Ambient
Showing 123501–123550 of 146505 results
-
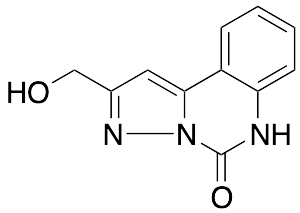
Pirquinozol
$2,377.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11H9N3O2
-
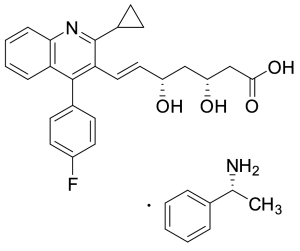
Pitavastatin (+)-Phenylethylamine Salt
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H24FNO4 • C8H11N
-

Pitavastatin (+)-Phenylethylamine Salt
$443.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H24FNO4 • C8H11N
-
Pitavastatin (1R)-N-Methyl-2-hydroxyethylamide
$133.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H33FN2O4
-
Pitavastatin (1R)-N-Methyl-2-hydroxyethylamide
$509.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H33FN2O4
-
Pitavastatin (1R)-N-Methyl-2-hydroxyethylamide
$1,063.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H33FN2O4
-
Pitavastatin (2R)-N-Methyl-2-hydroxypropylamide
$133.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H31FN2O4
-
Pitavastatin (2R)-N-Methyl-2-hydroxypropylamide
$615.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H31FN2O4
-
Pitavastatin (2R)-N-Methyl-2-hydroxypropylamide
$1,063.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C28H31FN2O4
-
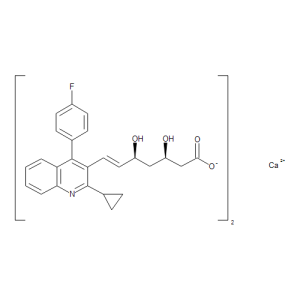
Pitavastatin Calcium
$150.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C25 H23 F N O4 . Ca
-

Pitavastatin Calcium
$235.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C25 H23 F N O4 . Ca
-

Pitavastatin Calcium
$358.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 2 C25 H23 F N O4 . Ca
-
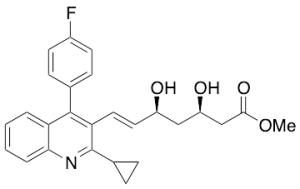
Pitavastatin Methyl Ester
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H26 F N O4
-

Pitavastatin Methyl Ester
$332.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H26 F N O4
-

Pitavastatin Methyl Ester
$708.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H26 F N O4
-
Pitavastatin N-Methyl,-2-methoxyethylamide
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H33FN2O4
-
Pitavastatin N-Methyl,-2-methoxyethylamide
$474.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H33FN2O4
-
Pitavastatin N-Methyl,-2-methoxyethylamide
$853.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H33FN2O4
-
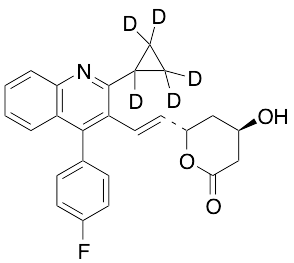
Pitavastatin-d5 Lactone
$449.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H17D5FNO3
-

Pitavastatin-d5 Lactone
$802.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H17D5FNO3
-

Pitavastatin-d5 Lactone
$7,075.95 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H17D5FNO3
-
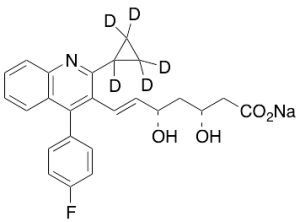
Pitavastatin-d5 Sodium Salt
$258.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H18D5FNNaO4
-

Pitavastatin-d5 Sodium Salt
$2,029.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H18D5FNNaO4
-

Pitavastatin-d5 Sodium Salt
$4,328.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C25H18D5FNNaO4
-

Pitofenone Hydrochloride
$163.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H25 N O4 . Cl H
-

Pitofenone Hydrochloride
$1,281.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H25 N O4 . Cl H
-
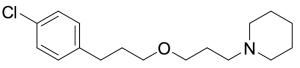
Pitolisant
$225.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H26 Cl N O
-

Pitolisant
$996.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H26 Cl N O
-

Pitolisant
$1,725.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H26 Cl N O
-
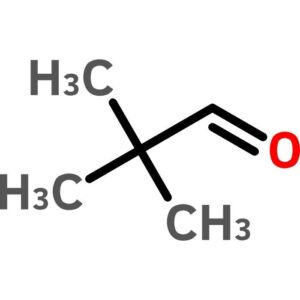
Pivalaldehyde
$184.17 Add to cart View Product DetailsPivalaldehyde
-
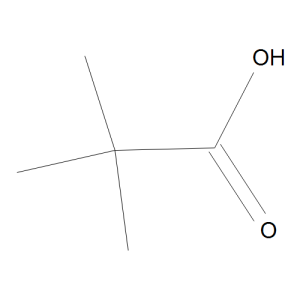
Pivalic Acid
$111.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H10 O2
-

Pivalic Acid
$212.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 H10 O2
-
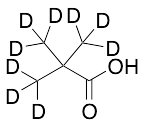
Pivalic acid-d9
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 D9 H O2
-

Pivalic acid-d9
$380.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 D9 H O2
-

