Ambient
Showing 139501–139550 of 146499 results
-
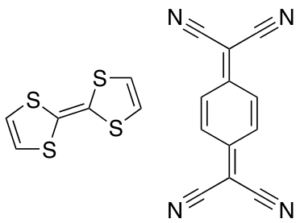
Tetrathiafulvalene – 7,7,8,8-Tetracyanoquinodimethane Complex
$62.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H4S4 . C12H4N4
-

Tetrathiafulvalene – 7,7,8,8-Tetracyanoquinodimethane Complex
$84.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H4S4 . C12H4N4
-

Tetrathiafulvalene – 7,7,8,8-Tetracyanoquinodimethane Complex
$120.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C6H4S4 . C12H4N4
-

Tetratriacontane
$60.38 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H70
-

Tetratriacontane
$84.53 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H70
-

Tetratriacontane
$231.15 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H70
-
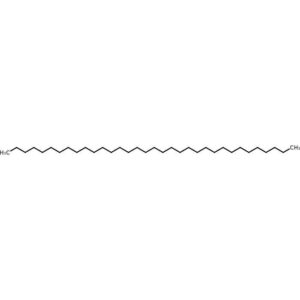
Tetratriacontane
$207.93 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetratriacontane
-

Tetratriacontane
$623.90 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetratriacontane
-

Tetratriacontane
$2,037.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetratriacontane
-
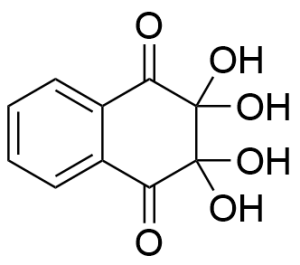
Tetraxolin
$169.05 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H8 O6
-

Tetraxolin
$678.79 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H8 O6
-

Tetraxolin
$1,317.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C10 H8 O6
-

Tetrazolium Blue Chloride
$88.85 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrazolium Blue Chloride
-

Tetrazolium Blue Chloride
$230.74 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrazolium Blue Chloride
-

Tetrazolium Blue Chloride
$815.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrazolium Blue Chloride
-

Tetrazolium Blue Chloride
$2,586.17 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrazolium Blue Chloride
-
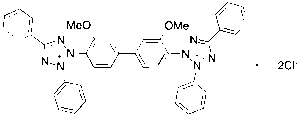
Tetrazolium Blue Chloride (>90%)
$68.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C40H32N8O2 . 2Cl
-

Tetrazolium Blue Chloride (>90%)
$257.03 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C40H32N8O2 . 2Cl
-

Tetrazolium Blue Chloride (>90%)
$473.51 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C40H32N8O2 . 2Cl
-

Tetrodotoxin
$580.46 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C11 H17 N3 O8
-
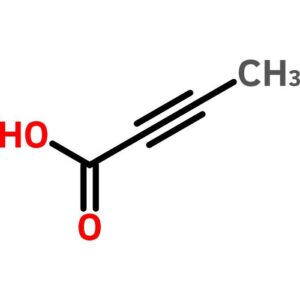
Tetrolic Acid
$47.92 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrolic Acid
-

Tetrolic Acid
$142.57 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrolic Acid
-

Tetrolic Acid
$574.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetrolic Acid
-
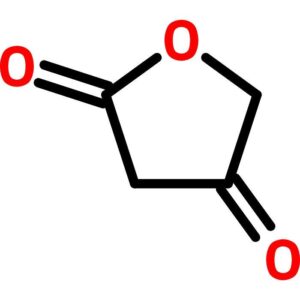
Tetronic Acid
$515.99 Add to cart View Product DetailsTetronic Acid
-

Tetronic Acid
$56.06 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H4O3
-

Tetronic Acid
$67.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H4O3
-

Tetronic Acid
$82.80 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C4H4O3
-

TEV Protease, His
$218.21 Add to cart View Product DetailsTobacco Etch Virus Protease is a highly site-specific cysteine protease that is found in the tags from fusion proteins. The optimal temperature for cleavage is 30°C; also it can be used at temperature as low as 4°C. It is recommended that the cleavage for each fusion protein be optimized by varying the amount of recombinant viral TEV protease, reaction time, or incubation temperature. It can be removed by Ni2+ affinity resin.
Recombinant Tobacco Etch Virus (TEV). The optimum recognition site for this enzyme is the sequence Glu-Asn-Leu-Tyr-Phe-Gln-(Gly/Ser) [ENLYFQ(G/S)] and cleavage occurs between the Gln and Gly/Ser residues, The most commonly used sequence is ENLYFQG. The protease is used to cleave affinity tags from fusion proteins. The optimal temperature for cleavage is 30°C. It is recommended that the cleavage for each fusion protein be optimized by varying the amount of recombinant viral TEV protease, reaction time, or incubation temperature. It can be removed by Ni2+ affinity resin.
Recombinant Tobacco Etch Virus Protease (rTEV) contains 231 amino acids with N-terminal His tagged. A fully biologically active molecule, rTEV has a molecular mass of 28.4 kDa and is obtained by proprietary chromatographic techniques at GenScript. -

