Ambient
Showing 131701–131750 of 146505 results
-
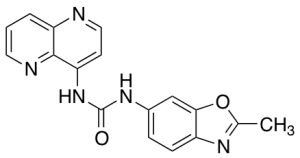
SB 334867
$166.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H13N5O2
-

SB 334867
$1,306.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C17H13N5O2
-

SB 3CT
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C15H14O3S2
-
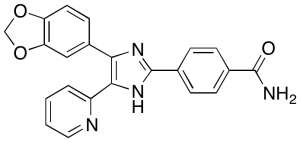
SB 431542
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H16 N4 O3
-

SB 431542
$199.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H16 N4 O3
-

SB 431542
$379.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H16 N4 O3
-

SB-203580
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H16 F N3 O S
-

SB-203580
$72.45 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C21 H16 F N3 O S
-

SC amino acid mixture (powder)
$306.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsSC amino acid mixture is also known as Hopkins mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-ADE
$160.72 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without Adenine) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-ADE-ARG-HIS-LEU-MET-THR-TRP-URA (POWDER)
$162.37 Add to cart View Product DetailsSC-ADE-ARG-HIS-LEU-MET-THR-TRP-URA (POWDER)
-

SC-ADE-HIS-LEU-LYS-TRP-URA
$162.37 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without Adenine, L-Histidine, L-Leucine, L-Lysine, L-Tryptophan and Uracil) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-ADE-HIS-LEU-TRP
$153.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without Adenine, L-Histidine, L-Leucine, L-Tryptophan) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-CYS-MET
$160.72 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without L-Cysteine and L-Methionine) S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-HIS
$348.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without L-Histidine) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-His-Leu (powder)
$160.72 Add to cart View Product DetailsSC-His-Leu (powder)
-

SC-HIS-LEU-TRP
$163.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without L-Histidine, L-Leucine, L-Tryptophan) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-HIS-LEU-TRP-URA
$173.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without L-Histidine, L-Leucine, L-Tryptophan, Uracil) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

Sc-His-Leu-Ura (powder)
$162.37 Add to cart View Product DetailsSc-His-Leu-Ura (powder)
-

Sc-His-Trp-Ura (powder)
$171.37 Add to cart View Product DetailsSc-His-Trp-Ura (powder)
-

SC-LEU
$339.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without L-Leucine) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-LEU-TRP
$183.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without L-Leucine, L-Tryptophan) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-LEU-TRP-URA
$171.37 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without L-Leucine, L-Tryptophan, Uracil) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-LEU-URA
$160.72 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without L-Leucine, Uracil) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-LYS
$169.61 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without L-Lys) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-TRP
$161.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without L-Tryptophan) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-TRP-URA
$183.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without L-Tryptophan, Uracil) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-URA
$219.77 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without Uracil) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-

SC-URA
$459.32 Add to cart View Product DetailsDropout SC aminoacid mixture formulation (without Uracil) for S. cerevisiae growth media. Also known as Hopkins Mixture and is available in complete and dropout formulations.
-
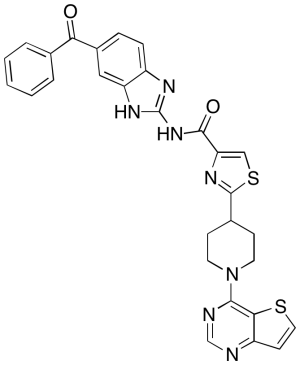
SC75741
$199.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H23N7O2S2
-

SC75741
$791.78 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C29H23N7O2S2
-
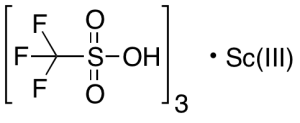
Scandium Triflate
$501.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C3H3F9O9S3 . Sc
-

Scandium(III) Acetate, Hydrate
$253.58 Add to cart View Product DetailsScandium(III) Acetate, Hydrate
-

SCC (SC1), mAb, Mouse
$307.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsSquamous
cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is one protein member of the serine protease
inhibitor (Serpin) family. Expression of SCCA is elevated in cancers of the cervix, lung, head and neck, and liver. As a result,
it is a useful biomarker for aggressive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). -

