Ambient
Showing 131101–131150 of 146499 results
-
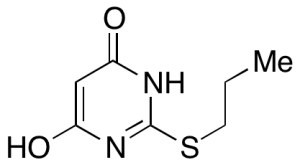
S-Propyl-2-thiobarbituric Acid
$1,298.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H10 N2 O2 S
-

S-Sodium Ethanethiosulfonate
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H5O2NaS2
-

S-Sodium Ethanethiosulfonate
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H5O2NaS2
-

S-Sodium Ethanethiosulfonate
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C2H5O2NaS2
-

S-Sulfo-L-cysteine Sodium Salt (~85%)
$61.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H6NO5S2Na
-

S-Sulfo-L-cysteine Sodium Salt (~85%)
$97.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H6NO5S2Na
-

S-Sulfo-L-cysteine Sodium Salt (~85%)
$369.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H6NO5S2Na
-
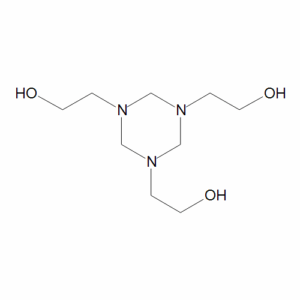
s-Triazine-1,3,5-triethanol
$79.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H21 N3 O3
-

s-Triazine-1,3,5-triethanol
$218.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H21 N3 O3
-

s-Triazine-1,3,5-triethanol
$1,305.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H21 N3 O3
-

s-Triazolo[3,4-alpha]phthalazine
$150.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H6 N4
-
![s-Triazolo[3,4-Alpha]phthalazine](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/xsys-masterimageshb2hd510596155392030T767500-300x245.png.pagespeed.ic.h-eXVpzDqp.png)
s-Triazolo[3,4-Alpha]phthalazine
$327.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H6 N4
-
![s-Triazolo[3,4-Alpha]phthalazine](https://advatechgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/xsys-masterimageshb2hd510596155392030T767500-300x245.png.pagespeed.ic.h-eXVpzDqp.png)
s-Triazolo[3,4-Alpha]phthalazine
$601.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 H6 N4
-
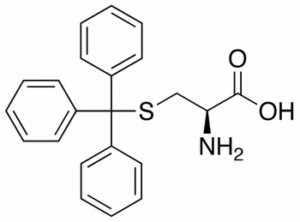
S-Trityl-L-cysteine
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H21 N O2 S
-

S-Trityl-L-cysteine
$106.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H21 N O2 S
-

S-Trityl-L-cysteine
$199.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H21 N O2 S
-
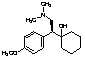
S-Venlafaxine
$266.51 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H27 N O2
-

S-Venlafaxine
$526.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H27 N O2
-

S-Venlafaxine
$1,785.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17 H27 N O2
-
S-Venlafaxine-di-p-toluoyl-L-tartrate Salt (2:1)
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C54H72N2O12
-
S-Venlafaxine-di-p-toluoyl-L-tartrate Salt (2:1)
$154.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C54H72N2O12
-
S-Venlafaxine-di-p-toluoyl-L-tartrate Salt (2:1)
$264.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : No Data Available
-
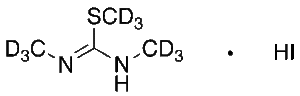
S,N,N’-Trimethylisothiouronium-d9 Iodide
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H2D9IN2S
-

S,N,N’-Trimethylisothiouronium-d9 Iodide
$1,537.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H2D9IN2S
-
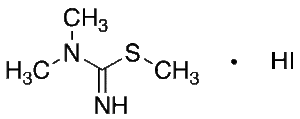
S,N,N’-Trimethylisothiouronium Iodide
$116.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H11lN2S
-

S,N,N’-Trimethylisothiouronium Iodide
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H11lN2S
-

S,N,N’-Trimethylisothiouronium Iodide
$369.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H11lN2S
-

S,S’-Ethylenebis(glutathione)
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H36 N6 O12 S2
-

