligand (CD40L/CD154/TRAP) is a membrane glycoprotein and differentiation antigen expressed on the surface of T-cells. The CD40 ligand stimulates B-cell proliferation and secretion of all immunoglobulin isotypes in the presence of cytokines. It also costimulates proliferation of activated T-cell and this is accompanied by the production of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL2. CD40 ligand has been shown to induce cytokine production and tumoricidal activity in peripheral blood monocytes.