TEV Protease, His
$43.13 Add to cart View Product DetailsTobacco Etch Virus Protease is a highly site-specific cysteine protease that is found in the tags from fusion proteins. The optimal temperature for cleavage is 30°C; also it can be used at temperature as low as 4°C. It is recommended that the cleavage for each fusion protein be optimized by varying the amount of recombinant viral TEV protease, reaction time, or incubation temperature. It can be removed by Ni2+ affinity resin.
Recombinant Tobacco Etch Virus (TEV). The optimum recognition site for this enzyme is the sequence Glu-Asn-Leu-Tyr-Phe-Gln-(Gly/Ser) [ENLYFQ(G/S)] and cleavage occurs between the Gln and Gly/Ser residues, The most commonly used sequence is ENLYFQG. The protease is used to cleave affinity tags from fusion proteins. The optimal temperature for cleavage is 30°C. It is recommended that the cleavage for each fusion protein be optimized by varying the amount of recombinant viral TEV protease, reaction time, or incubation temperature. It can be removed by Ni2+ affinity resin.
Recombinant Tobacco Etch Virus Protease (rTEV) contains 231 amino acids with N-terminal His tagged. A fully biologically active molecule, rTEV has a molecular mass of 28.4 kDa and is obtained by proprietary chromatographic techniques at GenScript. -
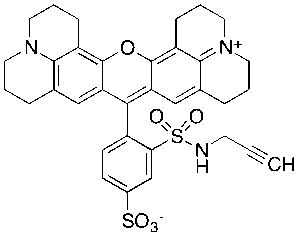
Texas Red 2’-Propargyl Sulfonamide 4’-Sulfate
$192.34 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H33N3O6S2
-

Texas Red 2’-Propargyl Sulfonamide 4’-Sulfate
$577.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34H33N3O6S2
-

Texas Red®-2-sulfonamidoethyl methanethiosulfonate
$144.04 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H37 N3 O8 S4
-

Texas Red®-2-sulfonamidoethyl methanethiosulfonate
$204.41 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C34 H37 N3 O8 S4
-

Tezacaftor
$71.59 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H27 F3 N2 O6
-

Tezacaftor
$275.14 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H27 F3 N2 O6
-

Tezacaftor
$452.81 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 H27 F3 N2 O6
-
Tezacaftor Metabolite M1
$136.28 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H25F3N2O6
-
Tezacaftor Metabolite M1
$615.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H25F3N2O6
-
Tezacaftor Metabolite M1
$1,062.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26H25F3N2O6
-

Tezacaftor-D4
$350.18 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 D4 H23 F3 N2 O6
-

Tezacaftor-D4
$1,614.60 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C26 D4 H23 F3 N2 O6
-

TFF3, Human
$2,018.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe Trefoil Factor peptides (TFF1, TFF2 and TFF3) are secreted in the gastrointestinal tract, and appear to play an important role in intestinal mucosal defense and repair. TFF-3 is expressed by goblet cells and in the uterus, and has also been shown to express in certain cancers, including colorectal, hepatocellular, and in biliary tumors. TFF3 may be useful as a molecular marker for certain types of cancer, but its role, if any, in tumorigenesis is unknown. TFF3 also promotes airway epithelial cell migration and differentiation.
-

TFF3, Human
$155.25 Add to cart View Product DetailsThe Trefoil Factor peptides (TFF1, TFF2 and TFF3) are secreted in the gastrointestinal tract, and appear to play an important role in intestinal mucosal defense and repair. TFF-3 is expressed by goblet cells and in the uterus, and has also been shown to express in certain cancers, including colorectal, hepatocellular, and in biliary tumors. TFF3 may be useful as a molecular marker for certain types of cancer, but its role, if any, in tumorigenesis is unknown. TFF3 also promotes airway epithelial cell migration and differentiation.
-
TG100-115
$94.01 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H14N6O2
-
TG100-115
$132.83 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C18H14N6O2
-

TG101348
$98.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H36 N6 O3 S
-

TG101348
$131.10 Add to cart View Product DetailsMolecular Formula : C27 H36 N6 O3 S
-

TGF-α, Human
$51.75 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtransforming Growth Factor-alpha (TGF-alpha), also known as sarcoma growth factor, TGF-type I and ETGF, is a member of the EGF family of cytokines. It is expressed in monocytes, brain cells, keratinocytes and various tumor cells. ProTGF-alpha signals through EGFR and acts synergistically with TGF-beta to promote the proliferation of a wide range of epidermal and epithelial cells. It may function as either a membrane-bound ligand or a soluble ligand. Membrane-bound proTGF-alpha plays a role in cell-cell adhesion and juxtacrine stimulation of adjacent cells. The soluble form of the cytokine is released from the membrane-bound form by proteolytic cleavage and acts as a mitogen for cell proliferation.
-

TGF-α, Human
$29.33 Add to cart View Product DetailsProtransforming Growth Factor-alpha (TGF-alpha), also known as sarcoma growth factor, TGF-type I and ETGF, is a member of the EGF family of cytokines. It is expressed in monocytes, brain cells, keratinocytes and various tumor cells. ProTGF-alpha signals through EGFR and acts synergistically with TGF-beta to promote the proliferation of a wide range of epidermal and epithelial cells. It may function as either a membrane-bound ligand or a soluble ligand. Membrane-bound proTGF-alpha plays a role in cell-cell adhesion and juxtacrine stimulation of adjacent cells. The soluble form of the cytokine is released from the membrane-bound form by proteolytic cleavage and acts as a mitogen for cell proliferation.
-

TGF-α, Human
$836.63 Add to cart View Product DetailsTransforming Growth Factor-alpha (TGF-α) , also known as sarcoma growth factor, TGF-type I and ETGF, is a member of the EGF family of cytokines. It is expressed in monocytes, brain cells, keratinocytes and various tumor cells. TGF-α signals through EGFR and acts synergistically with TGF-beta to promote the proliferation of a wide range of epidermal and epithelial cells. TGF-α is a transforming growth factor that is a ligand for the epidermal growth factor receptor, which activates a signaling pathway for cell proliferation, differentiation and development. This protein may act as either a transmembrane-bound ligand or a soluble ligand. The biological actions of TGF-α and EGF are similar. For instance, TGF-α and EGF bind to the same receptor. When TGF-α binds to EGFR it can initiate multiple cell proliferation events.






