Ambient
Showing 131901–131950 of 146505 results
-

SDA Medium-Ura (pouches)
$105.62 Add to cart View Product DetailsSDA Medium-Ura (pouches)
-

SDF-1α/CXCL12, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsStromal-Cell Derived Factor-1 alpha/ CXCL12 (SDF-1α) and SDF-1β, members of the chemokine α subfamily that lack the ELR domain, were initially identified using the signal sequence trap cloning strategy from a mouse bone-marrow stromal cell line. These proteins were subsequently also cloned from a human stromal cell line as cytokines that supported the proliferation of a stromal cell-dependent pre-B-cell line. SDF-1α and SDF-1β cDNAs encode precursor proteins of 89 and 93 amino acid residues, respectively. Both SDF-1α and SDF-1β are encoded by a single gene and arise by alternative splicing. The two proteins are identical except for the four amino acid residues that are present in the carboxy-terminus of SDF-1β and absent from SDF-1α. SDF-1/PBSF is highly conserved between species, with only one amino acid substitution between the mature human and mouse proteins. SDF-1/PBSF acts via the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and has been shown to be a chemoattractant for T-lymphocytes, monocytes, pro- and pre- B cells, but not neutrophils. Mice lacking SDF-1 or CXCR4 have been found to have impaired B-lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis, vascular development, cardiogenesis and abnormal neuronal cell migration and patterning in the central nervous system.
-

SDF-1α/CXCL12, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsStromal-Cell Derived Factor-1 alpha/ CXCL12 (SDF-1α) and SDF-1β, members of the chemokine α subfamily that lack the ELR domain, were initially identified using the signal sequence trap cloning strategy from a mouse bone-marrow stromal cell line. These proteins were subsequently also cloned from a human stromal cell line as cytokines that supported the proliferation of a stromal cell-dependent pre-B-cell line. SDF-1α and SDF-1β cDNAs encode precursor proteins of 89 and 93 amino acid residues, respectively. Both SDF-1α and SDF-1β are encoded by a single gene and arise by alternative splicing. The two proteins are identical except for the four amino acid residues that are present in the carboxy-terminus of SDF-1β and absent from SDF-1α. SDF-1/PBSF is highly conserved between species, with only one amino acid substitution between the mature human and mouse proteins. SDF-1/PBSF acts via the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and has been shown to be a chemoattractant for T-lymphocytes, monocytes, pro- and pre- B cells, but not neutrophils. Mice lacking SDF-1 or CXCR4 have been found to have impaired B-lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis, vascular development, cardiogenesis and abnormal neuronal cell migration and patterning in the central nervous system.
-

SDF-1α/CXCL12, Mouse
$194.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsStromal-Cell Derived Factor-1 alpha/ CXCL12 (SDF-1α) and SDF-1β, members of the chemokine α subfamily that lack the ELR domain, were initially identified using the signal sequence trap cloning strategy from a mouse bone-marrow stromal cell line. These proteins were subsequently also cloned from a human stromal cell line as cytokines that supported the proliferation of a stromal cell-dependent pre-B-cell line. SDF-1α and SDF-1β cDNAs encode precursor proteins of 89 and 93 amino acid residues, respectively. Both SDF-1α and SDF-1β are encoded by a single gene and arise by alternative splicing. The two proteins are identical except for the four amino acid residues that are present in the carboxy-terminus of SDF-1β and absent from SDF-1α. SDF-1/PBSF is highly conserved between species, with only one amino acid substitution between the mature human and mouse proteins. SDF-1/PBSF acts via the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and has been shown to be a chemoattractant for T-lymphocytes, monocytes, pro- and pre- B cells, but not neutrophils. Mice lacking SDF-1 or CXCR4 have been found to have impaired B-lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis, vascular development, cardiogenesis and abnormal neuronal cell migration and patterning in the central nervous system.
-