SCC (SC1), mAb, Mouse
$3,070.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsSquamous
cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is one protein member of the serine protease
inhibitor (Serpin) family. Expression of SCCA is elevated in cancers of the cervix, lung, head and neck, and liver. As a result,
it is a useful biomarker for aggressive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). -
SCC (SC1), mAb, Mouse
$26,066.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsSquamous
cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is one protein member of the serine protease
inhibitor (Serpin) family. Expression of SCCA is elevated in cancers of the cervix, lung, head and neck, and liver. As a result,
it is a useful biomarker for aggressive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). -

SCC (SC9), mAb, Mouse
$307.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsSquamous
cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is one protein member of the serine protease
inhibitor (Serpin) family. Expression of SCCA is elevated in cancers of the cervix, lung, head and neck, and liver. As a result,
it is a useful biomarker for aggressive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). -

SCC (SC9), mAb, Mouse
$3,070.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsSquamous
cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is one protein member of the serine protease
inhibitor (Serpin) family. Expression of SCCA is elevated in cancers of the cervix, lung, head and neck, and liver. As a result,
it is a useful biomarker for aggressive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). -

SCC (SC9), mAb, Mouse
$26,066.48 Add to cart View Product DetailsSquamous
cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is one protein member of the serine protease
inhibitor (Serpin) family. Expression of SCCA is elevated in cancers of the cervix, lung, head and neck, and liver. As a result,
it is a useful biomarker for aggressive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). -

SCCA Antibody (SC4), mAb, Mouse
$318.26 Add to cart View Product DetailsSquamous
cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is one protein member of the serine protease
inhibitor (Serpin) family. Expression of SCCA is elevated in cancers of the cervix, lung, head and neck, and liver. As a result,
it is a useful biomarker for aggressive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) -

SCCA Antibody (SC4), mAb, Mouse
$3,184.35 Add to cart View Product DetailsSquamous
cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is one protein member of the serine protease
inhibitor (Serpin) family. Expression of SCCA is elevated in cancers of the cervix, lung, head and neck, and liver. As a result,
it is a useful biomarker for aggressive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) -
SCCA Antibody (SC4), mAb, Mouse
$27,069.56 Add to cart View Product DetailsSquamous
cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is one protein member of the serine protease
inhibitor (Serpin) family. Expression of SCCA is elevated in cancers of the cervix, lung, head and neck, and liver. As a result,
it is a useful biomarker for aggressive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) -

sCD40L, Human
$1,030.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD40 ligand, CD40L (also known as CD154, TRAP or gp39), is a 261 amino acid type II transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the TNF family, CD40L is expressed predominantly on activated CD4+ T lymphocytes, and also found in other types of cells, like NK cells, mast cells, basophils and eosinophils. Human CD40L shares 78% amino acid identity with its mouse counterpart. The receptor of CD40L is CD40, a type I transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the TNF receptor family. CD40 is expressed on B lymphocytes, monocytes, dendritic cells and thymic epithelium. Although all monomeric, dimeric and trimeric forms of soluble CD40L can bind to CD40, the trimeric form of soluble CD40L has the most potent biological activity through oligomerization of cell surface CD40, a common feature of TNF receptor family members. CD40L mediates a range of activities on B cells including induction of activation-associated surface antigen, entry into cell cycle, isotype switching and Ig secretion and memory generation. CD40-CD40L interaction also plays important roles in monocyte activation and dendritic cell maturation.
-

sCD40L, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsCD40 ligand, CD40L (also known as CD154, TRAP or gp39), is a 261 amino acid type II transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the TNF family, CD40L is expressed predominantly on activated CD4+ T lymphocytes, and also found in other types of cells, like NK cells, mast cells, basophils and eosinophils. Human CD40L shares 78% amino acid identity with its mouse counterpart. The receptor of CD40L is CD40, a type I transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the TNF receptor family. CD40 is expressed on B lymphocytes, monocytes, dendritic cells and thymic epithelium. Although all monomeric, dimeric and trimeric forms of soluble CD40L can bind to CD40, the trimeric form of soluble CD40L has the most potent biological activity through oligomerization of cell surface CD40, a common feature of TNF receptor family members. CD40L mediates a range of activities on B cells including induction of activation-associated surface antigen, entry into cell cycle, isotype switching and Ig secretion and memory generation. CD40-CD40L interaction also plays important roles in monocyte activation and dendritic cell maturation.
-

