Ambient
Showing 100801–100850 of 146499 results
-

m-Cresol, High Purity
$80.35 Add to cart View Product Detailsm-Cresol, High Purity
-

m-Cresol, High Purity
$191.30 Add to cart View Product Detailsm-Cresol, High Purity
-

m-Cresol, High Purity
$505.80 Add to cart View Product Detailsm-Cresol, High Purity
-

m-Cresol, High Purity
$1,119.09 Add to cart View Product Detailsm-Cresol, High Purity
-

m-Cresol, High Purity
$8,834.19 Add to cart View Product Detailsm-Cresol, High Purity
-

M-CSF, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Human
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Human
$439.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Human(CHO-expressed)
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Mouse
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Mouse
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Mouse
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Rat
$2,307.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Rat
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Rat
$271.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Rat
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-

M-CSF, Rat
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMacrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (M-CSF), also known as Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1), is a hematopoietic growth factor. It can stimulate the survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, in addition to the spreading and motility of macrophages. In mammals, it exits three isoforms, which invariably share an N-terminal 32-aa signal peptide, a 149-residue growth factor domain, a 21-residue transmembrane region and a 37-aa cytoplasmictail. M-CSF is mainly produced by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. M-CSF interaction with its receptor, c-fms, has been implicated in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of of several diseases, including breast and endometrial cancers. The biological activity of human M-CSF is maintained within the 149-aa growth factor domain, and it is only active in the disulfide-linked dimeric form, which is bonded at Cys63.
-
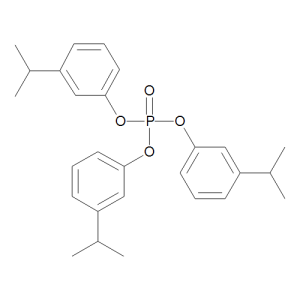
m-Cumenyl Phosphate
$131.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H33 O4 P
-

m-Cumenyl Phosphate
$538.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H33 O4 P
-

m-Cumenyl Phosphate
$993.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H33 O4 P
-
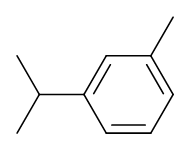
m-Cymene
$142.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H14
-

m-Cymene
$1,072.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H14
-
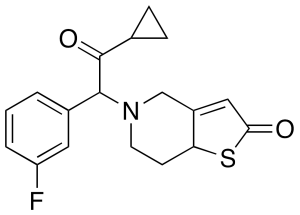
m-Fluoro Prasugrel Thiolactone(Mixture of Diastereomers)
$176.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H18FNO2S
-

m-Fluoro Prasugrel Thiolactone(Mixture of Diastereomers)
$1,391.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H18FNO2S
-
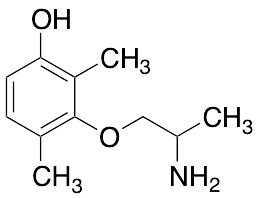
m-Hydroxy Mexiletine
$220.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11H17NO2
-

m-Hydroxy Mexiletine
$989.29 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11H17NO2
-

m-Hydroxy Mexiletine
$1,699.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11H17NO2
-

m-Hydroxybenzoic Acid
$74.24 Add to cart View Product Detailsm-Hydroxybenzoic Acid
-

m-Hydroxybenzoic Acid
$114.76 Add to cart View Product Detailsm-Hydroxybenzoic Acid
-
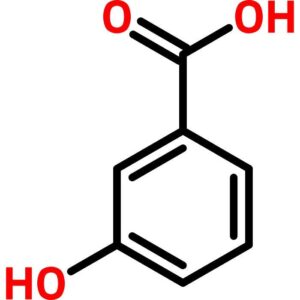
m-Hydroxybenzoic Acid
$352.77 Add to cart View Product Detailsm-Hydroxybenzoic Acid
-
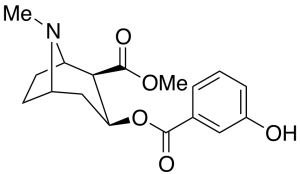
m-Hydroxycocaine
$204.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H21 N O5
-

m-Hydroxycocaine
$1,578.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H21 N O5
-
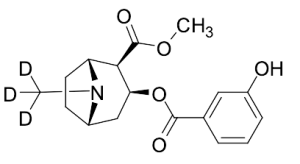
m-Hydroxycocaine-D3
$160.43 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H18D3NO5
-

m-Hydroxycocaine-D3
$1,255.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H18D3NO5
-

m-Hydroxyhippuric Acid
$181.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H9NO4
-

m-Hydroxyhippuric Acid
$1,410.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H9NO4
-
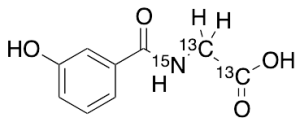
m-Hydroxyhippuric Acid-13C2, 15N
$232.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C713C2H915NO4
-

m-Hydroxyhippuric Acid-13C2, 15N
$1,732.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C713C2H915NO4
-
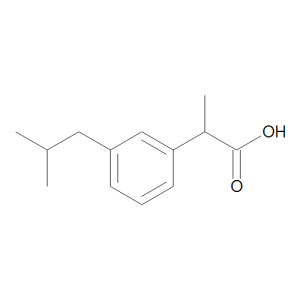
m-Isobutyl Ibuprofen
$240.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H18 O2
-

m-Isobutyl Ibuprofen
$1,868.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C13 H18 O2
-
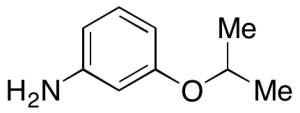
m-Isopropoxyaniline
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H13NO
-

m-Isopropoxyaniline
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H13NO
-

m-Isopropoxyaniline
$510.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9H13NO
-

M-MuLV Reverse Transcriptase
$50.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsGenScript M-MuLV Reverse Transcriptase (M-MLV) is derived from a cloned region of the pol gene of MMLV and isolated from an E. coli strain overexpressing this construct. To increase cDNA yields and get a higher percentage of longer transcripts, the M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase has been modified with reduced RNase H activity, and expressed free of exogenous RNases and other nucleases. The enzyme can synthesize a complementary cDNA strand initiating from a primer using RNA as template (cDNA synthesis), making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
-

M-MuLV Reverse Transcriptase
$163.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsGenScript M-MuLV Reverse Transcriptase (M-MLV) is derived from a cloned region of the pol gene of MMLV and isolated from an E. coli strain overexpressing this construct. To increase cDNA yields and get a higher percentage of longer transcripts, the M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase has been modified with reduced RNase H activity, and expressed free of exogenous RNases and other nucleases. The enzyme can synthesize a complementary cDNA strand initiating from a primer using RNA as template (cDNA synthesis), making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
-

M-NIFEDIPINE
$206.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H18 N2 O6