S,S’-Ethylenebis(glutathione)
$1,619.78 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H36 N6 O12 S2
-
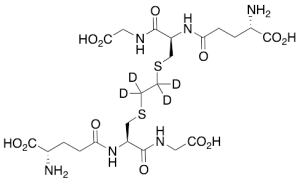
S,S’-Ethylenebis(glutathione)-d4
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H32D4N6O12S2
-

S,S’-Ethylenebis(glutathione)-d4
$1,599.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22H32D4N6O12S2
-
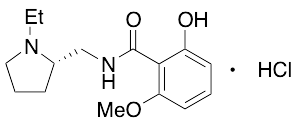
S(-)-BZM Hydrochloride
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15H23ClN2O3
-

S(-)-BZM Hydrochloride
$1,220.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15H23ClN2O3
-
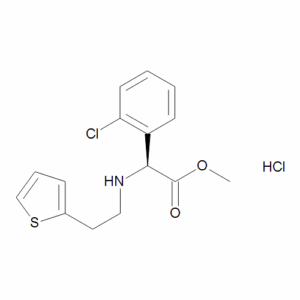
S(+)-N-(2-(2-Thienyl)ethyl)-2-chlorophenyl Glycine Methyl Ester Hydrochloride
$122.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H16 Cl N O2 S . Cl H
-

S(+)-N-(2-(2-Thienyl)ethyl)-2-chlorophenyl Glycine Methyl Ester Hydrochloride
$177.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15 H16 Cl N O2 S . Cl H
-
S1-tag Antibody, pAb, Rabbit
$87.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsThis Antibody recognizes both S1 tagged fusion proteins.
-

S100 (2AC), mAb, Mouse
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 protein family contains variety of members such as ββ homodimer and αβ heterodimer. It is a useful marker for monitoring brain damage and detecting secondary neurological injuries. The concentration of S100 A8/A9 hetero complex increases in blood when special diseases take places, such as rheumatoid arthritis, cystic fibrosis, multiple scerlosis, and HIV infections. S100A8/A9 protein is a potential serum marker for diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) or chronic pancreatitis (CP).
-

S100 (2AC), mAb, Mouse
$1,371.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 protein family contains variety of members such as ββ homodimer and αβ heterodimer. It is a useful marker for monitoring brain damage and detecting secondary neurological injuries. The concentration of S100 A8/A9 hetero complex increases in blood when special diseases take places, such as rheumatoid arthritis, cystic fibrosis, multiple scerlosis, and HIV infections. S100A8/A9 protein is a potential serum marker for diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) or chronic pancreatitis (CP).
-

S100 (2AC), mAb, Mouse
$11,643.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 protein family contains variety of members such as ββ homodimer and αβ heterodimer. It is a useful marker for monitoring brain damage and detecting secondary neurological injuries. The concentration of S100 A8/A9 hetero complex increases in blood when special diseases take places, such as rheumatoid arthritis, cystic fibrosis, multiple scerlosis, and HIV infections. S100A8/A9 protein is a potential serum marker for diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) or chronic pancreatitis (CP).
-

S100 (2BD1), mAb, Mouse
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 protein family contains variety of members such as ββ homodimer and αβ heterodimer. It is a useful marker for monitoring brain damage and detecting secondary neurological injuries. The concentration of S100 A8/A9 hetero complex increases in blood when special diseases take places, such as rheumatoid arthritis, cystic fibrosis, multiple scerlosis, and HIV infections. S100A8/A9 protein is a potential serum marker for diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) or chronic pancreatitis (CP)
-

S100 (2BD1), mAb, Mouse
$1,371.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 protein family contains variety of members such as ββ homodimer and αβ heterodimer. It is a useful marker for monitoring brain damage and detecting secondary neurological injuries. The concentration of S100 A8/A9 hetero complex increases in blood when special diseases take places, such as rheumatoid arthritis, cystic fibrosis, multiple scerlosis, and HIV infections. S100A8/A9 protein is a potential serum marker for diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) or chronic pancreatitis (CP)
-