Pivalic acid-d9
$671.89 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5 D9 H O2
-
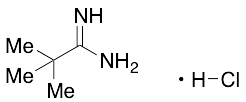
Pivalimidamide Hydrochloride
$111.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H13ClN2
-
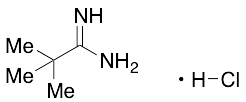
Pivalimidamide Hydrochloride
$157.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H13ClN2
-
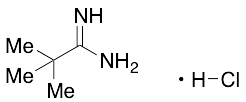
Pivalimidamide Hydrochloride
$624.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C5H13ClN2
-
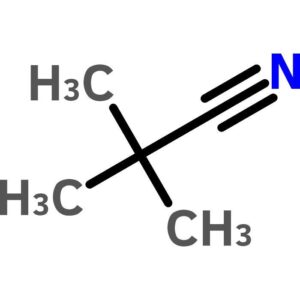
Pivalonitrile
$74.42 Add to cart View Product DetailsPivalonitrile
-

Pivalonitrile
$203.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsPivalonitrile
-

Pivalonitrile
$590.47 Add to cart View Product DetailsPivalonitrile
-
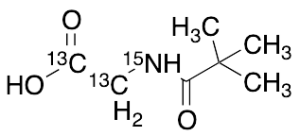
Pivaloylglycine-13C2,15N
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C513C2H1315NO3
-
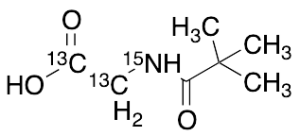
Pivaloylglycine-13C2,15N
$576.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C513C2H1315NO3
-
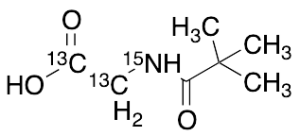
Pivaloylglycine-13C2,15N
$1,108.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C513C2H1315NO3
-

PIVKA II (1C5), mAb, Mouse
$392.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtein Induced by Vitamin K Absence or Antagonist-II (PIVKA-II), also known as Des-γ-carboxy-prothrombin (DCP), is an abnormal form of prothrombin. Normally, the prothrombin’s 10 glutamic acid residues (Glu) in the γ-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domain at positions 6, 7, 14, 16, 19, 20,25, 26, 29 and 32 are γ-carboxylated to Gla by vitamin-K dependent γ- glutamyl carboxylase in the liver and then secreted into plasma. In patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), γ-carboxylation of prothrombin is impaired so that PIVKA-II is formed instead of prothrombin. PIVKA-II is considered as is an efficient biomarker specific for HCC.
-

PIVKA II (1C5), mAb, Mouse
$3,924.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtein Induced by Vitamin K Absence or Antagonist-II (PIVKA-II), also known as Des-γ-carboxy-prothrombin (DCP), is an abnormal form of prothrombin. Normally, the prothrombin’s 10 glutamic acid residues (Glu) in the γ-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domain at positions 6, 7, 14, 16, 19, 20,25, 26, 29 and 32 are γ-carboxylated to Gla by vitamin-K dependent γ- glutamyl carboxylase in the liver and then secreted into plasma. In patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), γ-carboxylation of prothrombin is impaired so that PIVKA-II is formed instead of prothrombin. PIVKA-II is considered as is an efficient biomarker specific for HCC.
-

PIVKA II (1C5), mAb, Mouse
$33,292.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtein Induced by Vitamin K Absence or Antagonist-II (PIVKA-II), also known as Des-γ-carboxy-prothrombin (DCP), is an abnormal form of prothrombin. Normally, the prothrombin’s 10 glutamic acid residues (Glu) in the γ-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domain at positions 6, 7, 14, 16, 19, 20,25, 26, 29 and 32 are γ-carboxylated to Gla by vitamin-K dependent γ- glutamyl carboxylase in the liver and then secreted into plasma. In patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), γ-carboxylation of prothrombin is impaired so that PIVKA-II is formed instead of prothrombin. PIVKA-II is considered as is an efficient biomarker specific for HCC.
-

PIVKA II (2D7), mAb, Mouse
$392.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtein Induced by Vitamin K Absence or Antagonist-II (PIVKA-II), also known as Des-γ-carboxy-prothrombin (DCP), is an abnormal form of prothrombin. Normally, the prothrombin’s 10 glutamic acid residues (Glu) in the γ-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domain at positions 6, 7, 14, 16, 19, 20,25, 26, 29 and 32 are γ-carboxylated to Gla by vitamin-K dependent γ- glutamyl carboxylase in the liver and then secreted into plasma. In patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), γ-carboxylation of prothrombin is impaired so that PIVKA-II is formed instead of prothrombin. PIVKA-II is considered as is an efficient biomarker specific for HCC.
-

PIVKA II (2D7), mAb, Mouse
$3,924.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtein Induced by Vitamin K Absence or Antagonist-II (PIVKA-II), also known as Des-γ-carboxy-prothrombin (DCP), is an abnormal form of prothrombin. Normally, the prothrombin’s 10 glutamic acid residues (Glu) in the γ-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domain at positions 6, 7, 14, 16, 19, 20,25, 26, 29 and 32 are γ-carboxylated to Gla by vitamin-K dependent γ- glutamyl carboxylase in the liver and then secreted into plasma. In patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), γ-carboxylation of prothrombin is impaired so that PIVKA-II is formed instead of prothrombin. PIVKA-II is considered as is an efficient biomarker specific for HCC.
-

PIVKA II (2D7), mAb, Mouse
$33,292.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtein Induced by Vitamin K Absence or Antagonist-II (PIVKA-II), also known as Des-γ-carboxy-prothrombin (DCP), is an abnormal form of prothrombin. Normally, the prothrombin’s 10 glutamic acid residues (Glu) in the γ-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domain at positions 6, 7, 14, 16, 19, 20,25, 26, 29 and 32 are γ-carboxylated to Gla by vitamin-K dependent γ- glutamyl carboxylase in the liver and then secreted into plasma. In patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), γ-carboxylation of prothrombin is impaired so that PIVKA-II is formed instead of prothrombin. PIVKA-II is considered as is an efficient biomarker specific for HCC.