SDF-1α/CXCL12, Mouse
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsStromal-Cell Derived Factor-1 alpha/ CXCL12 (SDF-1α) and SDF-1β, members of the chemokine α subfamily that lack the ELR domain, were initially identified using the signal sequence trap cloning strategy from a mouse bone-marrow stromal cell line. These proteins were subsequently also cloned from a human stromal cell line as cytokines that supported the proliferation of a stromal cell-dependent pre-B-cell line. SDF-1α and SDF-1β cDNAs encode precursor proteins of 89 and 93 amino acid residues, respectively. Both SDF-1α and SDF-1β are encoded by a single gene and arise by alternative splicing. The two proteins are identical except for the four amino acid residues that are present in the carboxy-terminus of SDF-1β and absent from SDF-1α. SDF-1/PBSF is highly conserved between species, with only one amino acid substitution between the mature human and mouse proteins. SDF-1/PBSF acts via the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and has been shown to be a chemoattractant for T-lymphocytes, monocytes, pro- and pre- B cells, but not neutrophils. Mice lacking SDF-1 or CXCR4 have been found to have impaired B-lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis, vascular development, cardiogenesis and abnormal neuronal cell migration and patterning in the central nervous system.
-

SDF-1β/CXCL12, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsStromal-Cell Derived Factor-1 beta (SDF-1β), also known as SCYB12, PBSF and CXCL12, is an 8.3 kDa, heparin-binding member of the CXC (or alpha) family of chemokines and signal through the CXCR4 receptor. SDF-1α and β are reported to be monomers at neutral pH and physiologic ionic strength, On the cell surface, this may well facilitate SDF-1 interaction with its two receptors, CXCR4 and syndecan4. Heparin sulfate is known to protect SDF-1 from proteolysis, and CXCR4 exists constitutively as a dimer. Among its many functions, CXCL12 is known to influence lymphopoiesis, regulate patterning and cell number of neural progenitors, and promote angiogenesis (12, 13). It also enhances the survival of myeloid progenitor cells
-

SDF-1β/CXCL12, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsStromal-Cell Derived Factor-1 beta (SDF-1β), also known as SCYB12, PBSF and CXCL12, is an 8.3 kDa, heparin-binding member of the CXC (or alpha) family of chemokines and signal through the CXCR4 receptor. SDF-1α and β are reported to be monomers at neutral pH and physiologic ionic strength, On the cell surface, this may well facilitate SDF-1 interaction with its two receptors, CXCR4 and syndecan4. Heparin sulfate is known to protect SDF-1 from proteolysis, and CXCR4 exists constitutively as a dimer. Among its many functions, CXCL12 is known to influence lymphopoiesis, regulate patterning and cell number of neural progenitors, and promote angiogenesis (12, 13). It also enhances the survival of myeloid progenitor cells
-

SDS Easy Sol 20%
$279.92 Add to cart View Product DetailsSDS is an anionic detergent typically used to solubilize and denature proteins for electrophoresis. Most proteins bind SDS in a ratio of 1.4 grams SDS to 1 gram protein. The charges intrinsic to the protein become insignificant compared to the overall negative charge provided by the bound SDS.It is RNAse,DNAse, Protease free with an assay value of 20%.This solution is provided as a convenient ready-to-use firmat which eliminates the need to handle powdered SDS.
-

SDS Easy Solution (12%)
$127.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsSDS Easy Solution (12%)
-

SDS-urea Buffer
$147.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsSDS-urea Buffer
-

SDS-urea Buffer
$275.36 Add to cart View Product DetailsSDS-urea Buffer
-
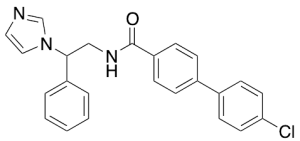
SDZ 285-428
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H20ClN3O
-

SDZ 285-428
$232.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H20ClN3O
-

SDZ 285-428
$357.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C24H20ClN3O
-
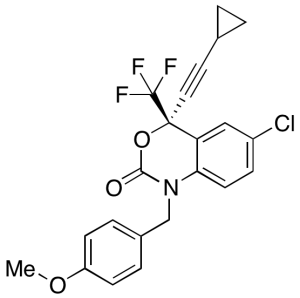
SE 563
$214.76 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H17 Cl F3 N O3
-

SE 563
$1,675.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C22 H17 Cl F3 N O3
-
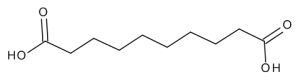
Sebacic Acid
$61.24 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H18 O4
-

Sebacic Acid
$94.88 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H18 O4
-
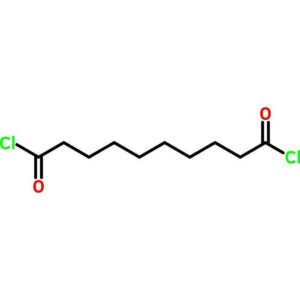
Sebacoyl Chloride
$58.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsSebacoyl Chloride
-

