Ambient
Showing 131151–131200 of 146499 results
-
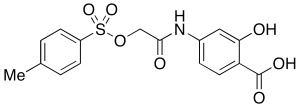
S2I-201
$292.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C16H15NO7S
-
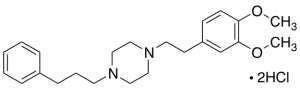
SA 4503 Dihydrochloride
$108.68 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H32N2O2 . HCl
-

SA 4503 Dihydrochloride
$363.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H32N2O2 . HCl
-

SA 4503 Dihydrochloride
$657.23 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C23H32N2O2 . HCl
-

SAA (6F9), mAb, Mouse
$104.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA (6F9), mAb, Mouse
$1,043.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA (6F9), mAb, Mouse
$8,883.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA (8C7), mAb, Mouse
$104.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA (8C7), mAb, Mouse
$1,043.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA (8C7), mAb, Mouse
$8,883.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA (ML95), mAb, Mouse
$104.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA (ML95), mAb, Mouse
$1,043.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA (ML95), mAb, Mouse
$8,883.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA (MLB2), mAb, Mouse
$104.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA (MLB2), mAb, Mouse
$1,043.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA (MLB2), mAb, Mouse
$8,883.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA Antigen
$232.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-

SAA Antigen
$2,320.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsSerum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein. The concentration of SAA in blood increases rapidly when tissue damage or inflammation occurs. It is considered as an early biomarker for the diagnosis of many inflammatory diseases. SAA can also be used as an important indicator of infection.
-
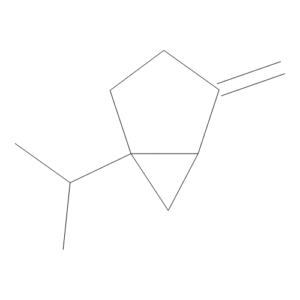
Sabinene (>70%)
$56.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H16
-

Sabinene (>70%)
$65.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H16
-

Sabinene hydrate
$55.20 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H18 O
-

Sabinene Hydrate
$121.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H18 O
-

Sabinene Hydrate
$203.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H18 O
-

Sabouraud dextrose agar w/o chloramphenicol
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsSabouraud Dextrose Agar can be used for the isolation, identification and maintainance of pathogenic and saprophytic fungi. It is suited for the cultivation of yeasts, molds and aciduric microorganisms.
-
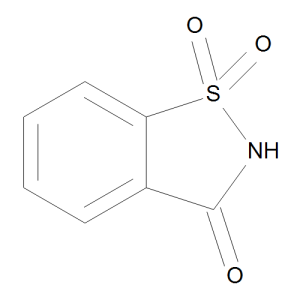
Saccharin
$69.00 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H5 N O3 S
-

Saccharin
$81.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H5 N O3 S
-

Saccharin
$120.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H5 N O3 S
-

Saccharin Calcium Hydrate (4:2:7)
$118.16 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 4 C7 H4 N O3 S . 2 Ca . 7 H2 O
-

Saccharin Calcium Hydrate (4:2:7)
$537.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : 4 C7 H4 N O3 S . 2 Ca . 7 H2 O
-

Saccharin Calcium, Crystal, USP
$14,007.22 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Calcium, Crystal, USP
-
Saccharin N-(2-Acetic Acid Ethyl Ester)(Piroxicam Impurity E)
$129.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H11 N O5 S
-
Saccharin N-(2-Acetic Acid Ethyl Ester)(Piroxicam Impurity E)
$426.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H11 N O5 S
-
Saccharin N-(2-Acetic Acid Ethyl Ester)(Piroxicam Impurity E)
$847.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H11 N O5 S
-
Saccharin N-(2-Acetic Acid Isopropyl Ester)(Piroxicam Impurity F)
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H13 N O5 S
-
Saccharin N-(2-Acetic Acid Isopropyl Ester)(Piroxicam Impurity F)
$358.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H13 N O5 S
-
Saccharin N-(2-Acetic Acid Isopropyl Ester)(Piroxicam Impurity F)
$755.55 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C12 H13 N O5 S
-

Saccharin Sodium Salt Dihydrate
$194.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H4 N O3 S . Na . 2 H2 O
-

Saccharin Sodium Salt Dihydrate
$375.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H4 N O3 S . Na . 2 H2 O
-

Saccharin Sodium Salt Dihydrate
$564.08 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C7 H4 N O3 S . Na . 2 H2 O
-

Saccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Crystalline, USP
$221.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Crystalline, USP
-

Saccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Crystalline, USP
$486.40 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Crystalline, USP
-

Saccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Crystalline, USP
$1,488.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Crystalline, USP
-

Saccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Crystalline, USP
$5,333.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Crystalline, USP
-

Saccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Crystalline, USP
$9,787.52 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Crystalline, USP
-

Saccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP
$94.67 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP
-

Saccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP
$221.70 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP
-

Saccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP
$472.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP
-

Saccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP
$1,490.39 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP
-

Saccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP
$5,525.22 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP
-

Saccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP
$13,007.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsSaccharin Sodium, Dihydrate, Powder, USP