S100 (2BD1), mAb, Mouse
$11,643.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 protein family contains variety of members such as ββ homodimer and αβ heterodimer. It is a useful marker for monitoring brain damage and detecting secondary neurological injuries. The concentration of S100 A8/A9 hetero complex increases in blood when special diseases take places, such as rheumatoid arthritis, cystic fibrosis, multiple scerlosis, and HIV infections. S100A8/A9 protein is a potential serum marker for diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) or chronic pancreatitis (CP)
-

S100 (beta-beta) (B7B), mAb, Mouse
$137.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 protein family contains variety of members such as ββ homodimer and αβ heterodimer. It is a useful marker for monitoring brain damage and detecting secondary neurological injuries. The concentration of S100 A8/A9 hetero complex increases in blood when special diseases take places, such as rheumatoid arthritis, cystic fibrosis, multiple scerlosis, and HIV infections. S100A8/A9 protein is a potential serum marker for diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) or chronic pancreatitis (CP).
-

S100 (beta-beta) (B7B), mAb, Mouse
$1,371.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 protein family contains variety of members such as ββ homodimer and αβ heterodimer. It is a useful marker for monitoring brain damage and detecting secondary neurological injuries. The concentration of S100 A8/A9 hetero complex increases in blood when special diseases take places, such as rheumatoid arthritis, cystic fibrosis, multiple scerlosis, and HIV infections. S100A8/A9 protein is a potential serum marker for diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) or chronic pancreatitis (CP).
-

S100 (beta-beta) (B7B), mAb, Mouse
$11,643.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 protein family contains variety of members such as ββ homodimer and αβ heterodimer. It is a useful marker for monitoring brain damage and detecting secondary neurological injuries. The concentration of S100 A8/A9 hetero complex increases in blood when special diseases take places, such as rheumatoid arthritis, cystic fibrosis, multiple scerlosis, and HIV infections. S100A8/A9 protein is a potential serum marker for diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) or chronic pancreatitis (CP).
-

S100A1, His, Human
$293.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 calcium-binding protein A1 (S100A1) is a small calcium binding protein with EF-hand structures and belongs to the S100 family. S100 proteins include at least 25 members which are located as a cluster on human chromosome 1q21. S100A1 is found in the heart, skeletal muscle, brain, and kidney.S100A1 mainly resides on the sarcoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and myofilaments. S100A1 may function in stimulation of Ca2+ induced Ca2+ release, inhibition of microtubule assembly, and inhibition of protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation. Reduced expression of this protein has been implicated in cardiomyopathies.
-

S100A1, His, Human
$120.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 calcium-binding protein A1 (S100A1) is a small calcium binding protein with EF-hand structures and belongs to the S100 family. S100 proteins include at least 25 members which are located as a cluster on human chromosome 1q21. S100A1 is found in the heart, skeletal muscle, brain, and kidney.S100A1 mainly resides on the sarcoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and myofilaments. S100A1 may function in stimulation of Ca2+ induced Ca2+ release, inhibition of microtubule assembly, and inhibition of protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation. Reduced expression of this protein has been implicated in cardiomyopathies.
-

S100A1, His, Human
$392.44 Add to cart View Product DetailsS100 calcium-binding protein A1 (S100A1) is a small calcium binding protein with EF-hand structures and belongs to the S100 family. S100 proteins include at least 25 members which are located as a cluster on human chromosome 1q21. S100A1 is found in the heart, skeletal muscle, brain, and kidney.S100A1 mainly resides on the sarcoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and myofilaments. S100A1 may function in stimulation of Ca2+ induced Ca2+ release, inhibition of microtubule assembly, and inhibition of protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation. Reduced expression of this protein has been implicated in cardiomyopathies.
-
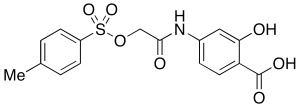
S2I-201
$111.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H15NO7S
-

S2I-201
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H15NO7S