Sebacoyl Chloride
$370.94 Add to cart View Product DetailsSebacoyl Chloride
-

Sebacoyl Chloride, Reagent
$154.69 Add to cart View Product DetailsSebacoyl Chloride, Reagent
-

Sebacoyl Chloride, Reagent
$360.11 Add to cart View Product DetailsSebacoyl Chloride, Reagent
-

Sebacoyl Chloride, Reagent
$539.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsSebacoyl Chloride, Reagent
-

Sebacoyl Chloride, Reagent
$2,778.19 Add to cart View Product DetailsSebacoyl Chloride, Reagent
-
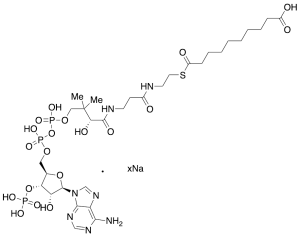
Sebacyl-CoA Sodium Salt
$324.30 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31H52N7O19P3S • xNa
-

Sebacyl-CoA Sodium Salt
$708.98 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31H52N7O19P3S • xNa
-

Sebacyl-CoA Sodium Salt
$1,348.09 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C31H52N7O19P3S • xNa
-

Sebuthylazine-d5 (ethyl-d5)
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 2H5 H11 Cl N5
-

Sebuthylazine-d5 (ethyl-d5)
$83.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 2H5 H11 Cl N5
-

Sebuthylazine-d5 (ethyl-d5)
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C9 2H5 H11 Cl N5
-

sec-Butyl 4-Hydroxybenzoate
$128.01 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-Butyl 4-Hydroxybenzoate
-

sec-Butyl 4-Hydroxybenzoate
$476.09 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-Butyl 4-Hydroxybenzoate
-

Sec-Butyl 4-Methylbenzenesulfonate
$62.96 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H16 O3 S
-

Sec-Butyl 4-Methylbenzenesulfonate (>80%, with an impurity of pTSA)
$83.66 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H16 O3 S
-

Sec-Butyl 4-Methylbenzenesulfonate (>80%, with an impurity of pTSA)
$171.64 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H16 O3 S
-
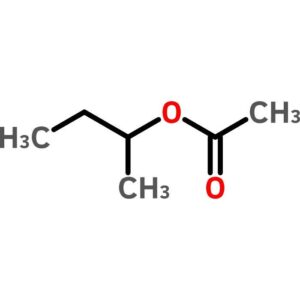
sec-Butyl Acetate
$35.34 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-Butyl Acetate
-

sec-Butyl Acetate
$170.30 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-Butyl Acetate
-
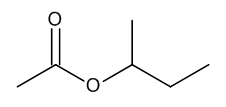
sec-Butyl Acetate
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H12 O2
-

sec-Butyl Acetate
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H12 O2
-

sec-Butyl Acetate
$103.50 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6 H12 O2
-

sec-Butyl Alcohol
$44.94 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-Butyl Alcohol
-

sec-Butyl Alcohol
$77.37 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-Butyl Alcohol
-

sec-Butyl Alcohol
$155.92 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-Butyl Alcohol
-

sec-Butyl Alcohol
$506.41 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-Butyl Alcohol
-
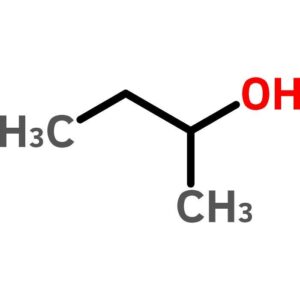
sec-Butyl Alcohol
$476.51 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-Butyl Alcohol
-

sec-Butyl Alcohol
$5,715.17 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-Butyl Alcohol
-

sec-BUTYL ALCOHOL
$574.86 Add to cart View Product Detailssec-BUTYL ALCOHOL
-
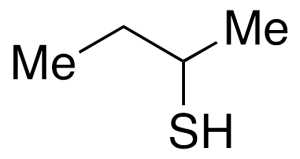
sec-Butyl Mercaptan
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H10S
-

sec-Butyl Mercaptan
$78.49 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H10S
-

sec-Butyl Mercaptan
$88.84 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H10S