SCF, Human (P. pastoris-expressed)
$1,177.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsStem cell factor (also known as SCF, KIT-ligand, KL, or steel factor) is a cytokine that binds to the c-KIT receptor (CD117). SCF can exist both as a transmembrane protein and a soluble protein. It stimulates the proliferation of myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid progenitors in bone marrow cultures and has been shown to act synergistically with colony stimulating factors. SCF plays an important role in the hematopoiesis during embryonic development. SCF can regulates HSCs in the stem cell niche in the bone marrow. SCF has been shown to increase the survival of HSCs in vitro and contributes to the self-renewal and maintenance of HSCs in-vivo.
-

SCF, Human (P. pastoris-expressed)
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsStem cell factor (also known as SCF, KIT-ligand, KL, or steel factor) is a cytokine that binds to the c-KIT receptor (CD117). SCF can exist both as a transmembrane protein and a soluble protein. It stimulates the proliferation of myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid progenitors in bone marrow cultures and has been shown to act synergistically with colony stimulating factors. SCF plays an important role in the hematopoiesis during embryonic development. SCF can regulates HSCs in the stem cell niche in the bone marrow. SCF has been shown to increase the survival of HSCs in vitro and contributes to the self-renewal and maintenance of HSCs in-vivo.
-

SCF, Human (P. pastoris-expressed)
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsStem cell factor (also known as SCF, KIT-ligand, KL, or steel factor) is a cytokine that binds to the c-KIT receptor (CD117). SCF can exist both as a transmembrane protein and a soluble protein. It stimulates the proliferation of myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid progenitors in bone marrow cultures and has been shown to act synergistically with colony stimulating factors. SCF plays an important role in the hematopoiesis during embryonic development. SCF can regulates HSCs in the stem cell niche in the bone marrow. SCF has been shown to increase the survival of HSCs in vitro and contributes to the self-renewal and maintenance of HSCs in-vivo.
-

SCF, Mouse
$1,177.31 Add to cart View Product DetailsStem cell factor (also known as SCF, KIT-ligand, KL, or steel factor) is a cytokine that binds to the c-KIT receptor (CD117). SCF can exist both as a transmembrane protein and a soluble protein. It stimulates the proliferation of myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid progenitors in bone marrow cultures and has been shown to act synergistically with colony stimulating factors. SCF plays an important role in the hematopoiesis during embryonic development. SCF can regulates HSCs in the stem cell niche in the bone marrow. SCF has been shown to increase the survival of HSCs in vitro and contributes to the self-renewal and maintenance of HSCs in-vivo.
-

SCF, Mouse
$86.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsStem cell factor (also known as SCF, KIT-ligand, KL, or steel factor) is a cytokine that binds to the c-KIT receptor (CD117). SCF can exist both as a transmembrane protein and a soluble protein. It stimulates the proliferation of myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid progenitors in bone marrow cultures and has been shown to act synergistically with colony stimulating factors. SCF plays an important role in the hematopoiesis during embryonic development. SCF can regulates HSCs in the stem cell niche in the bone marrow. SCF has been shown to increase the survival of HSCs in vitro and contributes to the self-renewal and maintenance of HSCs in-vivo.
-

SCF, Mouse
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsStem cell factor (also known as SCF, KIT-ligand, KL, or steel factor) is a cytokine that binds to the c-KIT receptor (CD117). SCF can exist both as a transmembrane protein and a soluble protein. It stimulates the proliferation of myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid progenitors in bone marrow cultures and has been shown to act synergistically with colony stimulating factors. SCF plays an important role in the hematopoiesis during embryonic development. SCF can regulates HSCs in the stem cell niche in the bone marrow. SCF has been shown to increase the survival of HSCs in vitro and contributes to the self-renewal and maintenance of HSCs in-vivo.






